* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology and Food Chains
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
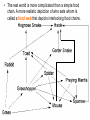
Ecology and Food Chains SPECIES POPULATION COMMUNITY ECOSYSTEM BIOME BIOSPHERE • Organism: any form of life. • Organisms are classified into species: organisms that resemble one another in appearance, behavior, chemistry and genetic code. • Population: all members of the same species living in a specific area at the same time The place where a population lives is its habitat • The populations of all the different species occupying and interacting in a particular place make up the community • An ecosystem is a community of different species interacting with one another and their non-living environment of matter and energy • Biomes are large regions with a distinct climate and specific life forms. Each biome is made up of many ecosystems. BIOSPHERE • The parts of earth that contain/support life. Factors that affect living things are: • Biotic factors – things that are alive or were alive (other organisms) • Abiotic factors – things that are non-living Abiotic Factors • • • • • • Temperature Water Wind Sunlight Rocks/soil Catastrophes • All living things need energy to survive and grow. • The source of this energy is the sun. Producers: Called autotrophs Can make sugar (glucose) by photosynthesis Examples: Algae, grasses, trees, etc. Consumers: Called heterotrophs Depend on other living organisms for food; They cannot make their own food. Primary Consumers: Herbivores eat vegetation Ex. : Grasshoppers, rabbits, snails, etc. Secondary Consumers: Carnivores eat herbivores Ex. : cats, foxes, owls, etc. Tertiary Consumers: Top carnivores (eat other consumers) Ex. : Lions, bears, wolves, etc. Decomposers: They decompose (break down) dead organic material and return important nutrients to the soil which helps plants grow. Ex. : Bacteria and mushrooms Scavengers • An organism that eats dead or decaying matter. Trophic level • Refers to the organism’s position in the food chain • Autotrophs are at the base (first trophic level). • Organisms that eat autotrophs are called herbivores or primary consumers (second trophic level). • An organism that eats herbivores is a carnivore and a secondary consumer. (third trophic level) • A carnivore that eats a carnivore that eats a herbivore is a tertiary consumer (forth trophic level). • Omnivores eat both animals and plants. Feeding Levels Energy and Nutrient Flow Through the Ecosystem The movement of energy is shown by the dark arrows. The movement of nutrients is shown by the white arrows. Inorganic nutrients are cycled, energy is not recycled – it is lost. ENERGY • At each level of the food chain, about 90% of the energy is lost in the form of heat. • The total energy passed from one level to the next is only about one-tenth (10%) of the energy received from the previous organism. • As you move up the food chain, there is less energy available. • Animals located at the top of the food chain need a lot more food to meet their energy needs. Food Chains • A food chain is the path of food from a given final consumer back to a producer. grass grasshopper mouse snake • The real world is more complicated than a simple food chain. A more realistic depiction of who eats whom is called a food web that depicts interlocking food chains. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TE6wq G4nb3M (ecology song) Example of a food chain (out of order) and the associated trophic (feeding) levels - complete Organisms Type Trophic Levels Raven Grasshopper Ladybug Grasses Mushrooms Bacteria Example of a food chain (out of order) and the associated trophic (feeding) levels Organisms Raven Grasshopper Ladybug Grasses Mushrooms Bacteria Type Tertiary Consumer (top carnivore) Primary Consumer (herbivore) Secondary Consumer (carnivores) Producer (plants) Decomposer Trophic Levels Fourth Second Third First Feed off all levels