* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dec 13 - University of San Diego
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ficus rubiginosa wikipedia , lookup
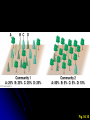
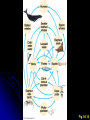
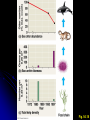
I. Community Ecology H. Community Structure 1. Species Diversity • a. b. Two components Species richness Relative abundance (evenness) Fig. 54.10 I. Community Ecology H. Community Structure 2. Trophic Structure • • Energy transferred between trophic levels Simple model = food chain Fig. 54.13 I. Community Ecology H. Community Structure 2. Trophic Structure • • Food chain concept often too simple • Omnivory? • Feeding by predator on multiple prey at different trophic levels • Decomposers More realistic model = food web Fig. 54.14 I. Community Ecology H. Community Structure 3. Influential Species • Some species have disproportionate impact on community a. Dominant species • Highest abundance or biomass • Usually superior at competition or avoiding predation b. Keystone species • Occupy crucial ecological niches • Removal can have profound effects on community structure Fig. 54.17 Fig. 54.18 I. Community Ecology H. Community Structure 3. Influential Species a. b. c. Dominant species Keystone species Foundation species • Engineers – Modify habitat through activity • Ex: Beaver – Cuts down trees, builds dams • Facilitators – Provide structure for habitat • Ex: Black rush – Shades soil reduced evaporation and salt buildup, oxygenates soil Fig. 54.9 I. Community Ecology H. Community Structure 4. Control of Community Structure a. Bottom-up model • Variation at lower trophic levels produces variation at higher trophic levels • Ex: Fertilizing plants leads to increased biomass of large predators b. Top-down model • Variation at higher trophic levels produces variation at lower trophic levels • Ex: Removing top predators leads to increased biomass of primary producers