* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 - Kenton County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
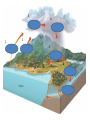
3.1 – What is Ecology? Interactions and Interdependence • Ecology – the study of interactions among organisms and their environment • Oikos (ec) – Greek word meaning house • Ology – means study of Levels of Organization • The levels of organization that ecologists study include: • Individuals • Species – group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring • Populations – group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area and interbreed • Communities – several populations that live together in an area • Ecosystem – The interaction of all the organisms and the environment in a given area • Biome – a group of ecosystems that have the same climate • Biosphere – part of Earth in which life exists including land, water and atmosphere • It extends about 8km above the Earth’s surface to about 11km below • If you could shrink earth to the size of an apple, the biosphere would be thinner than the apple’s peel Biotic and Abiotic Factors • Biotic Factors – all the living organisms in an ecosystem • • Example: tree, bird, bacteria, fungi Abiotic Factors – nonliving factors in an ecosystems • Example: temperature, precipitation, wind, soil, sunlight, humidity • Habitat – area where an organism lives including biotic and abiotic factors • Niche – the role and position a species has in its environment • No two species can share the same niche in the same habitat 3.2 – Energy Flow • Sunlight is the main energy source for life • Autotrophs • Make their own energy • Convert sun energy into chemical energy • Also called a producer • Plants are the main autotrophs on land • Algae are the main autotrophs in water • Some autotrophs can produce food in the absence of light • Chemoautotrophs – organisms use chemical energy to produce carbohydrates • Live in… • Volcanic vents • Deep ocean • Hot springs • Marshes • Heterotrophs • Get energy from other organisms • Unable to make its own energy • Also called consumers • Types of Heterotrophs • Herbivores • Eats only plants • Example: cows, deer, rabbits, bees, elephants, squirrels • • Carnivores • Eats only animals • Example: snakes, dogs, lions, crocodiles Omnivores • Eats plants and animals • Example: humans, bears, crows • • • Detrivores • Eat decomposing bits of organic matter • Example: mites, earthworms, snails, crabs Decomposers • Break down organic matter • Example: bacteria and fungi Scavenger • Ingest nonliving plants and animals • Example: vulture, termite, beetle Feeding Relationships • Food Chain – a straight line series of steps by which energy is stored and passed on to higher trophic levels • Food Web – a network of crossing interlinked food chains that shows all the possible feeding relationships at each trophic level • Trophic Levels – the different feeding relationships in an ecosystem. • Plants and other producers are 1st trophic level • Consumers make up the 2nd, 3rd, or higher trophic levels • Each consumer depends on the trophic level below it for energy • Energy is transferred from one trophic level to another and is never 100% • At each trophic level only 10% of the energy taken in by the organism is stored. • Energy is passed through no more than four or five trophic levels Ecological Pyramids • Ecological Pyramid – a diagram that shows the relative amounts of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web 3-3 Cycles of Matter Properties of Water • Water is perhaps the most important compound in living organisms • Water serves as a means of material transportation in organisms. • • Hydrogen bond – attraction between opposite charged molecules (H+ O-) • • Ex. Blood (is mostly water) Are important because they help hold many large molecules such as proteins together. Water resists changes in temperature • Water requires more heat to increase its temperature. • Water is like an insulator • • Water is one of the few substances that expands when it freezes. • • • maintains homeostasis Ice is less dense than liquid Cohesion – attraction between like molecules • Cohesion creates tension • Tension – inward pulling on water molecules at the surface Adhesion – attraction between different molecules • Biogeochemical Cycles – chemicals and nutrients are transferred from environment into organisms then back to the environment The Water Cycle • Evaporation – process by which water changes from a liquid to a gas • Transpiration – loss of water from plants by the process of evaporation • How does water move up a plant? • Xylem – tubes in plants that transport water from roots to leaves. • On sunny days, water evaporates from leaves • Adhesion & Cohesion pulls up more water molecules into leaf cells • Condensation – water vapor changes to a liquid • Precipitation – water returns to the earth (rain, snow, hail) Click to view animation. 3 1 4 2 5 6 7 6 5 CO2 2 1 Burning Fossil Fuels Volcanic Activity 3 Burning Trees Photosynthesis 4 Respiration 7 Organism eats plants C6H12O6 8 11 Oil 10 Decomposition 9 Coal Root Uptake Gaseous Nitrogen N2 1 6 2 Nitrogen Fixation Ammonification Denitrification Bacteria in the soil convert Bacteria convert wastes and decomposing organics to Bacteria convert N2 → NH3 → NH4 NO3 → N2 NH3 → NH4 5 Autotrophs can take up NH4 and NO3 3 4 Nitrification Bacteria convert NH4 → NO2 → NO3 • Humans are harming the nitrogen cycle by: • Deforestation • Conversion of grasslands for agriculture • Sewage enters waterways • Fossil fuel burning • Vehicles having combustion engines releases NO2