* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reconstruction - American Leadership Academy
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Freedmen's Colony of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era wikipedia , lookup
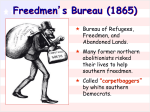
Chapter 22 The problems of peace What to do with the leaders of the Confederation? ○ Most were jailed for two years and released, which southern jury would convict them? ○ Finally pardoned by President Johnson in 1868 A generation was wiped out and the Southern economic and social structures were gone Cities were in ashes with only foundations left Cotton fields lay in ruin with no seed and no labor to sow them Slaves represented $2 billion worth of southern investments Freedmen define Freedom Ending slavery was inconsistent from place to place and was freedom was very hard for the blacks to obtain Many slaves were loyal to their masters and refused to leave while others resorted to violence against them on emancipation day Many took new names, clothes, etc, and demanded respect Thousands hit the roads looking for family, testing freedom, or leaving the South The Freedmen’s Bureau Created by Congress March 3, 1865 ○ Designed to help give them skills, education, both formal and about how the world works ○ Set up as the first welfare agency Provided food, clothing, medical care, and education Taught over 200,000 freedmen to read and write Headed by General Oliver O. Howard - Failed to redistribute the land to the blacks Political Reconstruction Lincoln believed the South never had left the Union so their restoration would be simple ○ 10% reconstruction plan When 10% of a states’ voters took an oath of allegiance, pledged to abide by emancipation they could form a new state government, then the president had to allow the state to reenter the Union Congress believed the states left the Union and lost all rights when they left and could only be let in as a conquered province ○ Showed the split in the Republican Party over reconstruction Wade-Davis Bill 1864 ○ 50% of the states’ voters had to take the oath of allegiance and demanded more safeguards to protect emancipation ○ Lincoln pocket vetoed it - Andrew Johnson’s Reconstruction policy - Any of the leading Confederates with more than $20,000 were disenfranchised but they could still get pardons if they petitioned him - Special state conventions to repeal the ordinances of secession, repudiate all Confederate debts, ratify the 13th amendment, then they could be readmitted The Governments that were created were anti black and upset the Republicans Lincoln’s 10% Plan Amnesty (pardon those that fought against the Union during the war) Abide by Emancipation and free the slaves 10% of the states’ voters had to take an oath of allegiance to the Union Once that was all done the states could reenter the union Johnson’s Plan Continuation of Lincoln’s Plan Rich southerners (with more than $20,000) had to ask the president for a pardon Couldn’t vote or hold public office until granted a pardon Governors appointed until they hold special constitutional conventions to uphold the 13 amendment After all that was done they could hold elections The Baleful Black Codes Black Codes ○ Were set up to regulate what the newly freed blacks could ○ ○ ○ ○ do Mississippi’s were the harshest and the first created 1st and foremost designed to maintain a subservient labor force Blacks were forced to sign labor contracts and severe penalties were inflicted if they didn’t honor them Blacks couldn’t serve on juries, couldn’t own land, lease it, couldn’t vote These all but undid the 13th amendment and the ideals of freedom Most blacks became sharecroppers, they got to use the land in payment they gave up a large portion of their crop ○ The system kept them in debt and they couldn’t leave Congressional Reconstruction Many Confederate leaders showed up in December of 1865 to claim their congressional seats, this made the Republicans very angry and they expelled all of the Southern representatives on December 4, 1865 Emancipation actually increased the political power in the South, blacks now counted as a full person not 3/5’s On December 6, 1865 Johnson declared the rebellious states were reconstructed and accepted them into the Union Johnson Clashes with Congress Johnson vetoed a bill renewing the Freedmen’s Bureau, later passed over his veto Civil Rights Bill 1866 ○ Gave the blacks citizenship and attempted to end the Black Codes ○ Johnson vetoed it and Congress passed it over his veto 14th Amendment ○ Conferred civil rights on the freedmen ○ Reduced representation to states that refused the blacks’ right to vote ○ Disqualified from federal office confederate officers ○ Guaranteed the federal debt while it denounced the confederate debt ○ Due process of law clause Republican Principles and Programs Republicans had a veto proof Congress, could do what they wanted Radicals were led by Charles Sumner in the Senate ○ Black equality and freedom Thaddeus Stevens in the House ○ Defended runaway blacks and was a friend of blacks to the end Congress wanted to keep the South out as long as possible to bring about a forced revolution in their society Wanted above all to give the blacks the right to vote Reconstruction by the sword Reconstruction Act March 2, 1867 ○ Divided the South into 5 military districts commanded by a Union general and policed with Union troops ○ Also disenfranchised thousands of Confederates ○ Very strict conditions for readmission into the Union Ratify the 14th amendment Guarantee full suffrage to the freedmen 15th amendment ○ Guaranteed right to vote to every adult male regardless of race Three states were ready for readmission by 1870 ○ Started as Republican but once the troops were gone they slipped back into “home rule” with the South being solid democrats Realities of Radical Reconstruction Blacks voted in the South before they did in the North Union League ○ Network of political clubs that educated people about their civic duties and campaigned for Republicans ○ Built black churches and schools, recruited militias to protect blacks from whites Black men were elected as representatives to the state constitutional conventions, they held the political power in the South ○ 14 black congressmen and 2 senators, mayors, lt. governors, etc Scalawags-Southerners that favored the Union Carpetbaggers-northern went South to make $ The new governments made much needed reforms, most stayed when the “home rule” returned Very corrupt governments in the North and South Ku Klux Klan (Invisible Empire of the South) Formed in Tennessee in 1866 Used fear to intimidate the blacks Louisiana 1868 in 2 days 200 blacks were beaten or killed Force Acts of 1870-71 ○ Use of Federal troops to end the intimidation Most areas ignored the 14th and 15th amendments By 1890 widespread disenfranchised by intimidation, fraud, tricks, etc. Impeachment 1867 Tenure of Office Act-vetoed and passed over it ○ Required the President to ask the Senate before firing his cabinet ○ Designed to keep Stanton in office Johnson fired Stanton in 1868 House voted 126-47 to impeach Senate tried the case and were one vote shy of kicking him out ○ Afraid of setting a dangerous precedent ○ No VP, would have been Ben Wade the Pres. Pro Temp of the Senate that many didn’t like Heritage of Reconstruction South saw it as worse than the war itself ○ Empowerment of the blacks, federal intervention, etc It was very confusing nobody was quite sure what to do to solve the problem Racism kept both sides from carrying out the necessary reforms to give blacks equality ○ Economic reforms, land redistribution, and protection of the rights