* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Domain and Range
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
History of the function concept wikipedia , lookup
Musical notation wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Structure (mathematical logic) wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard calculus wikipedia , lookup
Principia Mathematica wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Function (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Function of several real variables wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Domain and Range
Definition
• A relation is a correspondence between two sets
such that to each element of the first set, there is
assigned one or more elements of the second set.
. If x and y are two elements in these sets and if a
relation exists between x and y, then we say that
x corresponds to y, and write xy or as the
ordered pair (x,y).
• A function is a relation where each element in
the domain is related to only one value in the
range by some rule.
• Domain
– – set of all first elements or set of all values of x
– -set of permissible inputs
• Range
– – set of all second elements or the set of all values
of y
– -set of all resulting output
Ordered Pairs
Domain - set of all first elements
Range – set of all second elements
Function – the first elements are unique
Example:
A={ (2,5), (3,6), (-2,5), (-3,6)}
Domain: {-3,-2,2,3}
Range: {5,6}
Function: YES
Graph
• Domain is the interval in the x-axis that has
corresponding points in the graph
• Range is the interval in the y-axis that has
corresponding points in the graph
Review of Interval Notation
• Interval notation translates the information
from the real number line into symbols.
• To indicate that an endpoint is included, we
use a square bracket; to exclude an endpoint,
we use parentheses.
Symbols used for important sets
• N is the set of natural numbers 1, 2, 3, ...
• Z denotes the integers 0, 1, -1, 2, -2, .... Why Z?
The German word for 'number' is 'Zahl'.
• Q denotes the set of rational numbers (fractions).
• denotes the set of all real numbers, consisting
of all rational numbers and irrational numbers
such as .
• C denotes the set of all complex numbers.
• is the empty set, the set which has no
elements.
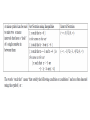
Write the following sets in interval
notation and as inequality
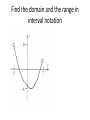
Find the domain and the range in
interval notation
Find the domain and the range in
interval notation
Domain and Range of Equations
When finding the domain of a function, ask
yourself what values can't be used. Your
domain is everything else.
Basic rules to consider:
1. The domain of all polynomial functions is the
Real numbers R.
2. Square root functions can not contain a negative
underneath the radical. Set the expression
under the radical greater than or equal to zero
and solve for the variable. This will be your
domain.
3. Rational functions can not have zeros in the
denominator. Determine which values of the
input cause the denominator to equal zero, and
set your domain to be everything else.
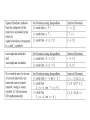
Algebraically determine the following domains. Use correct set notation.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
d(y) = y + 3
2
g(k) = 2k + 4k - 6
b(n) = 2n 8
m(t ) 9 3t
x 5
u( x )
2x 4
1
a(r ) r
r 1