* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.3-Kingdom on the Nile-
Egyptian language wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
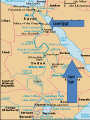
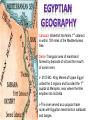
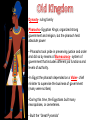
Every spring, the rains from the interior of Central Africa race down and feed the Nile In ancient times, Egyptians eagerly awaited the annual flood to soak the land with life- giving water and deposited a rich layer of silt. Dikes, reservoirs, and irrigation ditches were built by the government to help control the flooding and store water for the dry season “Black Land” was the area in which all farming took place because of the rich soil. “Red Land” was the sun- baked desert that stretches across North Africa Lower Egypt Upper Egypt BC AD 0 Cataract- Waterfall; the Nile’s 1st cataract is within 100 miles of the Mediterranean Sea Delta- Triangular area of marshland formed by deposits of silt and the mouth of some rivers 3100 BC- King Menes of Upper Egypt united the 2 regions and founded the 1st capital at Memphis, near where the Nile empties into its Delta. The river served as a popular trade route with Egyptian merchants in sailboats and barges. Dynasty- ruling family Pharaohs- Egyptian Kings; organized strong government and religion, but the pharaoh held absolute power • Pharaohs took pride in preserving justice and order and did so by means of Bureaucracy- system of government that includes different job functions and levels of authority. •In Egypt the pharaoh depended on a Vizier- chief minister to supervise the business of government (many were scribes) •During this time, the Egyptians built many necropolises, or cemeteries. • Built the “Great Pyramids” 1.Power Struggles 2.Crop Failures 3.Cost of building the pyramids Corruption and rebellions were common 1700 BC- Egypt was conquered by the Hyksos. The Egyptians impressed the Hyksos by catching onto the military technique of using horse- drawn chariots. The Hyksos adopted the Egyptian beliefs, customs, and even names and eventually became the New Kingdom 1450 BC was height of the New Kingdom and Egyptians were in contact with people in southwestern Asia and parts of Africa Three Powerful Rulers: Hatshepsut, Thutmose III, and Ramses II Egypt’s 1st female ruler 1472 BC- 1458 BC she encourage trade with the eastern Mediterranean lands and along the Red Sea coast of Africa. Stepson was Thutmose III Took over as Pharaoh once he reached adulthood Great military general Stretched Egypt’s borders to their greatest extent ever Ruled for 66 years Best known of all rulers because he boasted of his conquests on numerous temples and monuments. Ironically, his greatest victory may never have actually taken place. After 1100 BC Egyptian power began to decline because. . - Invaders such as the Assyrians and Persians conquered the Nile Region. 332 BC the last Egyptian dynasty ended as the Greeks took control 30 BC Roman armies displaced the Greeks Explain the impact of the Nile River on Egyptian civilization? Explain how pharaohs, bureaucracy, and viziers work together? Analyze the importance and impact of the Old Kingdom? Discuss the turbulence of the Middle Kingdom? Analyze the impact of Hatshepsut, Thutmose III, and Ramses II on the New Kingdom? Discuss the reasons behind the collapse of Egypt?