* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
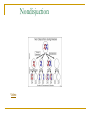
Chapter 7 Sexual Reproduction and the Diversity of Life Ways of Reproduction Reproduction Asexual Sexual Binary Fission Hermaphroditic Budding Separate Sexes Fragmentation Conjugation Spore Formation Vegetative Rep. The Difference Between Asexual and Sexual Asexual Reproduction – a single cell ( the mother cell) duplicates the same genetic information and becomes two daughter cells. Sexual Reproduction – genetic information from two cells is combined to form the new genetic code for a new organism. Sexual Reproduction Types: Conjugation, Hermaphrodites, Separate Sexes Conjugation – two cells come together and exchange small pieces of their genetic information (bacteria) Hermaphrodites – organisms that create both male and female sex cells. Occurs in organisms that have restricted movement (sponges) Sexual Reproductions continued Separate Sexes – In complex organisms specialized sex cells (sperm and egg) combine to form a zygote. Offspring are not identical to either the parent or further offspring (humans and some plants) Fertilization Fertilization External- a process where male sperm cells are combined with female egg cells outside the female’s body (fish) Internal- a process in the male sperm is united with the female egg inside the female’s body (humans) Homework Read Section 7.1, pages202-205 Do questions 1-6 on page 205 Answers to 7.1 1. A zygote is a fertilized egg. 2. Conjugation is a genetic recombination mechanism. 3. Animals that contain both male and female sex cells are referred to a hermaphroditc. Sponges, tapeworms, earthworms, and barnacles are both male and female. 4. a) internal fertilization: mammals, birds, earthworm B) external fertilization: fish, amphibians, invertebrates 5. Females contain two X chromosomes, while males contain a single X and a Y. 6. a) 11 b) 22 c) 22 d) 11 Meiosis The process of forming sex cells, A human body cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. The gametes - sperm or eggs - contain half this number of chromosomes, which is why meiosis is sometimes called 'reduction division'. Meiosis continued Organisms that reproduce sexually contain 2 types of cells. 1) Somatic- cells that reproduce by mitosis, when cells divide each daughter cell is identical as the mother cell (skin and muscle cells 2) Reproductive- produce sex cells which only have half the number of chromosomes (haploid cell) Meiosis View video link http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=s wf::535::535::/sites/dl/free/0072437316/1 20074/bio19.swf::Stages%20of%20Meio sis Draw stages of meiosis into your notebooks (page 206/7 from textbook) Homework Read section 7.2, pages 206-207 Do questions 1-8 on page 207 Answers to 7.2 Questions 1. Somatic have a full compliment of chromosomes (diploid). Reproductive cells have one of the pairs of homologous chromosomes (haploid cells). 2. Chromosomes that are simiar in size, shape, and gene arrangement are homologous. 3. Meiosis 1 is the reduction division phase and Meiosis 2 is the division of the double stranded chromosomes. Answers continued 4. Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Meiosis One division Two divisions Two cells produced Four cells produced Cells are identical Cells contain half the chromosome of a parent 5. Meiosis reduces the chromosome number in sex cells from diploid to haploid. 6. 39 chromosomes 7. Yes they have the same number. 8. Genes code for the same characteristic but they may not be identical. Parts of the Flower Use diagram as reference to part descriptions on next slide The Male Parts Pollen – the male sex cells of the flower Filament - This is the stalk of the Anther. Anther - The Anthers contain pollen sacs. The sacs release pollen on to the outside of the anthers that brush against insects on entering the flowers. * The filament and the anthers are collectively known as the Stamen The Female Parts of the Flower Egg the female sex cells of the flower Stigma Is covered in a sticky substance that the pollen grains will adhere to. Style The style raises the stigma away from the Ovary to decrease the likelihood of pollen contamination. Ovary This protects the egg and once fertilization has taken place it will become the fruit. Homework Read section 7.3, pages208-209 Be prepared to label the parts of the cell as seen on page 210 in the textbook Do questions 1-6 on page 209 Answers to page 209 1. Flowering plants contain both male and female sex cells. 2. Male sex cell (pollen) and female sex cell (eggs). 3. During reproduction, the pollen sends a sperm down through the pistil with the male gamete in it. The sperm makes its way to the female sex cells in a process called fertilization. Answers Continued 4. Once fertilized, the female sex cells of the flower become seeds. The petals of the flower slowly shrivel and disappear. The surrounding ovary becomes larger and develops into the fruit. 5. Seeds (b,c) have spikes that get entangled in animal’s fur. Maple and poppyseed have large flat structures that catch the wind. Dandelions act as parachutes that get carried by the wind. 6. Since the fruit is generally appetizing, animals eat fruits and scatter the seeds via the hind end. Strategies for Increasing Food Production Strategies Selective BreedingOffspring with the same desired characteristics CrossbreedingPollen is taken from one plant and fertilized with the egg of another Cloning Grafting Exact duplication Sections of one plant Is combined with another Homework Read section 7.5, pages212-213 Do questions 1-3 on page 213 Answers 1. As the world population increases, food production must increase or people will starve. 2. Grafting allows a tree to produce a different type of fruit quickly. Selective breeding identifies plants with the most desirable traits. 3.In both cloning and grafting no sexual reproduction takes place so no new combination of genes will take place; therefore no diversity Atypical Meiosis Atypical meiosis is the term given when meiosis does not separate the chromosomes correctly. Nondisjunction is the failure to separate two homologous chromosomes * Understand Figure 1 on page 222 Nondisjuction Video Nondisjunction Orders Down Syndrome: too many chromosomes, mental disabilities (47) Turner Syndrome: too few chromosomes, females don’t mature sexually/shorter (45) Klinefelter Syndrome: too many chromosomes, males cannot reproduce (47) Homework Read section 7.9, pages 222-223 Do questions 1-5 on page 223 Chapter 7 Review Do questions 3-13 on pages 228-229 Answers to Chpt. Review Questions 3. Sexual reproduction causes the recombination of genetic info from different organisms. The new combination of genes can produce new traits. 4. a) asexual b) sexual c) sexual d) asexual 5. Because only one chromosome pair from each parent combines is a fertilized egg, different children, formed by different sperm and egg cells, will have new gene combinations. 6. Description Produces 4 cells Meiosis Mitosis X Daughter cells are clones of mother cell Haploid cells produced X X Skin cells X Formation of sex cells X Two stages of cell division X 7. The sperm cells unite with the female sex cells in a process called fertilization. The fertilized cells become seeds which in turn grow new plants. 8. Male- pollen, anther and filament Female- stigma, style, ovary 9. 10. a) female A b) 9,8,7 respectfully c) fertilization d) zygote 11. a) 23 b) Meiosis occurred c) 46 12. a) stage 2 b) fertilization 23 pairs 13 Genetic information from two different individuals is combined. This creates genetic diversity. c) mitosis d)