"Or this whole affair is a failure": a special treasury agent`s
... condition brought by the Union occupation of the Sea Islands. Tragically, they also reveal that the Experiment was on the road to what could be a violent pre-mature conclusion within a couple of months after it began if drastic changes did not take place and fast. Fortunately, the Experiment did not ...
... condition brought by the Union occupation of the Sea Islands. Tragically, they also reveal that the Experiment was on the road to what could be a violent pre-mature conclusion within a couple of months after it began if drastic changes did not take place and fast. Fortunately, the Experiment did not ...
The Rebels Are Bold, Defiant, and Unscrupulous in Their
... control of the county. Both groups wanted to maintain black subservience, but conflict splintered the community as white and black residents reshaped the postwar landscape. Political struggles in this period included violence and intimidation as returning Confederates and their home front sympathiz ...
... control of the county. Both groups wanted to maintain black subservience, but conflict splintered the community as white and black residents reshaped the postwar landscape. Political struggles in this period included violence and intimidation as returning Confederates and their home front sympathiz ...
16 The Union Reconstructed
... land. “All I want is to git to own fo’ or five acres ob land, dat I can build me a little house on and call my home,” a Mississippi black said. Through a combination of educational and economic independence, basic means of controlling one’s own life, labor and land, freedpeople like Lizzie would mak ...
... land. “All I want is to git to own fo’ or five acres ob land, dat I can build me a little house on and call my home,” a Mississippi black said. Through a combination of educational and economic independence, basic means of controlling one’s own life, labor and land, freedpeople like Lizzie would mak ...
File
... Shouting the battle-cry of Freedom. So we’re springing to the call from the East and from the West, Shouting the battle-cry of Freedom; And we’ll hurl the rebel crew from the land we love the best, Shouting the battle-cry of Freedom. Day /9.3 ...
... Shouting the battle-cry of Freedom. So we’re springing to the call from the East and from the West, Shouting the battle-cry of Freedom; And we’ll hurl the rebel crew from the land we love the best, Shouting the battle-cry of Freedom. Day /9.3 ...
Reconstruction under Lincoln
... taken a tough stand against the Confederacy. "Treason is a crime;' he had declared, "and crime must be punished:' Conflict, however, would soon erupt between Johnson and Congress over Reconstruction. Johnson's Reconstruction Plan Johnson issued his Reconstruction plan in May 1865, less than a month ...
... taken a tough stand against the Confederacy. "Treason is a crime;' he had declared, "and crime must be punished:' Conflict, however, would soon erupt between Johnson and Congress over Reconstruction. Johnson's Reconstruction Plan Johnson issued his Reconstruction plan in May 1865, less than a month ...
Emancipation Hell - Abbeville Institute
... Congress that feared the cost; Treasury Secretary Salmon Chase worried that its sweeping power to annul state laws would not be upheld by Federal courts, a fear that Lincoln had earlier expressed, and that "universal emancipation" would set off "depredation and massacre" across the South; Seward sai ...
... Congress that feared the cost; Treasury Secretary Salmon Chase worried that its sweeping power to annul state laws would not be upheld by Federal courts, a fear that Lincoln had earlier expressed, and that "universal emancipation" would set off "depredation and massacre" across the South; Seward sai ...
Nov. 18 From Presidential to Radical reconstruction
... “We know these men -- know them well -- and we assure you that, with the majority of them, loyalty is only ‘lip deep,’ and that their professions of loyalty are used as a cover to the cherished design of getting restored to their former relations with the Federal Government, and then, by all sorts o ...
... “We know these men -- know them well -- and we assure you that, with the majority of them, loyalty is only ‘lip deep,’ and that their professions of loyalty are used as a cover to the cherished design of getting restored to their former relations with the Federal Government, and then, by all sorts o ...
14The Union Reconstructed American Stories
... congressional opponents retorted that the ex-Confederate states were now “conquered provinces” and that Congress should resolve the constitutional issues and direct Reconstruction. Politically, differences between Congress and the White House over Reconstruction mirrored a wider struggle between the ...
... congressional opponents retorted that the ex-Confederate states were now “conquered provinces” and that Congress should resolve the constitutional issues and direct Reconstruction. Politically, differences between Congress and the White House over Reconstruction mirrored a wider struggle between the ...
Chapter 22 Outline The Ordeal of Reconstruction I. The Problems of
... iv. The church became the focus of the Black community life in the years following the war. 1. Emancipation also meant education for Blacks, but despite all the gains Blacks made, they still faced severe discrimination and would have to wait a century before truly attaining their rights. III. The Fr ...
... iv. The church became the focus of the Black community life in the years following the war. 1. Emancipation also meant education for Blacks, but despite all the gains Blacks made, they still faced severe discrimination and would have to wait a century before truly attaining their rights. III. The Fr ...
The Ordeal of Reconstruction
... ii. Johnson would be known as “Sir Veto” and “Andy Veto” e. June 1866 ...
... ii. Johnson would be known as “Sir Veto” and “Andy Veto” e. June 1866 ...
Chapter 22 Power point - Tipp City Exempted Village Schools
... Codes made many abolitionists wonder if the price of the Civil War was worth it, since Blacks were hardly better after the war than before the war. They were not “slaves” on paper, but in reality, their lives were little different. The master-slave relationship had been reintroduced even though slav ...
... Codes made many abolitionists wonder if the price of the Civil War was worth it, since Blacks were hardly better after the war than before the war. They were not “slaves” on paper, but in reality, their lives were little different. The master-slave relationship had been reintroduced even though slav ...
The Ordeal of Reconstruction, 1865-1877 A. The Problems of Peace
... other benevolent, fraternal and mutual aid societies (protected newly won freedom) 5. Emancipation also meant education for many blacks; learning to read and write had been a privilege generally denied to them under slavery; freedmen wasted no time establishing societies for self-improvement, which ...
... other benevolent, fraternal and mutual aid societies (protected newly won freedom) 5. Emancipation also meant education for many blacks; learning to read and write had been a privilege generally denied to them under slavery; freedmen wasted no time establishing societies for self-improvement, which ...
GUIDED READING- Read each section of this chapter by
... ______ Slaves responded to emancipation during the war years in all of the following ways EXCEPT that they A) tried to join the Union Army B) vandalized their masters’ homes and farms C) changed their names D) remained loyal to their masters E) married former mistresses _____ Who were the Exodusters ...
... ______ Slaves responded to emancipation during the war years in all of the following ways EXCEPT that they A) tried to join the Union Army B) vandalized their masters’ homes and farms C) changed their names D) remained loyal to their masters E) married former mistresses _____ Who were the Exodusters ...
Chapter 22 Notes - Beaufort County Schools
... The Radicals wanted a slower Reconstruction where they could bring about major social and economic change to the South. Moderate Republicans just didn't want to go quite that far with Reconstruction. They were reluctant to get the federal government directly involved in people's lives. ...
... The Radicals wanted a slower Reconstruction where they could bring about major social and economic change to the South. Moderate Republicans just didn't want to go quite that far with Reconstruction. They were reluctant to get the federal government directly involved in people's lives. ...
Chapter 24 Notes
... 1. In order to control the freed Blacks, many Southern states passed Black Codes, laws aimed at keeping the Black population in submission; some were harsh, others were not as harsh. i. Blacks who “jumped” their labor contracts, or walked off their jobs, were subject to penalties and fines, and the ...
... 1. In order to control the freed Blacks, many Southern states passed Black Codes, laws aimed at keeping the Black population in submission; some were harsh, others were not as harsh. i. Blacks who “jumped” their labor contracts, or walked off their jobs, were subject to penalties and fines, and the ...
userfiles/141/my files/ch 4 sect 3?id=2180
... Presidential Reconstruction (first two years of recovery) 1863- Before war ended, Pres Lincoln had issued his Ten Percent Plan: Forgiveness and Readmission to the Union when……. - 10% of state voters pledged loyalty to the Union Proclamation of Amnesty ...
... Presidential Reconstruction (first two years of recovery) 1863- Before war ended, Pres Lincoln had issued his Ten Percent Plan: Forgiveness and Readmission to the Union when……. - 10% of state voters pledged loyalty to the Union Proclamation of Amnesty ...
Chapter 22 Notes - George`s AP US Survival Blog
... From the church arose other support communities and groups that assisted the blacks in protecting their newly won freedom. With Emancipation came education also. The Freedmen quickly established schools by raising funds to purchase land, build schoolhouses, and hire teachers. Unfortunately, the dema ...
... From the church arose other support communities and groups that assisted the blacks in protecting their newly won freedom. With Emancipation came education also. The Freedmen quickly established schools by raising funds to purchase land, build schoolhouses, and hire teachers. Unfortunately, the dema ...
Reconstruction - Lake Chelan School District
... Guarantee stable labor supply now that blacks were emancipated. ...
... Guarantee stable labor supply now that blacks were emancipated. ...
Chapter 22: The Ordeal of Reconstruction 1865-1867
... 1.After the war, there were many questions over what to do with the free Blacks, such as how to reintegrate the Southern states into the Union, what to do with Jefferson Davis, and who would be in charge of Reconstruction? 2.The Southern way of life had been ruined, as crops and farms were destroyed ...
... 1.After the war, there were many questions over what to do with the free Blacks, such as how to reintegrate the Southern states into the Union, what to do with Jefferson Davis, and who would be in charge of Reconstruction? 2.The Southern way of life had been ruined, as crops and farms were destroyed ...
Reconstruction - Cloudfront.net
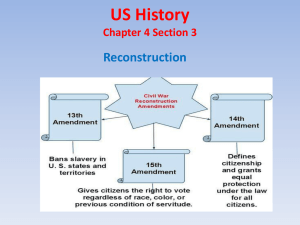
... crime, whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within the United States, or any place subject to their jurisdiction.” The Congress shall have power to enforce by appropriate legislation, the provisions of this article. 13th: Slavery14th Abolished ...
... crime, whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within the United States, or any place subject to their jurisdiction.” The Congress shall have power to enforce by appropriate legislation, the provisions of this article. 13th: Slavery14th Abolished ...
A - Humble ISD
... 1. In order to control the freed Blacks, many Southern states passed Black Codes, laws aimed at keeping the Black population in submission; some were harsh, others were not as harsh. i. Blacks who “jumped” their labor contracts, or walked off their jobs, were subject to penalties and fines, and thei ...
... 1. In order to control the freed Blacks, many Southern states passed Black Codes, laws aimed at keeping the Black population in submission; some were harsh, others were not as harsh. i. Blacks who “jumped” their labor contracts, or walked off their jobs, were subject to penalties and fines, and thei ...