* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The normal ECG Cardiac cycle and cardiac sounds/ Pressure
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
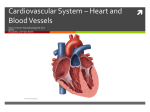
The normal ECG Cardiac cycle and cardiac sounds/ Pressure changes in atria and ventricles Syllabus ECG General description Leads and Vectors (Including Einthoven’s triangle) P wave P-R interval QRS complex ST segment T wave Q-T interval Non-Pacemaker action potentials - Phase 0 - Phase 1 - Phase 2 - Phase 3 - Phase 4 Refractory period - Absolute - Relative Pacemaker action potentials - Phase 0 - Phase 3 - Phase 4 Regulation of conduction Regulation of pacemaker activity Cardiac cycle and cardiac sounds/ Pressure changes in atria and ventricles Atrial systole Isovolumetric ventricular contraction Ventricular Ejection Isovolumetric ventricular relaxation Ventricular filling Wiggers diagram - ECG - Heart sounds - Left ventricular pressure - Aortic pressure - Carotid pressure - Radial pressure - Right ventricular pressure - Pulmonary artery pressure - Left atrial pressure - Jugular venous pressure - Left ventricular volume Questions 1) A 65 year old female is admitted to ICU after an elective AAA repair. Two hours after admission her blood pressure is 95/55 and HR 115/min. She is a known hypertensive. a) Draw normal CVP trace (10) b) Draw the waveforms produced as one inserts a pulmonary artery catheter (20) c) Discuss the role of the CVP and pulmonary artery catheter as monitors of intravascular volume (20) 2 a) Compare and contrast the actional potentials of a left ventricular cardiomyocyte and the sinoatrial node (30) b) Discuss the regulation of pacemaker activity (15) c) Discuss the cardiac refractory period (5) References 1) Review of Medical Physiology. William F. Ganong. 22nd Edition. Chapters 28 and 29 2) Miller’s Anaesthesia. Ronald D. Miller. 7th Edition. Chapter 40 - Cardiovascular Monitoring 3) CVphysiology.com Pathophysiology of myocardial ischaemia, shock, hypertension and cardiac failure 1) Myocardial Ischaemia a) Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis b) Pathophysiology of chronic stable angina c) Pathophysiology of unstable angina/NSTEMI d) Pathophysiology of STEMI e) Pathophysiology of perioperative myocardial infarction References: a) Choose a standard medical textbook for basic pathophysiology. I advise: Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. Kasper, Braunwald, Fauci, et al. 16th Edition or later. If you are using 16th Ed then: 224: The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis 226: Ischemic heart disease 227: Unstable angina and non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction 228: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction Focus on the pathophysiology sections of the above unless very keen to expand horizons. b) Peroperative cardiac events in patients undergoing noncardiac surgery: a review of the magnitude of the problem, the pathophysiology of the events and methods to estimate and communicate risk. Devereaux, PJ; et al. CMAJ 2005; 173(6):627-34 2) Shock a) Cardiovascular pathophysiology-especially sepsis Reference: Sepsis and the Heart. Merx, MW; Weber, C. Circulation 2007; 116: 793-802. 3) Hypertension a) Essential - Pathophysiology - Target organ effects b) Secondary - Renal - Endocrine - Neurogenic - Drugs - Miscellaneous References: a) Choose standard medical textbook as basic reference. Again I advise Harrison’s. 230: Hypertensive vascular disease-focus on pathophysiology b) Stoelting’s Anaesthesia and Co-existing Disease. Hines, RL; Marschall, KE. 5th Edition. Chapter 5: Systemic and Pulmonary Hypertension-focus on first section on Pathophysiology. c) Is a rethink of our approach to hypertension necessary? Coetzee, A; Levin, A. SAJAA; November 2005: 117-123 4) Cardiac failure a) Systolic b) Diastolic Reference Heart Failure. Jessup, M; Brozena, S. NEJM 2003; 348:2007-18 Myocardial blood flow and metabolism Syllabus Anatomy - Epicardial coronary arteries & territories - Microanatomy Coronary blood flow - ml/min - ml/100g/min - % of cardiac output Coronary perfusion pressure Variation of coronary blood flow with cardiac cycle Control of coronary blood flow Measurement of coronary blood flow Myocardial oxygen consumption and oxygen extraction ratio Myocardial metabolism Myocardial supply-demand balance Stunning Hibernation Ischaemic preconditioning Questions 1) A 59 year old male patient presents for a hemicolectomy. He is diabetic, hypertensive and a smoker with a 30 pack-year history. During surgery there is significant blood loss and he becomes tachycardic and hypotensive. ST segment depression is noted. a) Compare and contrast myocardial blood flow to the right and left ventricles. (10) b) Discuss the determinants of myocardial oxygen delivery. (20) c) Discuss strategies to improve myocardial oxygen balance that may be of relevance to the above patient. (20) References 1) Review of Medical Physiology. William F. Ganong. 22nd Edition. Chapter 32-Circulation Through Special Regions and Chapter 29-Origin of the Heartbeat & Electrical Activity of the Heart. 2) Clinical Anesthesiology. G. Edward Morgan, Maged S. Mikhail, Michael J. Murray. 4th Edition. Chapter 19-Cardiovascular Physiology & Anesthesia. 3) CVphysiology.com