* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7 - Student Sourcing
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
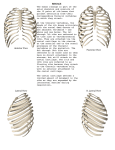
Chapter 7 The Axial Skeleton I. The Axial Skeleton- 80 Bones A. B. C. D. II. The Skull 8 Cranial Bones and 14 Facial Bones Bones Associated w/Skull 7 (3 per ear and the hyoid bone) Thoracic Cage 24 Ribs & the Sternum Vertebral Column 24 Vertebrae, the Sacrum and the Coccyx The Skull (22 bones) A. Cranial Bones- enclose brain, fluid, blood vessels: 1. Occipital Bone (1)- Posterior 2. Frontal Bone (1)- Anterior 3. Parietal Bones (2)- Superior 4. Temporal Bones (2)- Lateral 5. Sphenoid-1 6. Ethmoid-1 B. Facial Bones- protect and support entrances to digestive & respiratory tracts: 1. Superficial Facial Bones- provide attachment sites for muscles that control facial expressions and assist in manipulating food a. Maxillary-1 b. Lacrimal-2 c. Nasal-2 d. Zygomatic-2 e. Mandible-1 2. Deeper Facial Bones- help separate the oral and nasal cavities a. Palatine bones-1 b. Nasal concha- 2 c. Vomer-1 C. Associated Bonesa. Auditory ossicles- 3 per ear b. Hyoid bone (neck)- ligaments attach it to temporal bone D. Sutures- immovable joints- connected by dense fibrous connective tissue a. Lamboidal- Connects occipital to the parietal bones b. Coronal - Connects the frontal to the parietal bones c. Squamous- Connects the temporal to the parietal bones d. Sagittal- Between the left and right parietal bones e. Occipitomastoid- between the occipital bone and mastoid process *Sinuses- lighten bones & provides framework for mucus membrane *Joints (articulations)- two bones connect III. The Vertebral Column- Supports and Protects A. 4 Spinal Curves- S-Shaped fully developed by age 10 1. Cervical 2. Thoracic 3. Lumbar 4. Sacral B. 4 Regions- each vertebrae separated by Intervertebral Disks 1. Cervical- C1-C7 “Breakfast at 7” a. C1- Atlas articulates with occipital condyles of the skull b. C2- Axis articulates with C1, pivot for rotation of atlas c. Small and light- only job is to support the head d. Muscles stabilize massive head on small vertebrae has limits i.e.- whiplash 2. Thoracic- T1-T12 “Lunch at 12” a. Larger Body, smaller vertebral foramen b. Articulate with ribs 3. Lumbar- L1-L5 “Dinner at 5” a. Largest vertebrae b. Bear the most weight c. Large spinous process for lower back muscle attachment that reinforce the lumbar curve 4. Sacral- Sacrum and Coccyx a. Sacrum- Composed of 5 fused sacral vertebrae (fused by age 30) protects reproductive, digestive and urinary organs b. Coccyx (tailbone- 3-5 fused vertebrae) attachment site for ligaments for a muscle that constricts the anal opening. IV. The Thoracic Cage- made of thoracic vertebrae, ribs and sternum A. Protects organs of the thoracic cavity and serves as attachment points for muscles B. The Ribs (costae)- 12 pairs 1. Pairs 1-7 “True Ribs” or Vertebrosternal Ribs a. Connect to the sternum via costal cartilage 2. Pairs 8-10 “ False Ribs” or Vertebrochondral Ribs a. Connect to the cartilage of rib pair 7 which then connects to the sternum 3. Pairs 11-12 “False Ribs” or Floating Ribs a. Only attached to vertebrae 4. Sternum- “breastbone” a. Manubrium- articulates with the collar bones b. Body- rib pairs 1-7 attach here c. Xyphoid Process- diaphragm and rectus abdominus attach here