* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Road To A Brain Healthy Life: What`s Normal, What`s Not
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Substance use disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Mentally ill people in United States jails and prisons wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Substance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatric institutions wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Mental health professional wikipedia , lookup
Community mental health service wikipedia , lookup
Deinstitutionalisation wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Homelessness and mental health wikipedia , lookup
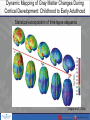
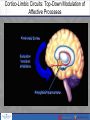
The Road To A Brain Healthy Life: What's Normal, What's Not: Teenagers Melissa P. Lopez-Larson, M.D. Child, Adolescent and Adult Psychiatrist Psychiatrist: Round Valley Clinic, Park City Adjunct Assistant Professor, University of Utah Teenager Years – The Perfect Storm • On average 12 to 22 years of age • Transition period to adulthood • Hormonal fluctuations –steroid hormones impact brain development with limbic structures seeing an increase in sex hormones prior to full frontal lobe development • Robust brain development changes during this time leading to growth in cognitive, emotional and social domains • Critical time period for development and often the time of increased risk for mental health issues Brain Health and Development Genes Hormones Experiences/Environ ment Hormonal Changes during Puberty Dynamic Mapping of Gray Matter Changes During Cortical Development: Childhood to Early Adulthood Statistical extrapolation of time lapse sequence (Gogtay et al., 2004) Cortico-Limbic Circuits: Top-Down Modulation of Affective Processes Prefrontal Cortex Executive function/ Inhibition Amygdala/hippocampus Typical Personality and Behavioral Changes • Mild to moderate mood lability and sensitivity • Challenging of authority and limit testing • Peer influence stronger than parental influence • Higher risk behaviors than typical for given Teen • Experimentation – try on new roles/personalities; drugs and alcohol • Gradual changes over the course of teenage years • More self-conscious General warning signs • Abrupt changes in personality and attire • Isolation – from parents and/or peers • Refusing to talk openly with parents • Abrupt changes in peer group • Poor appetite or restricting food intake • Sleeping to little or to much • Obsession with social media General warning signs • High risk behaviors – excessive alcohol and drug use, stealing, lying, legal issues • Moderate to severe irritability including any aggression • Severe oppositionality and unwillness to follow any rules • Decline in school grades and/or school refusal • Quitting sports or other activities they use to enjoy • Increase in physical complaints, i.e. Stomach aches, headaches, pain, etc… Teens at Increased Risk • Any prior history of mental health or learning issues as a child, i.e. anxiety, ADHD, depression • Bullying including past and present • Family history of mental health issues • Major transitions or stressful events in life (even if positive) • parental divorce • geographical move • change in schools • loss of a loved one • the more transitions the higher the risk Teens at Increased Risk • History of trauma/abuse including witnessing abuse or domestic violence • Can include sibling-on-sibling violence • History of head injury/concussions • History of chronic medical conditions: diabetes, ulcerative colitis, etc… • Use of drugs and alcohol**** • Remember each teen is different and what is a warning sign in one is not in another. Warning Signs of Depression in Adolescents • Depressed or down mood • Mood lability: crying and irritability • Isolation – including parents and peers –although usually will still hang out with friends • Loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities • Sleeping to much or not enough • Increased or decrease in appetite with weight changes Warning Signs of Depression in Adolescents • Suicidal statements or gestures or other parasuicidal behaviors • Excessive guilt • Expression of hopelessness or negativity about the future • Often has overlapping symptoms with anxiety • Increase in drug and alcohol use Warning signs of Anxiety in Adolescents • Excessive worrying about everything • Fear of being judged • Perfectionism • Social anxiety – few friends/isolation • Irritability • School refusal • Having to have things “a certain way” and ritualistic or repetitive behaviors Warning signs of Bipolar Disorder • Severe mood swings lasting days to weeks: “highs and lows” • Very high risk and out of control behaviors • Increase in drug and alcohol use • Grandiosity • More social, more ideas and projects, etc • Pressured and fast speech • Lack of need for sleep Warning Signs of Psychotic Disorder • Auditory and visual hallucinations • Severe withdrawal and isolation with few to no friends • Paranoia • Disorganized or confused thinking • School refusal and poor grades • Poor hygiene • Increase in drug and alcohol use Warning Signs of an Eating Disorder • Drastic changes in eating patterns – more restrictive • Eating alone • Going to the bathroom shortly after meals • Increase or excessive exercise regimen • Pre-occupied by appearance and spending a lot of time in front of mirror • Wearing baggy clothing • Poor self-image Warning Signs of Addiction Issues • Change in personality and mood • More irritable and defiant • Use of substances by him/herself • Legal issues • Lying and stealing behaviors • Can mimic many different mental health issues and can increase risk for mental health issues. • Often is comorbid with other mental health issues. General Tips for Parents • Be vigilant and if you are worried then you probably should be • Keep lines of communication open • Listen- don’t rush to fix things • Model behavior you would like to see in your teen • Set firm boundaries Tips for Parents • Pick your battles wisely • Consequences for breaking certain house rules should be enforced but communicating why is important – not just “because I said so” • Consistency • Don’t be afraid to ask for help: friends, family, pediatrician, clergy, school counselors, teachers, etc… • In general 2 or more warning signs should prompt an evaluation by a professional Available Treatment Options • Outpatient 1. Individual – CBT, supportive, interpersonal therapy – specialize in working with teens 2. Group therapy – can be very helpful for Teens given the increased importance of peer relationships 3. Mediation management • Intensive Outpatient/Day Treatment • Residential – long and short-term and therapeutic day schools • Inpatient hospitalization • Specific treatment programs: Addiction, eating disorders, behavioral disorders Summary • Adolescence is a “Perfect Storm” with hormonal and brain changes occurring around the time of a major transition period in ones life. • Recognizing age-appropriate versus potential warning signs for underlying mental health issues – Teen specific • When in doubt ask for help – if you are worried then you are probably right. • Talk openly about mental health issues with kids, family, friends, etc… to help reduce stigma, get support, info, etc. • Sources of additional information: Connect, NAMI, NIMH Questions?