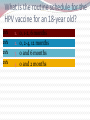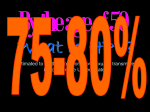* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Papilloma Virus 2017
Poliomyelitis eradication wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Thiomersal controversy wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Cysticercosis wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination policy wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
HIV vaccine wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Human papillomavirus infection wikipedia , lookup
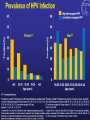
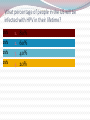
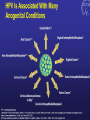
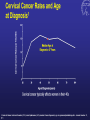
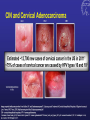
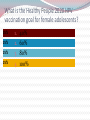
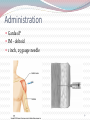
Kenneth McCall, BSPharm, PharmD, BCGP Associate Professor | UNE Immunization Update: Maine Pharmacy Association April 2017 October 13-15, 2017 Portland, Maine HPV Overview Nonenveloped, double-stranded DNA virus1; necessary cause of cervical cancer.2 More than 100 types of HPV viruses identified; 30 to 40 infect the anogenital tract.3,4 – HPV 16 and 18 account for ~70% of cervical cancers worldwide.5 – HPV 16 and 18 are also associated with precancerous lesions.6 1. Howley PM. In: Fields BN et al, eds. Fundamental Virology. Lippincott-Raven;1996:2045–2076. 2. Walboomers JM et al. J Pathol. 1999;189:12–19. 3. Schiffman M et al. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003;127:930–934. 4. Wiley DJ et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35(Suppl 2):S210–S224. 5. Dunne EF et al. JAMA. 2007;297:813–819. 6. Clifford GM et al. Br J Cancer. 2003;89:101–105. 41 What percentage of people in the US will be infected with HPV in their lifetime? 25% 1. 80% 25% 2. 60% 25% 3. 40% 25% 4. 20% Natural History of High-Risk HPV Infection and Potential Progression to Cervical Cancer1 ~1 Year Transient Infection HPV Infection 2–5 Years Persistent Infection Low-Grade Dysplasia CIN 1 4–5 Years High-Grade Dysplasia CIN 2/3 9–15 Years >2 Years Invasive Cancer CIN = cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. 1. Reprinted from Pagliusi SR, Aguado MT. Vaccine. 2004;23:569–578. Copyright© 2004, with permission from Elsevier. 43 Healthy People 2020 goal is 80% What is the Healthy People 2020 HPV vaccination goal for female adolescents? 25% 1. 40% 25% 2. 60% 25% 3. 80% 25% 4. 100% Recent HPV Vaccine News FDA approved Gardasil 9 in December, 2014. Cervarix withdrawn from US Market in October, 2016, due to low sales. CDC recommends HPV vaccine 2-dose schedule for certain patients, December, 2016. Meites E, Kempe A, Markowitz LE. Use of a 2-Dose Schedule for Human Papillomavirus Vaccination — Updated Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2016;65:1405–1408. HPV Vaccine Recommendations POPULATION # OF HPV DOSES INTERVAL Persons initiating HPV vaccine at ages 9 through 14 years, except immune-compromised persons 2 0, 6-12 months* Persons initiating HPV vaccine at ages 15 through 26 years and immuno-compromised persons initiating HPV vaccine at ages 9 through 26 years 3 0, 1-2, 6 months** *In a 2-dose schedule of HPV vaccine, the minimum interval between the first and second doses is 5 months. ** In a 3-dose schedule of HPV vaccine, the minimum intervals are 4 weeks between the first and second doses, 12 weeks between the second and third doses, and 5 months between the first and third doses. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination HPV vaccines are not live vaccines and can be administered to persons who are immunocompromised as a result of infection (including HIV infection), disease, or medications. HPV vaccine can be administered to persons with a history of genital warts, abnormal Papanicolaou test, or positive HPV DNA test. What is the routine schedule for the HPV vaccine for an 18-year old? 25% 1. 0, 1-2, 6 months 25% 2. 0, 2-4, 12 months 25% 3. 0 and 6 months 25% 4. 0 and 2 months A patient misses the 3nd dose of the HPV vaccine series by a month. What is the best option? 25% 1. The HPV vaccine is no longer indicated. 25% 2. Give 3rd dose now to complete series. 25% 3. Repeat the second dose. 25% 4. Restart the series with the first dose. A patient who has begun the HPV vaccine series becomes pregnant. What should be done? 25% 1. The HPV vaccine is no longer indicated. 2. The next dose should be delayed until the 25% 25% 25% 3rd trimester. 3. The next dose should be delayed until aft pregnancy. 4. The patient should complete the series on an accelerated schedule. Administration Gardasil® IM - deltoid 1 inch, 25 gauge needle 30 Storage Refrigeration at 36 to 46 F Do not Freeze Administer as soon as possible – total time out of fridge should not exceed 72 hours The mother of a 12-year-old boy requests the HPV vaccination. Select the correct vaccine and series. 25% Gardasil®: 3 dose series 25% Cervarix®: 3 dose series 25% Gardasil®: 2 dose series 25% Cervarix®: 2 dose series The mother of a 12-year-old boy who has a history of cancer and B lymphocyte antibody deficiency requests the HPV vaccination. Select the correct vaccine and series. 25% Gardasil®: 3 dose series 25% Cervarix®: 3 dose series 25% Gardasil®: 2 dose series 25% Cervarix®: 2 dose series An 18-year-old man requests the HPV vaccine. He has no contraindications. Select the correct vaccine and series. 25% Gardasil®: 3 dose series 25% Cervarix®: 3 dose series 25% Gardasil®: 2 dose series 25% Cervarix®: 2 dose series A 12-year-old girl needs to start the HPV vaccine series and she also needs a Tdap booster. Which of the following statements about the administration of HPV and Tdap vaccines is true? 0% 1. Same day, opposite arm, separate syringe 0% 2. Same day, same arm, mixed in 1 syringe 0% 3. Must be separated by at least 7 days 0% 4. Must be separated by at least 4 weeks