* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download t=0
Magnetosphere of Saturn wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
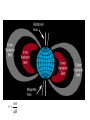
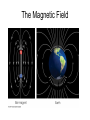
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
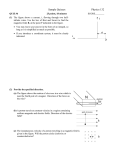
Problem 2 Find the torque about the left hand segment on the loop as a function of θ, the angle the plane makes with the horizontal plane. Motion in magnetic field 1) Uniform B , 2) Uniform B , 3) Nonuniform vB vB B mv r qB The angular velocity v v qB r mv m qB Uniform magnetic field, vB Uniform B, v B When a charged particle has velocity components both perpendicular and parallel to a uniform magnetic field, the particle moves in a helical path. The magnetic field does no work on the particle, so its speed and kinetic energy remain constant. Example: A proton ( 1.60 1019 C, m 1.67 1027 kg) is placed in the uniform magnetic field directed along the x-axis with magnitude 0.500 T. Only the magnetic force acts on the proton. At t=0 the proton has velocity components vx 1.50 105 m / s, v y 0, vz 2.00 105 m / s. Find the radius of the helical path, the angular speed of the proton, and the pitch of the helix (the distance traveled along the helix axis per revolution). Nonuniform B. A magnetic bottle. mv r qB The Magnetic Field Current carrying wires 1820 Hans Christian Oersted Hans Christian Ørsted Biot-Savart Law Infinitesimally small element of a current carrying wire produces an infinitesimally small magnetic field dS i ( ds r ) dB 3 r i r 0 i (ds r ) dB 4 r3 0 is called permeability of free space 0 4 10 7 webers /( amp meter) 4 10 7 N /( amp) 2 (Also called Ampere’s principle) The Field Produced by a Straight Wire 0 i B 2 a