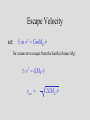* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Orbital Paths
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational wave wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Special relativity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Woodward effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
History of physics wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
History of optics wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
First observation of gravitational waves wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
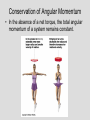
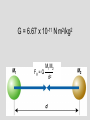
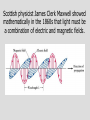
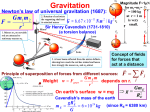
Who cares about momentum (mv)? Conservation of linear Momentum • In the absence of a net force, the total linear momentum of a system remains constant. But this is just Newton’s first law!! mv = constant Conservation of Angular Momentum • In the absence of a net torque, the total angular momentum of a system remains constant. Universal Law of Gravitation Between every two objects there is an attractive force, the magnitude of which is directly proportional to the mass of each object and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the centers of the objects. Fg a M1M2 d2 G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2/kg2 Fg = G M1M2 d2 F= G circumference = m m 1 2 2pR R2 R m1 m2 v = distance / time v = 2pR / P 2 F = m1a = m1 v / R = G m1 m2 R2 v2 = G m2/R 4p2 R 2 / P 2 = G m /R 2 4p2 R 3 = G m P 2 P2 = (4p2/Gm2) R3 2 • Gravitational Potential Energy for the surface of the Earth is: mgr (where r is the radius of the Earth) F = ma = mg = GmME/r2 = m (GME /r2) so: and: g = GME /r2 mgr = m(GME /r2) r So, Gravitational Potential Energy = m(GME /r) Escape Velocity set: ½ m v2 = GmME /r for a mass m to escape from the Earth (of mass ME) ½ v2 = GME /r vesc = 2GME /r Orbital Paths • Extending Kepler’s Law #1, Newton found that ellipses were not the only orbital paths. • possible orbital paths – ellipse (bound) – parabola (unbound) – hyperbola (unbound) Changing Orbits orbital energy = kinetic energy + gravitational potential energy conservation of energy implies: orbits can’t change spontaneously An object can’t crash into a planet unless its orbit takes it there. An orbit can only change if it gains/loses energy from another object, such as a gravitational encounter: If an object gains enough energy so that its new orbit is unbound, it has reached it’s escape velocity. How do we do astronomy? We look at stuff We collect stuff that travels to us from far away – matter and radiation – this is what we mean by “look” What is light? Four Ways in Which Light can Interact with Matter emission absorption transmission reflection But, what is light? • In the 17th Century, Isaac Newton argued that light was composed of little particles while Christian Huygens suggested that light travels in the form of waves. • In the 19th Century, Thomas Young demonstrated that light bends slightly around corners and acts like interfering waves. Light A vibration in an electromagnetic field through which energy is transported. Light as a wave f=c Light as a particle E= a hf f photon Planck’s constant h = 6.6 x 10-34 J s Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell showed mathematically in the 1860s that light must be a combination of electric and magnetic fields.