* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The American Civil War 1860 – 1865
Cavalry in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
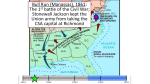
Unit 5: The Civil War and Reconstruction (1850-1877) The Civil War (1861 – 1865) Daily Learning Targets • I can identify and analyze the technological, social, and strategic aspects of the Civil War. • I can analyze the influence of President Lincoln’s philosophy of union on the course of the Civil War. Exit Slip: The Union in Crisis 1. A strong fugitive slave law and California’s admission to the Union as a free state were all part of the a. Missouri Compromise. b. Compromise of 1850. c. Wilmot Proviso. d. Wade-Davis Bill. 2. Uncle Tom's Cabin (1852) convinced many Northerners that a. slaves lived better than factory workers. b. slavery was a necessary evil. c. slavery was cruel and morally wrong. d. slaves were generally happy in bondage. 3. “Bleeding Kansas” earned its nickname from clashes over a. the Gadsden Purchase. c. slavery. b. religious differences. d. land ownership. 4. Why was abolitionist John Brown executed in 1859? a. for attempting to seize an arsenal at Harper’s Ferry and start a slave rebellion b. for killing hundreds of Native Americans on a western reservation c. for beating Senator Charles Sumner with a cane d. for causing violence and bloodshed in the Kansas territory Secession! South Carolina is first to leave on Dec. 20, 1860. Six others follow to CSA by 1861. Eventually 11 total in CSA. Lincoln Takes Office • March 4, 1861 – Republican President Lincoln took a firm, but kind & conciliatory tone toward the South. • He didn’t want to bother slavery where it was, but he did want to stop it from spreading into the Western territories. • He pledged to preserve the Union - #1 Goal! Southern War Strategy • After Confederate forces attacked & captured Fort Sumter in Charleston, SC (April 12, 1861) 4 more states joined the CSA. • President Lincoln declared that war would be necessary to achieve his #1 goal! So he decided to resupply Fort Sumter. • The CSA Generals and President Jefferson Davis planned a defensive war as they just had to outlast the Union not conquer the North. • CSA hoped Great Britain and/or France would help and had superior military leadership. Northern War Strategy • The Union developed a strategy called the Anaconda Plan. They hoped to: 1. Use strong Navy to Blockade all Southern Ports 2. Control the Mississippi River and divide the CSA in two 3. Capture and occupy the Confederate capital of Richmond, VA Stalemate: From Bull Run to Antietam • July 21, 1861 – “Stonewall” Jackson rallies CSA at Bull Run, VA – a CSA victory. Both sides realized it would be a long war. • CSA General R.E. Lee, America’s greatest general, achieved a draw at the Battle of Antietam, MD. 25,000 died on Sept. 17, 1862 making it the bloodiest day of the war. • The CSA won a string of stunning and impressive victories against the superior Union army & Lincoln spent the first years looking for leadership. • In spite of Union victories at Shiloh, TN, Perryville, KY, New Orleans, LA, and the lower Mississippi Valley, at the end of 1862, a stalemate existed in the East. The Emancipation Proclamation • Issued in the Fall 1862 and effective Jan. 1, 1863 • Freed all slaves in areas of the U.S. still under CSA control • Although it was criticized by some, it meant the war would end slavery if Union indeed won. • Lincoln changed his wartime strategy. • Eventually 180,000 African Americans would serve in the Union Army. The Impact of the War in the North and South • Mines, factories, railroad, and weapons production soared. • The government encouraged Western settlement for soldiers who would give two years of service in return for land. This boosted food production. • New York Draft Riots (1863) and similar protests occurred in the North in opposition to compulsive military service for men 20-45. Free blacks and wealthy whites were targeted. Why? • Lincoln suspended the Constitutional right of Habeas Corpus that protects persons from imprisonment without the filing of specific charges and many arrested for suspected disloyalty. • In the South, property was devastated and the economy was wrecked by inflation – price increases due to concern about the value of Confederate money. 1863: The Turning Point • July 1-3, 1863 – Lee leads his Army of N.VA North to PA and the greatest battle of the war begins. • 23,000 Union and 28,000 CSA casualties at Gettysburg, PA. Lee’s only major mistake of the war was Picket’s Charge on Day 3. • Lee would never invade Union again! • July 4, 1863 – General Ulysses S. Grant, the Unions most successful commander, captures Vicksburg on Mississippi River. • By early 1864 Grant is chosen by Lincoln to take command of the Union Army. Sherman’s March to the Sea and Total War • Sept. 2, 1864 – Gen. Sherman captures Atlanta, GA • Marches to Savannah, GA and orders a 300 mile-long and 50 mile-wide swath of destruction designed to end the CSA’s will & ability to fight. • Turns north through Carolinas in Dec. 1864 to meet Grant & end war • Civilians and slaves suffer immensely; it was controversial. The Election of 1864 • The capture of Atlanta and “Bayonet Voters” aid Lincoln’s re-election hopes. • He was opposed by Democrat and ex-General George McClellan – a peace candidate who wanted to end the war • Lincoln and Andrew Johnson (VP and Democrat) form the Union Party and win 212/233 electoral votes Lee Surrenders to Grant! April 9, 1865 • Richmond, the CSA capital, was in ruins, Sherman wasted Georgia and the Carolinas, & Lee’s army was desperate & worn down. • President Davis and officials fled from Grant & later captured • Lee was humble and Grant was very generous at Appomattox, VA • 640,047 Union and 483,026 CSA casualties of war; America’s bloodiest war in history. Exit Slip – The Civil War Begins 1. Which side planned a defensive war? a. Union b. Confederacy c. Mexico 2. At the end of 1862 __________. a. the Union was winning b. the Confederacy was winning c. both sides were locked in a stalemate 3. This act by President Lincoln freed all slaves in states of the Confederacy not under Union rule? a. Emancipation Proclamation b. 3/5 Compromise c. 13th Amendment d. Homestead Act Exit Slip – The Civil War 1. Who was the commander of all Confederate forces after 1862? a. Longstreet b. Bragg c. Lee 2. This battle of July 1863 was turning point of the Civil War? a. Antietam b. Gettysburg c. Chickamauga 3. This city was totally destroyed during Sherman’s March? a. Atlanta b. Savannah c. Charleston 4. Which side won the Civil War? a. Union b. Confederacy c. It was a draw