* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Mendelian Genetics
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
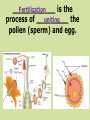
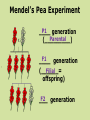
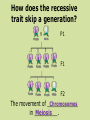
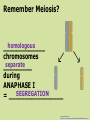
https://conradchrabol.wordpress.com/mendels-early-works/ Intro to Mendelian Genetics Honors Biology What is Genetics? The science that studies Heredity ___________. Heredity is passing of characteristics from parent to offspring. https://www.the-joke-box.com/picture/192/genetics.html The Father of Genetics: Gregor Mendel was an ____________ Austrian monk that was born in 1822. In the monastery, he studied traits genetic ______ and gave us a genes basic understanding of _______ and how they work. https://www.lexile.com/book/details/9780810954755/ Mendel’s experiments were designed by using pea plants ____________ in the monastery garden Pea plants have both male ___________ and female __________ parts pollen Pea plant transfer _______ (sperm) to the egg located in same the _______ plant, resulting in one ________ parent. This is called ______________ Self-Pollination Fertilization ____________ is the uniting process of _________ the pollen (sperm) and egg. Mendel’s Pea Experiments: Mendel started his experiments with peas that were true-breeding _________________ = if allowed to self pollinate _________________ they would produce offspring identical ____________________ to themselves. Mendel’s Pea Experiment removed pollen Mendel ____________________ making parts and added pollen ____________ another plant. from _______ This allowed him to cross-breed _____________ plants different with ______________ characteristics and study ________ the results http://hus.yksd.com/distanceedcourses/YKSDbiology/lessons/FourthQuarter/Ch apter11/11-1/images/MendelExperiment.gif specific characteristic A _____________________ is trait called a ____________ Mendel tested 7 different traits _________________ in peas. Pearson Education Inc,; Publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall When Mendel crossed truePURE breeding (________) PLANTS Contrasting with 2 ______________ traits: (EX: Tall crossed with short) Mendel’s Pea Experiment P1 generation ____ Parental (_________) F1 ____ generation Filial (______= offspring) F2 generation ___ He always found the same pattern: showed one 1. ONLY ______ trait ____________ F1 generation in the ____ BUT . . . Both 2. ___________ traits F2 were found in ____ missing generation. The ________ returned trait __________ in a 3:1 _________ ratio. It’s all about the patterns! Image modified from: http://www.laskerfoundation.org/rprimers/gnn/timeline/1866.html http://www.biology.lifeeasy.org/2502/explain-the-law-ofdominance-using-a-monohybrid-cross http://www.tubechop.com/watch/7029990 Mendel decided that there must factors be a pair of ___________ that control ________each trait and that one factor __________ must be able to hide _______ the other. The factors Mendel referred to are now known as genes _______ that are carried on homologous the _____________ chromosome _____________. http://www.biologyjunction.com/karyotype_lab.htm A gene is a stretch of DNA or RNA that determines a certain trait. Genes can have two or more allele different CHOICES. An _______ is one of the choices for the gene. Example: Eye color Dominant __________________ = An allele hides that ________ the presence of another allele Recessive __________________ = An allele is hidden by that __________________ the presence of another allele http://io9.com/yet-another-lesson-that-shouldbe-banished-from-biology-1204061434 Dominant is represented by a CAPITAL LETTER ____________. Recessive is represented by lowercase letter a ____________. How does the recessive trait skip a generation? P1 F1 F2 Chromosomes The movement of ____________ in _________. Meiosis Remember Meiosis? homologous _____________ chromosomes separate _________ during ANAPHASE I SEGREGATION = _________________ Image modified from: http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/Crossover.gif received F1 offspring __________ ____ an allele for tallness from their tall _______ parent and an allele for short shortness from their ________ parent. http://gladewaterbiology.blogspot.com/2009/11/law-of-dominance.html The F1 plants ALL LOOK TALL ___________ but are carrying ___________ an allele for short _____________ What’s happening in F1 CROSS? SEGREGATION LAW OF ___________________ alleles are separated when the F1 plants made gametes ______________ When these gametes recombined to make the F2 generation, the short _____________ trait reappears _______________ in ¼ of the offspring http://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=514