* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download userfiles/141/my files/ch 4 sect 3?id=2180
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Forty acres and a mule wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
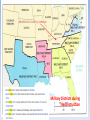
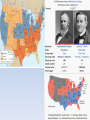
US History Chapter 4 Section 3 Reconstruction Main Idea Conflicting plans for dealing with the post-Civil War South had long lasting effects on government and the economy Reading Focus What were the different plans for presidential Reconstruction? What was congressional Reconstruction? What happened when Radical Republicans took charge of Reconstruction? Why did Reconstruction end, and what were its effects on American history? Rebuilding the South FINANCIAL COSTS OF THE WAR US Civil War had a great impact on the social, political, and economic aspects, primarily in the South Southern Livestock killed: 40% South: > 20% of Male population killed > Destruction of railroads, farms, plantations, livestock > Uncertain future for 4 million newly freed blacks Total National wealth held by South in 1860: 30% How would South reintegrate back into the Union? This Post-war recovery period is known as Reconstruction Southern farm machinery destroyed: 50% Drop in South’s total property wealth: 66% Total National wealth held by South in 1870: 12% Presidential Reconstruction (first two years of recovery) 1863- Before war ended, Pres Lincoln had issued his Ten Percent Plan: Forgiveness and Readmission to the Union when……. - 10% of state voters pledged loyalty to the Union Proclamation of Amnesty - State could organize new government and Reconstruction -Banned slavery Lincoln’s reconstruction plan was controversial because of the belief of: > Readmission of the states was a power of congress-not president > Secession was unlawful and states had never left > States should go through admission process like territories Congress Plan- (Wade-Davis Bill) called for the majority of states white male population to pledge loyalty April 14, 1865- Lincoln was assassinated by Southerner John Wilkes Booth at Fords Theatre in Washington- VP Andrew Johnson 17th Pres. of US Assassination of Abraham Lincoln • • • • • Booth jumps to the stage but breaks his leg in the process • Yells “Sic semper tyrannis” (Thus be it ever to tyrants …or The South shall live) • A massive manhunt occurred and Booth was cornered in a barn near Bowling Green, Virginia • Booth was shot by Union Soldiers • Lincoln died on the 15th and was hailed a hero by the nation (even some confederates) • 4 others sent to prison for Lincoln conspiracy April 14, 1865 Lincoln lifts Union Blockade Gives notice to leaders that he wants to bring rebellious states back to Union That evening he and his wife attends a play called “My American Cousin” John Wilkes Booth- shoots Lincoln in back of head Lincoln Assassination https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VIk593OFtM President Andrew Johnson (D) Andrew Johnson had been appointed (before VP) to be the TN Governor during the war Known for being very stubborn and uncompromising Views of Reconstruction were similar to Lincoln’s but he also wanted wealthy white southern men to be pardoned Besides this, Republicans in Congress were concerned his plans did not address Freedmen rights Southern Response Since slavery was banned , southern states passed a series of “Black Codes” > Laws that discriminated against blacks >Gave whites almost unlimited power > Intent was to keep blacks in the farming industry (Cheap Labor) > No southern state would establish schools for blacks > Codes varied from state to state > Enforced by sheriffs Some white citizens in the South put masks over their head and terrorized blacks and those who supported blacks: Ku Klux Klan 1866 Congressional Reconstruction Many northerners supported Andrew Johnson’s Reconstruction plan but were upset by the ‘Black Codes’ Radical Republicans: Members of Congress who wanted tougher rules for restoring state governments > Wanted Freedmen to have political and economic equality Problem Johnson urged the southern states to protect the Freedmen’s rights but didn’t do anything to ensure it was being done 1865- Congress did create the Freedman's Bureau prior to the end of the war with the mission of helping newly freed blacks > Teachers began opening schools > Provided clothing, shelter, food, for both whites and blacks Mainly Northerners Congress vs President Johnson Congress passed the Civil Rights act of 1866 which gave blacks citizenship and same legal rights as whites….. “Johnson be like: Yeah Right…that ain’t happening!” Even though bill passed both House and Senate, Johnson vetoed it which prompted moderate republicans to help radical republicans to take control of Reconstruction Johnson vs Congress Congress passed the Bill anyway (3/4 vote) ….first time in history…..led by Thaddeus Stevens who wanted to ensure the Civil Rights Act was not somehow overturned, so he drafted the 14th Amendment Lincoln Plan (1863) • Offered a pardon to all supporters of the confederacy if they swore allegiance to the Union and pledged to abolish slavery. • When 10% of the men eligible to vote in 1860 did this, the state qualified for reentry into the U.S. • New state constitutions had to outlaw slavery • No protections for freed blacks Andrew Johnson Plan • Became his plan after Lincoln was assassinated • Amnesty to whites who signed loyalty oaths • New state constitutions had to outlaw slavery • No vote for blacks • No role / protections for freed blacks RECONSTRUCTION PLANS Radical Republicans (Congress- Thaddeus Stevens) • Promoted equal protection and rights for freed blacks • Military occupation of the South to oversee changes • Voting Rights for black males • (13th) 14th and 15th Amendments Final Reconstruction Plan 1867-1868: Congress passed (over Johnson’s veto) four reconstruction acts which divided the South into five military districts: You can be readmitted if: -Ratify the 14th Amendment -Write new state constitution that guarantees freedmen the right to vote (15TH Amendment) -Form new government to be elected by ALL male citizens Congress passed the “Office of Tenure Act” of 1867 “Can’t fire member of cabinet” ……then Johnson tried to fire a member This set off final battle between Johnson and Congress which led to the first ever Impeachment proceedings against Johnson Admitted to Union by Johnson Military Districts during Reconstruction Republicans in Charge Election of 1868- Johnson vs. War Hero Ulysses S. Grant Victor! …..Grant was the Republicans quickly pushed the 15th Amendment through to guarantee the voting rights of African-Americans (Effective in 1870) As congress took control of Reconstruction, political power in south shifted: “Scalawags”- white southerners who supported reconstruction changes “Carpetbaggers”- Northerners who came to the South to take part in South’s rebirth Freedmen joined both to improve social and economic conditions Black Codes were repealed in every state Responses to Freedom Most African-Americans went North or West but many stayed in the South… So what changed? Education Religion / Other Sharecropping Tenant farming 4K Schools built Churches Landowner provided land, tools, and seed Farmer rented land from owner Hundreds of colleges Fire Departments Farmer gave landowner 1/3 or ½ of what he grew Could grow any crop Trade Associations Employment Agencies Despite industrial growth in the South, it truly did not benefit Freedmen or other poor southerners End of Reconstruction Violence plagued the South during Reconstruction with the KKK being the most active group > Blacks were main targets > Freedmen Bureau teachers > Murdered public officials and scared many into resignation Congress passed Enforcement Acts 1870-1871 placing heavy penalties on anyone trying to prevent a qualified voter from voting > Also gave Military power to punish Klan members Many people dissatisfied with Reconstruction: > people upset because Union troops were in South > Republican State governments appeared ineffective > Blacks unhappy about their poverty Compromise of 1877 Ended Reconstruction 1876 Presidential election: * Rutherford B. Hayes (R) Ohio * Samuel Tilden (D) New York Electoral Vote Count WOW! That’s close 185 184 Disputed results in certain states…so….. House of Representatives appoints a 15 man commission to decide results (8 to 7 Republican) Hayes is decided as the POTUS…..BUT….there is a Bargain that occurred (sometimes called the Bargain of 1877) Terms of Bargain: a. Hayes representatives agrees to pull military out of the South / to recognize Democratic control of the entire south / and not to use military intervention in racial affairs of the south b. Tilden’s representatives agree NOT to contest Hayes victory but would respect southern civil and political rights of blacks Reconstruction Ends https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pwye1vN DYDQ T T F Republican Rutherford B. Hayes won the election when a Republican-dominated commission gave him the disputed votes. T T