* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Math Vocabulary and Properties
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Elementary arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
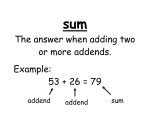
Basic Math Vocabulary AddendThe numbers you add. Ex. 2+3=5, both the numbers 2 and 3 are addends. SumThe answer to an addition problem. Ex. 2+3=5, the number 5 is the sum. MinuendThe first term in a subtraction problem. Ex. 5-3=2, the number 5 is the minuend. SubtrahendThe second term in a subtraction problem. Ex. 5-3=2, the number 3 is the subtrahend. DifferenceThe answer to a subtraction problem. Ex. 5-3=2, the number 2 is the difference. FactorThe numbers you multiply. Ex. 5x3=15, both the numbers 5 and 3 are factors. ProductThe answer to a multiplication problem. Ex. 5x3=15, the number 15 is the product. DividendThe number that is divided. The first, or the top, or inside number. Ex. 15÷3=5, or 15 3 = 5, 𝑜𝑟 the number 15 is the dividend. DivisorThe number that is divided into another number. The second, or bottom, or outside number. Ex. 15÷3=5, or 15 3 = 5, 𝑜𝑟 the number 3 is the divisor. QuotientThe answer to a division problem. Ex. 15÷3=5, or 15 3 = 5, 𝑜𝑟 the number 5 is the quotient. Inverse OperationsReverse or Opposite operations that “undo” each other or cancels each other out. Addition and Subtraction are inverse (opposite) operations. Ex. 2+3=5 5-3=2 Multiplication and Division are inverse (opposite) operations. Ex. 8x3=24 24÷3=8 VariablesLetters used to represent numbers. Ex. a+b a+3=8 Fact FamilyA group of three (3) numbers related by addition/subtraction or by multiplication/division. Ex. Ex. Addition fact family for the numbers 2, 3, and 5 is: 2+3=5 5-3=2 3+2=5 5-2=3 Multiplication fact family for the numbers 3, 5, and 15 is: 5x3=15 15÷3=5 3x5=15 15÷5=3 Absolute ValueThe distance a number is from zero. It is ALWAYS positive, because distance cannot be negative. Ex. |-4|=4 |4|=4 both are 4 units or spaces from zero on the number line. Properties of Addition and Multiplication Commutative Property of Addition – Switching the order of the addends does not change the answer (or the sum). Ex. 2+3=5 or 2+3=3+2 3+2=5 Commutative Property of Multiplication – Switching the order of the factors does not change the answer (or the product). Ex. 2x3=6 or 2x3=3x2 3x2=6 Associative Property of Addition – Changing the grouping, or parentheses, of the addends does not change the answer (or the sum). Note: It must involve 3 or more numbers and parentheses. Ex. (2+3) + 4 = 9 or (2+3) + 4 = 2 + (3+4) 2 + (3+4) = 9 Associative Property of Multiplication – Changing the grouping, or parentheses, of the factors does not change the answer (or the product). Note: It must involve 3 or more numbers and parentheses. Ex. (2x3) x 4 = 24 or (2x3) x 4 = 2 x (3x4) 2 x (3x4) = 24 Identity Property of Addition – Adding zero (0) to a number or variable does not change the number or variable. **Zero is the additive identity. Ex. 2+0=2 a+0=a Identity Property of Multiplication – Multiplying one (1) times a number or variable does not change the number or variable. **One is the multiplicative identity. Ex. 2x1=2 ax1=a Zero Property of Multiplication – Multiplying zero (0) times a number or a variable gives an answer of zero, ALWAYS. Ex. 2x0=0 ax0=0