* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download X-Ray Generators
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
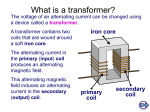
Resident Physics Lectures (Year 1) Christensen, Chapter 3 X-Ray Generators George David, MS FAAPM, FACR Associate Professor of Radiology Requirements to Produce X-Rays Filament Voltage High Voltage anode + high voltage source filament filament voltage source X-Ray Generator Supplies electrical power to x-ray tube high voltage between anode & cathode filament voltage Controls exposure timing Turns exposure on and off Filament heated before exposure High voltage switched on and off anode + high voltage source filament filament voltage source Voltage Voltage from US power company Home 120 / 240 V Industrial 480 V 240 V Voltage required Home Most stuff: 120 V AC / Dryer: 240 V Door bell: 15 V Computer 5 V X-Ray Filament: 8-12 V High voltage: 40-150 kV (40,000 – 150,000) Transformers Magical devices that allow voltage to be changed to any desired value Current Flow and Magnetic Fields Magnetic field surrounds conductor carrying electric current Magnetic field concentrated by coiling conductor Magnetic Field N Magnetic Field S Current Flow Transformer Construction Transformers have 2 coils of wire coils not in electrical contact with each another When electric current passed through one coil magnetic field develops around first coil second coil near enough to feel magnetic field Magnetic Field Current Flow Transformer Coil Designations Incoming AC Power Primary Coil primary coil to which power is applied secondary coil which feels magnetic field of primary coil Secondary Coil(s) Transformer Coils When secondary coil feels changing (increasing or decreasing) magnetic field of primary coil power induced in secondary coil no physical connection Incoming AC Power Primary Coil Secondary Coil(s) Turns Ratio Definition TR=NS / NP number of windings of secondary coil divided by number of windings of primary coil 40 / 20 for transformer below NP = 20 NS = 40 Transformer Theory transformers do not work with direct (unchanging) current (DC) Current induced in secondary coil only when primary coil current / magnetic field is changing Input DC Voltage & Current No Output Voltage Voltage Time Time Transformer Theory Transformers alter both voltage & current of AC waveforms Voltage in secondary can be > or < voltage in primary Input AC Voltage & Current Output AC Voltage & Current Transformer Law Voltage Ratio = Turns Ratio # Sec. Coils Turns Ratio = ---------------# Prim. Coils NS VS ----- = ----NP VP Sec. Voltage = ------------------Prim. Voltage Transformer Types Step down Transformer # primary coils > # secondary coils primary voltage > secondary voltage Step up Transformer • # primary coils < # secondary coils • primary voltage < secondary voltage How Does a Transformer Magically Increase Voltage without Some Source of Power? Transformer Law (cont.) Current ratio is inverse of voltage ratio # Sec. Coils Sec. Voltage Prim. Current ----------------- = --------------- = ----------------# Prim. Coils Prim. Voltage Sec. Current NS VS IP ----- = ----- = ----NP VP IS VPRIM X IPRIM = VSEC X ISEC Transformers Power = Voltage X Current Electrical power not changed Current exchanged for voltage Voltage goes up – current goes down Voltage goes down – current goes up Power Power is rate of energy usage Power defined as Voltage X Current Units Voltage => Volts Current => Amps Power => Watts •Voltage => Kilovolts •Current => milliamps •Power => Watts Power Power = Voltage X Current Transformer primary power = secondary power transformer neither creates nor consumes power PowerPRIM = PowerSEC VPRIM X IPRIM = VSEC X ISEC Transformer Ratio Ratio = Output voltage / Input voltage Most transformers have fixed ratios X-Ray requires variable ratios Accommodate selection of different kVs Autotransformer Taps Only one winding Incoming AC voltage connected across coils primary Input Output voltage proportional NP NS to # coils between taps secondary Primary Secondary Autotransformer Voltage law for autotransformers same as for transformers Variable ratio transformer Secondary voltage adjustable by moving to a Input NP different tap changes # secondary coils NS NS VS ----- = ----NP VP Primary NS Generator Components control console kVp adjust mA adjust or mAs adjust time adjust transformer high voltage (step up) filament low voltage (step down) electronics cabinet support circuitry X-ray Circuit Timer Circuit Autotransformer mA selector Rectifier Circuit + Line High Voltage Transformer Filament Transformer Timer Circuit Rectifier Circuit Autotransformer mA selector + Line High Voltage Transformer Filament Transformer Line Incoming line voltage connected to generator through a circuit breaker. Typ. 220-240 volt AC single phase 240, 480 volt AC three phase Circuit Breaker Generator connected to power line through a circuit breaker Limits current from power line to generator Allows generator to be disconnected from power line Incoming Power Line Generator Circuit Breaker Line Autotransformer mA regulator Timer Circuit Rectifier Circuit Fixed ratio + Variable ratio High Voltage Transformer Filament Transformer •Auto transformer • Variable ratio transformer allowing operator to specify kVp •High voltage transformer • Boosts output of autotransformer by fixed ratio Timer Circuit Autotransformer mA regulator Rectifier Circuit + Line High Voltage Transformer Filament Transformer Timer •Starts & stops exposure •Turns transformer primary (low voltage) on & off Exposure Timing Manual Operator sets time Automatic (Phototimed) Equipment measures radiation Terminates exposure when designated radiation is measured Phototiming Detector in front of receptor Must be essentially invisible Radiation Sensor Grid Image Receptor Phototiming Fields 1, 2, or 3 fields may be selected individually or in combination proper positioning critical Timer Circuit Rectifier Circuit Autotransformer mA regulator + Line High Voltage Transformer Filament Transformer Timer •Develops DC high voltage for x-ray tube High Voltage Transformer Grounded metal box filled with oil electrical insulator Function Develops proper high voltage for tube Also contains rectifier circuit Rectification allows current flow in one direction only Transformers only work with alternating current (AC) Rectifier changes alternating current output of high voltage transformer to direct current DC voltage applied to tube Timer Circuit Rectifier Circuit Autotransformer mA regulator + Line High Voltage Transformer Filament Transformer mA regulator •Circuitry for mA selection •Adjusts mA on the fly during exposure. Timer Circuit Rectifier Circuit Autotransformer mA selector + Line High Voltage Transformer Filament Transformer Filament Transformer Changes AC voltage to smaller voltage required by filament (8-12 volts typical) Power Storage Generators Use batteries Application Remote locations Inadequate power from power line or power line not accessible Outlet inaccessible Battery-Powered Generators Batteries used for x-ray transport Independent of power line during exposure Disadvantages Require charging Heavy