* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Welcome to this lesson today on the thyroid and parathyroid glands
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Signs and symptoms of Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypopituitarism wikipedia , lookup
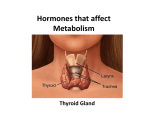
Welcome to this lesson today on the thyroid and parathyroid glands. Today we will be discussing the structure and function of these glands. So the thyroid and parathyroid are located in the neck. And they work closely together to manage blood calcium levels. So if we take a look at this picture right here, we're going to identify the thyroid and parathyroid. So this here is our thyroid gland. And the parathyroid glands, there's actually four of them that are located on the thyroid. So I'll just kind of draw them in right here. These would be the parathyroid glands. And as I mentioned, we have four total. So we're going to talk separately about each of these glands and the role that they play in our body in the endocrine system. So the thyroid gland secretes thyroid hormone. And thyroid hormone is abbreviated as TH. So this thyroid hormone plays a role in metabolism, growth, and optimal functioning of the central nervous system. The thyroid gland also secretes a hormone called calcitonin. And calcitonin is a hormone that helps to regulate blood calcium levels by lowering blood calcium levels if they get too high. So if blood calcium levels get too high, the osteoblasts in the bone will be signaled to store that access calcium within the bone. And then the parathyroid gland secretes parathyroid hormone, also abbreviated as PTH. And so parathyroid hormone also plays a role in regulating blood calcium levels. So what parathyroid hormone does is helps to raise blood calcium levels if the blood calcium levels get too low. So it will signal osteoclasts to release calcium from the bone. So these two hormones actually play a role in bone remodeling. And this process helps to maintain homeostasis of blood calcium levels. So the thyroid gland and the parathyroid gland play a large role in maintaining homeostasis of blood calcium levels, either by lowering blood calcium levels or raising blood calcium levels with the help of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. So we're going to take a look at some disorders here that can occur with the thyroid and parathyroid. So a simple goiter is one type of disorder that can affect the thyroid gland. So in order for the production of thyroid hormone, iodine is necessary. So if a person does not get enough iodine in their diet, what happens is that lobes of the thyroid will enlarge and swell up. So again, simple goiters are the swelling or enlargement of lobes of the thyroid caused by a diet deficient in iodine. Generally in the US this is not much of a problem now, since you can buy iodized salts. So that's where we get a good majority of our iodine. Hyperthyroid is a condition in which there is excess thyroid hormone in the blood, which can lead to a high heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and sweating. So Graves' disease is actually a disease that causes hyperthyroidism. So in effect, Graves' disease is an autoimmune disease that basically in a nutshell stimulates overproduction of thyroid hormone. And then that overproduction of thyroid hormone leads to this condition of a hyperthyroid. And then hypothyroid is low blood thyroid levels. So hyper- is high. And hypothyroid is low thyroid hormone levels. So with these low thyroid hormone levels, as we mentioned thyroid hormone controls metabolism, growth, and CNS functioning. So basically if thyroid hormone levels are low, it can lead to things like weight gain. A person might feel sluggish. And they might be intolerant to very, very cold or very high temperatures. So these two disorders are disorders that are caused by fluxes in thyroid levels, thyroid hormone levels within the blood. So this lesson has been an overview on the structure and function of the thyroid and parathyroid.