* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download First Civilizations PowerPoint Lecture
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
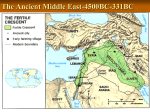
PALEOLITHIC, NEOLITHIC, AND RIVER VALLEY SOCIETIES Mr. Robert Humphreys Paleolithic Life- Hunter/Gatherers Homo sapiens emerged in Africa Had larger brain Developed in Africa and spread out over the world Paleolithic Life- Hunter/Gatherers Paleolithic humans were nomadic huntergatherers Most important discoveries/inventions- fire and stone tools Why would fire be useful? Tools and innovations geographically specific What tools might you develop if you life in Alaska vs. the Mediterranean region? Paleolithic Life- Hunter/Gatherers Developed art- example: cave paintings Organized into small political groups- kinship groups or multiple kinship groups called clans Not necessarily self-sufficient- evidence of trade is evident from this period Beginning of spiritual beliefs to explain the world Animism- belief in spirits of nature Shamans- people believed to have special abilities to cure the sick and influence the future Less socio-economic separation than in later times Why do you think nomadic people had less social stratification than later people living in cities? Paleolithic Life- Hunter/Gatherers Gender roles: more gender equality than later times Men: hunting, fishing, defense Women: gathering, medicine, childcare Neolithic Revolution Climate warmed at end of Paleolithic End of Paleolithic times- agriculture discovered (probably by women!) Small agricultural settlements began to develop Neolithic Revolution: change from hunting and gathering to systematic agriculture and domestication of animals Farming first developed in Mesopotamia around 8000 BCE Farming slowly developed through trial and error and discovery, then spread to other regions Domestication of animals began with herd animals like goats and sheep Spread of Agriculture Neolithic Revolution Geography is key! People domesticated plants and animals that were already wild in their region Wheat in Middle East Rice in Southeast Asia Corn in Mesoamerica Neolithic Revolution A Chain Reaction Agriculture People settle in villages (grow into cities) food surpluses specialization of labor trade characteristics of civ. Neolithic Life Huge population increase Pre- Neolithic Population: 5-8 million By 4000 BCE: 60-70 million Neolithic Life Human interaction with the environment determined LOTS about Neolithic life Resources available determined the types of tools, weapons, homes, foods, clothing, etc that Neolithic people used Originally ruled by council of elders but authority in many places moved to one ruler over time Neolithic Life Close knit societies with lots of shared resources- ovens, fields, grain storage, worked together to build irrigation, clear land, etc Private property limited to personal possessions Possessions linked to agriculture and survival- clay pottery, woven baskets, wool and linen clothing, more advanced tools and weapons made from metal, plows As agriculture led to larger and more stable settlements, more organization became necessary Neolithic people also had interaction with other groups and there is archeological evidence of trade between settlements Development of Civilization Characteristics of Civilization Cities Organized central governments Complex religions Social classes Job specialization and the arts/architecture Literature: Reading/Writing Increased populations Cities Early cities developed near rivers Positives: water supply, transportation, communication, trade Challenges: flooding, need to develop irrigation to control water Led to development of govt- need to organize people for building projects Government Central government needed to control labor, storage of food, dispersion of food to people, mediate disputes and keep order Many early governments centered around priests, later warriors or kings Eventually governments became more complex and gained new responsibilities such as: tax collecting, law making, public works, military organization. Complex Religion Almost all were polytheistic Gods to represent nature and control human activities Priest class developed to gain gods’ favor through rituals and sacrifices Early kings regarded as gods themselves or representatives of gods Exception: Hebrews were first monotheistsJudaism Monumental architecture developed to connect with religious beliefs Social Classes With specialization of labor came social classes People ranked according to their professions Generated class differences Priests (“We talk to god, you don’t.) Aristocrats/warriors (“We have weapons, you don’t.”) Common people (“I guess we work...?”) Slaves (“Uh, oh!!!”) Job Specialization and the Arts Artisans: people who produce things Examples: bricklayers, blacksmiths, weavers Production of luxuries as society moved past subsistence Metal technology (bronze, then iron) Monumental architecture- often tied to religion Egyptian temple Mayan temple Mesopotamian ziggurat Writing Probably first used by priests Chinese calligraphy Earliest writing used pictographs Symbols later added to represent words and then sounds Scribes were trained to read, write, and record information about religion, trade, government activity Cuneiform in Mesopotamia considered first writing system First alphabet later developed by Phoenicians in Middle East Mesopotamian cuneiform Egyptian hieroglyphs Environmental Impact Soil erosion- how would this occur from both farming and grazing animals? What other problems would occur with intensive farming over time? Uniqueness of Civilization Civilization was not inevitable from the Neolithic Revolution Many people remained nomadic for thousands of years Pastoral nomads also developed- animal herders who moved around finding food for animals (important transmitters of early technology!) Impact of Geography • Flooding of Tigris and Euphrates unpredictable Mesopotamia • No natural barriers • Limited natural resources for making tools or buildings • Flooding of the Nile predictable Egypt • Nile an easy transportation link between Egypt’s villages • Deserts were natural barriers • Indus flooding unpredictable Indus River Valley • Monsoon winds • Mountains, deserts were natural barriers • Huang He flooding unpredictable China • Mountains, deserts natural barriers • Geographically isolated from other ancient civilizations Mesoamerica & • Mountains and ocean natural barriers • Warm temperatures and moderate rainfall Andes • Geographically isolated from other ancient civilizations Journal Complete “Worst Mistake” reading for first journal activity as soon as you come in Take out powerpoint outline and be ready to go Four Major River Valley Civilizations Mesopotamia Located in Middle East between Tigris and Euphrates Rivers Aka Fertile Crescent and Cradle of Civilization Why civilization here? Frequent flooding created fertile farmland, warm climate Sumerians migrated in Mesopotamia and settled between 5000 and 4000 BCE Mesopotamia- Sumerians Sumerians were divided into independent city-states Government was a theocracy led by a king who was considered a god Kings were military leaders- built huge stone walls to protect cities Sumerians were polytheistic- cities revolved around a main temple dedicated to the god of the city- built on top of a ziggurat Mesopotamia- Sumerians Relied on flooding of the Tigris and Euphrates to fertilize the soil and help with farming Flooding was unpredictable so Sumerians developed irrigation techniques to control the water Food surplus led to specialization of labor and social classes Lots of trade with other civilizations over land and by sea Mesopotamia- Sumerians Patriarchal Social Classes- based on money and occupation King Priests, officials, aristocracy Merchants and artisans Farmers Servants and slaves Mesopotamia- Sumerians Sumerians developed first writing system called cuneiform Without an alphabet, writing was extremely complex and time consuming to learn, so scribes became a specialized job Usually carved into wet clay and then dried Mesopotamia Because Mesopotamia was a flat piece of land with few natural boundaries, it was continually invaded Akkadians, Babylonians, Assyrians, Chaldeans, Persians, etc. controlled parts of Mesopotamia at different times in ancient history What do you think would allow some societies to conquer others? Other Key Civilizations in the Middle East Babylonians- invaded Mesopotamia and built a huge empire Known for King Hammurabi’s Code Other Key Civilizations in the Middle East Phoenicians- lived along eastern Mediterranean Known for first alphabet Other Key Civilizations in the Middle East Hebrews (Israelites) Judaism- first monotheistic religion 10 Commandments Mesopotamia- Important Achievements Writing- cuneiform Wheel and wheeled vehicles (chariots) Number system Bronze Iron (weapons and tools) Code of laws (Hammurabi’s Code) Plows Literature- Epic of Gilgamesh Lots more! Egypt and Geography Civilization in Egypt developed along the Nile River longest river in the world Nile Delta for farming- diffused from Mesopotamia Natural boundaries for protection Developed irrigation to deal with flooding Worshipped gods of nature Egyptian History and Government History of Egypt began around 3100 B.C. when Upper and Lower Egypt were united and created the first Egyptian dynasty Pharaoh- political and religious leader- seen as a god Bureaucracy- administrative organization helped rule and carry out orders Egyptian Religion Egyptians were polytheistic had many gods associated with nature and heavenly bodies (like the sun) flooding of the Nile symbolized new life Sun god: Ra- why would the sun be an important god? Egyptian Social Classes Egyptian Gender Roles Men: head of the family Women: in charge of the home and children More freedom than other societies- could make contracts and own property wealthy women could sometimes gain power through their powerful families 4 women became pharaohs (examples: Hatshepsut and Cleopatra) Egyptian Arts and Writing hieroglyphics- system of writing using pictures and symbols complex system that took a long time to learn Egyptians wrote on stone and later on papyrus artists were expected to follow certain formulas and styles the human body was often shown in a combination of profile, semi profile, and frontal view Monumental architecturepyramids The Three Kingdoms The Old Kingdom Labeled as the “Age of the Pyramids” In early Egyptian history, opposite sides of the Nile River were in competition of domination of the land. King Menes had managed to unify both Upper and Lower Egypt around 3100 BCE. Egypt had managed to hold its power and influence in the region for quite some time, ultimately losing it’s power in 2181BCE due to famine and starvation from a drought that swept the region. It wasn’t until King Mentuhotep reunited Egypt and revitalized under the Middle Kingdom. Inaccessible to people; “Too Cool for you” personality. The Middle Kingdom Labeled as the “Golden Age” Due to the economic growth and expansion of the Egyptian rule. Very different compared to the Old Kingdom, largely in part because the Pharaoh was now accessible, considering them to be a “shepherd to the people” Life along the Nile flourished with trade, economic gain, promise in arts and literature. Pharaohs weren’t buried in the pyramids but rather hidden tombs to thwart criminals from stealing possessions. Hierarchy/Social classes created and enforced. The New Kingdom (1550-1070 BCE): Highly militaristic agenda; Dominated the region and surrounding areas. Kingdom reached it’s height under Amenhotep III, through new reconstructions and improvements to temples and buildings. Religious movements began to generate steam and cause problems amongst the Egyptians, which would lead to their downfall. After Amenhotep III’s death, his son Amenhotep IV came to power and attempted to incorporate this new religious change into his empire, which proved disastrous. Egyptian Advancements - learned math that helped them to build huge monuments - developed a 365 day calendar - practice of embalming (preserving a dead body) - medical knowledge- treated broken bones and diseases Indus River Valley first civilization in India Harappan civilization developed along Indus River Large cities- Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro city populations up to 40,000 Laid out in grid pattern (what does this say about govt?) Sewer systems Walls of protection Public wells Used kiln dried bricks Indus River Valley- Aryan Invasion Harappan civilization weakened over time, probably due to natural disasters and environmental destruction Conquered by Aryan nomadic invaders Began to set up class structure with Aryans on top (later became the caste system) Aryans also brought belief system that would later become Hinduism Indus River Valley Aryans brought Sanskrit language which was eventually turned into writing Important Vedas- literature- became basis of Hinduism collection of Aryan hymns, poems, stories Upanishads- important religious ideas emerged such as karma, reincarnation, and brahmin Ancient China- Huang He (or Huang Ho) First civilization developed along Huang He River 1. Xia Dynasty (pre-history) 2. Shang Dynasty (1750-1122 BC - Mostly a farming society which was often at war 3. Zhou Dynasty (1045-256 BC) - Began the “Mandate of Heaven” idea Ancient China- Huang He (or Huang Ho) the rulers of China under the Zhou dynasty claimed that they ruled under the Mandate of Heaven believed that heaven (supernatural force) kept order through the Zhou ruler ruler ruled by a mandate (authority to command) from Heaven ruler is then supposed to rule with efficiency and fairness towards the people ruler supposed to rule according to the Dao (“the way”) in order to keep the gods pleased if the gods were not pleased, the ruler could be overthrown Ancient China- Huang He (or Huang Ho) - - - - Chinese believed in supernatural forces Used oracle bones to communicate with the gods Believed spirits of ancestors could help them communicate with the gods Ancestor veneration very important- offerings and sacrifices made to ancestors Americas Civilization didn’t always develop on rivers Mesoamerica and Andes regions became important centers for civilization Developed farming independently of rest of world Americas Chavin developed along coast of Peru Farmed with irrigation: corn, potatoes, quinoa Domesticated llamas for meat and wool Ruins of large temple at Chavin de Huantar Americas Olmecs built civilization in Mesoamerica Farmed: corn, beans, squash, avocados Traded extensively Built huge pyramids Developed writing and a calendar Global Connections These civilizations did NOT exist independent of each other All of them traded extensively with others (often with smaller civilizations in the area) Some traded with each other such as Mesopotamia and Indus Valley