* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Perception
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
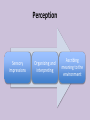
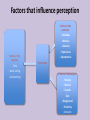
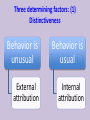
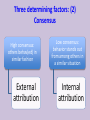
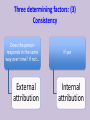
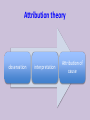
Organizational Psychology Lecture 3 Perception and attribution Perception Sensory impressions Organizing and interpreting Ascribing meaning to the environment Why is perception important to OB? Peoples’ behavior is based on their perception of what reality is not on reality itself Factors that influence perception Factors in the perceiver - Attitudes - Motives - Interests - Experience Factors in the situation - Time - Work setting - Social setting - Expectations Perception Factors in the target - Novelty - Motion - Sounds - Size - Background - Proximity - Similarity Person Perception Making judgments about thers Attribution theory Judgments we make Observed behavior of another person Meanings we attribute We determine the source of causation of that behavior 1. Distinctiveness Internal 2. Consensus vs 3. Consistency External causes Differences between internal vs external causation Internally caused behavior Under the control of the individual • Employee is late for work: he was partying and then overslept • Colleague is gaining weight: he is socializing a lot and overeating • Manager is in tensed mood: he wants to evoke fear in us purposefully Externally caused behavior What the situation forced the individual to do • Employee is late for work: must have run into tied up traffic due to some accident on the way • Colleague is gaining weight: could have some health issues, maybe thyroid • Manager is in tensed mood: he must have been under fire during yesterday’s board meeting Three determining factors: (1) Distinctiveness Behavior is unusual Behavior is usual External attribution Internal attribution Three determining factors: (2) Consensus High consensus: others behav(ed) in similar fashion External attribution Low consensus: behavior stands out from among others in a similar situation Internal attribution Three determining factors: (3) Consistency Does the person responds in the same way over time? If not… External attribution If yes Internal attribution Attribution theory observation interpretation Attribution of cause Most important finding: fundamental attribution error While making judgments about the behavior of other people 1. We tend to overestimate the effects of internal factors; e.g. sales dropped recently my sales agents are just lazy 2. We tend to underestimate the effects of the external factors; sales dropped recently – it cannot be the innovative product introduced by the competitor Most important finding: fundamental attribution error While making judgments about our own behavior 1. We tend to attribute our own success to internal factors; e.g. ability, effort 2. We tend to blame failure on the external factors; e.g. bad luck, poor performance of others Fundamental attribution error: cultural differences • non-Western managers are less likely to use self-serving bias: tend to assume responsibility for failure • Asian cultures: group-based attributions – more likely to blame institutions or whole organizations • Western cultures – individuals should get blame or praise Shortcuts in judging others: selective perception Other information Other information Interests Background Experience Attitudes Shortcuts in judging others: halo effect We draw a general impression about an individual on the basis of a single characteristic; here: appearance Shortcuts in judging others: contrast effect Our reaction is influenced by other persons we have recently encountered; attention: job interviews Shortcuts in judging others: stereotyping • Less difficult to deal with unmanageable number of stimuli if we use heuristics • Problem occurs when we generalize inaccurately or too much • We usually stereotype based on: – Gender – Age – Race – Religion – Ethnicity – Weight Stereotypes operate emotionally and often below the level of conscious awareness Specific applications of shortcuts in Organizations 1. Employment interview – We form impressions of others within tenth of a second: first glance – Good applicant: absence of negative characteristics 2. Performance expectations – Self-fulfilling prophecy: one’s behavior is determined by others’ expectations – Expectations become reality 3. Performance evaluations – Depend on the perceptual process: subjective – Some are luckily evaluated objectively: sales people