* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro-to-AI-lect-1 - Geometric and Intelligent Computing Laboratory
Chinese room wikipedia , lookup
Kevin Warwick wikipedia , lookup
Alan Turing wikipedia , lookup
Technological singularity wikipedia , lookup
Lisp machine wikipedia , lookup
Artificial intelligence in video games wikipedia , lookup
Turing test wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
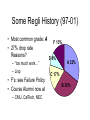
MCS 380/590 Intro to Artificial Intelligence William C. Regli Geometric and Intelligent Computing Laboratory Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Drexel University http://gicl.mcs.drexel.edu What is Artificial Intelligence? Alan M.Turing (1912-1954) Computing machinery and intelligence. Mind, Vol. LIX. 433460, 1950 • Computers will be intelligent. • Debate then and now: – Will this just be a symbiotic relationship (computer as tool)? – Or will computers be “conscious”? The Turing Test • Imitation Game: – – – – – Judge, man, and a woman All chat via Email. Man pretends to be a woman. Man lies, woman tries to help judge. Judge must identify man after 5 minutes. 2. Turing Test – – Replace man or woman with a computer. Fool judge 30% of the time. What Turing Said “I believe that in about fifty years' time it will be possible, to programme computers, with a storage capacity of about 109, to make them play the imitation game so well that an average interrogator will not have more than 70 per cent chance of making the right identification after five minutes of questioning. The original question, "Can machines think?" I believe to be too meaningless to deserve discussion. Nevertheless I believe that at the end of the century the use of words and general educated opinion will have altered so much that one will be able to speak of machines thinking without expecting to be contradicted.” Alan M.Turing, 1950 “Computing machinery and intelligence.” Mind, Vol. LIX. 433-460 About the Class… Textbooks • Russell and Norvig, Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, the Prentice Hall Series in Artificial Intelligence. ISBN 0-13-103805-2. • Paul Graham, ANSI Common LISP, Prentice Hall, 1996. ISBN 0-13-370875-6. Course Contents • • • • • Search Knowledge Representation Logical Reasoning Planning Symbolic Computation and The Lisp Language Pre-Requisites • • • • MCS 260: Data Structures MCS 360: Programming Languages Programming proficiency: C/C++ & Java Ability to do proofs (180/270) and reason with discrete mathematics (sets, graphs, nodes, functions, relations, etc) Workload and Grading • Assignments every week – programming and/or written, 8-9 total • Plan on 10hrs/week outside of class • Breakdown – 40% exams – 30% programming – 30% homework • Note the “Failure Policy” in syllabus • No late assignments or makeups Some Regli History (97-01) • Most common grade: A F 13% • 27% drop rate Reasons? D 8% – “too much work…” – Lisp • F’s: see Failure Policy • Course Alumni now at – CMU, CalTech, NEC A 32% C 17% B 30% Questions?