* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecological Principles
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Polar ecology wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
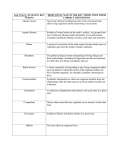
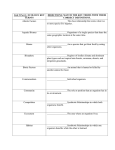
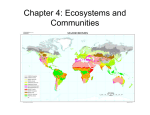
Ecological Principles Objectives • Define Ecology • Compare and contrast biotic and abiotic factors • Describe the three types of symbiosis ECOLOGY • is the study of the interactions among organisms and their environment • studied by an ecologist THE ENVIRONMENT • An organism’s surroundings • Composed of living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic)things • Biotic Factors: humans, plants, birds, fungi, bacteria, protists • Abiotic Factors: water, light, temperature, air, soil LIVING RELATIONSHIPS • Describes the associations that organisms have with other organisms of a different species within the environment Symbiosis • A relationship between organisms in which at least one of them benefits • Three types of symbiosis in ecosystems are mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. Mutualism (+, +) Both species benefit from being in relationship with one another ex. honeybee & flower Commensalism (+, 0) • • • • • One organism benefits while the other is unaffected (neither helped nor harmed) Ex. robin in a tree Parasitism (+, -) • One organism benefits at the expense of the other • One organism benefits, other harmed but not not killed • Example: deer tick on a deer Predation (+, -) • one organisms benefits by hunting, killing, and feeding on another organism • AKA predator – prey relationship fox & rabbit • predator = organism that hunts, kills, and feeds off another • prey = organism that is hunted & killed Competition • Occurs when organisms in the same ecosystem are competing with each other for resources such as food, water, sunlight, and living spaces Objectives • Describe plants and animals found in various biomes • Identify the biome that we live in BIOMES • A large region that contains similar plant and animal ecosystems and is characterized by certain climate conditions. • Biomes can be terrestrial (land) or aquatic (water). Terrestrial Biomes Temperate Deciduous Forest • Trees (birch, oak, maple, elm) lose leaves in fall • Animals such as bears, deer, rabbits, squirrels, & many species of birds Coniferous Forest • Cone shaped trees (fir, pine, spruce) • Moose, bears, lynxes wolves • Snow covered ground during long winters Tropical Rain Forest • Made up of tall trees with broad leaves that form a dense canopy of vegetation • Animals include a wide variety of snakes, lizards, colorful birds, and many kinds of monkeys Grassland • Made up of grasses & plants that produce colorful flowers • Called a prairie in U.S. • Has rich, fertile soil • Well suited for growing crops • Animals include bison, mice, and prairie dogs Desert • Arid or dry • Very little yearly rainfall • Vegetation sparse, consists of plants like cacti • Animals include snakes, lizards, and jackrabbits Tundra • Very cold conditions • Very little vegetation • Contains permafrost (permanently frozen soil located underneath topsoil • Animals include musk oxen & wolves Aquatic Biomes • Aquatic biomes can be freshwater or marine • Freshwater biomes include rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, and wetlands • Wetlands are land areas that remain wet for all or part of the year. They include swamps & marshes • Marine biomes consist of the oceans • Oceans have 4 distinct zones: intertidal neritic oceanic benthic • Intertidal – where ocean meets the land. Animals include shellfish & birds • Neritic – numerous fishes, sea turtles, squids, coral reefs • Oceanic – open ocean; most of zone cold & dark; not much life. Fishes & whales • Benthic – ocean floor; bottom feeder animals like starfish, anemones, sponges