* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Drugs - Kyschools.us
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Urban legends about drugs wikipedia , lookup
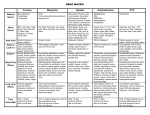
DRUGS Marijuana Health Effects of Marijuana Is marijuana a gate way drug? DEPRESANTS DEFINITION: to diminish or reduce nervous or functional activity synonyms: downer, sedative TYPES • Alcohol • Barbiturates (sleepers, downers, tranquilizers) • Benzodiazepines (Valium, Ativan, Librium, Xanax) WHAT THEY LOOK LIKE Alcohol is a clear liquid, but most typically comes in the form of beer, wine or liquor (also cough syrup, cooking vanilla, mouthwash, etc.) Benzodiazepines and Barbiturates most commonly come in pill form HOW TO INGEST Mouth (drinking liquids, swallowing pills) POSSIBLE WITHDRAW SYMPTOMS Shakiness Sweats Nausea Headache Anxiety Rapid heart beat Craving Hallucinations Increased blood pressure Seizures/Convulsions SHORT-TERM EFFECTS • Effects speech, vision, balance, memory & judgment. • After one or two drinks, a person has lost some of their coordination skills. • Drinking a small amount of alcohol, may make you feel relaxed, self confident, drowsy, or dizzy. Could also be hostile, depressed & withdrawn. • If too much alcohol is taken into the body at once, the drug will cause the heart & lungs to stop working and the person will die. AKA: Alcohol poisoning or overdosing on alcohol. • Alcohol lowers inhibitions and impairs judgment leading to risky behaviors such as driving while intoxicated or unprotected sex. LONG TERM EFFECTS A single glass of red wine each day has been shown to help prevent heart disease in some adults. These beneficial effects have not been found true for youth. Some of the effects of heavy, long term alcohol abuse are: liver disease, cancer, stomach ulcers, brain damage, behavior change, nervous system damage, inflammation of the pancreas, heart disease, high blood pressure, stroke. Heavy drinkers are more likely to contract diseases and infections. MOST SIGNIFCANT PROBLEMS • Addiction • Possibility of a potentially fatal overdose • Causes or prolongs existing depressions and anxiety symptoms • Using while pregnant can cause severe, permanent damage to the developing fetus. Opiates DEFINITION: substance having sedative or narcotic effects containing opium or its derivatives Opium: A bitter, yellowish-brown, strongly addictive narcotic drug prepared from the dried juice of unripe pods of the opium poppy TYPES • Heroin (Horse, Junk, Smack, Snow, "H", Brown) • Morphine • Codeine (OxyContin, Tylenol with Codeine) • Methadone HOW TO INGEST • Nose- snorting in powered form • Lungs- inhaling • Mouth- swallowing pill • IV- injection into a vein SIGNS/SYMPTOMS OF WITHDRAW Chills and hot flashes Cramps Tremors Loss of appetite Insomnia Dilated pupils Watery eyes Runny nose Yawning fits Sweating Panic attacks Nausea Muscle aches Lethargy Diarrhea Bone aches Symptoms can last from 10-14 days SHORT TERM EFFECTS • Slowed pulse, rate of breathing and lowered blood pressure • Intense "rush" obtained from intravenous injection • Feeling of euphoria, relaxation, drowsiness & mental confusion • Higher doses/overdose can cause: sleep; very low blood pressure, slowed heart rate and respiration; low body temperature; muscle constriction; cold clammy skin, coma and death. • Physical & emotional responses to pain are numbed • Apathy and an inability to concentrate • Nausea, vomiting, sweating, chills LONG TERM EFFECTS • Chronic constipation • Impaired vision • Mood swings and instability • Tolerance develops, the user can no longer get the pleasurable effects, but must continue taking the drug to prevent withdrawal. MOST SIGNIFICANT PROBLEMS High possibility of a potentially fatal overdose Addictive with strong, painful withdrawal symptoms May possibly contribute to depression or anxiety STIMULANTS DEFINITION - a drug that temporarily quickens some vital process TYPES • Cocaine (Crack, Blow, Snow, Toot, White, Rock, Flake) • Amphetamine, Methamphetamine (Ritalin) (Meth, Uppers, Bennies, Crank, Crystal) • Caffeine (Coffee) HOW TO INGEST • Nose- snorting powered form • Lungs- inhaling pipe smoke • Mouth- swallowing pills, drinking coffee SIGNS/SYMPTOMS • Depression • Guilt feelings • Body complaints • Irritability • Skin-picking • Insomnia • Anorexia (loss of appetite) • Anhedonia (loss of pleasure) • Cravings SHORT TERM EFFECTS – Low doses may cause alertness, increased energy, restlessness, dizziness, euphoria, confusion, reduced appetite, increased talkativeness, breathing and heart rate, elevated blood pressure – Higher doses the effects are greater and may also include feelings of impulsiveness, increased strength and mental capacity, headache, blurred vision, fever, sweating, and irregular heart beat, loss of coordination, irritability, panic attacks, seizures, violent behavior, stroke, heart attack and coma – Intoxication is followed by a 'crash' period, during which the user feels exhausted and wants to sleep. LONG TERM EFFECTS –Malnutrition, fatigue, sleeplessness –Severe anxiety, tension, high blood pressure –Lowered resistance to disease –Long term users may also exhibit bizarre or violent behavior –Amphetamine Psychosis may develop in heavy users. This condition includes symptoms such as hallucinations, paranoid delusions and compulsive behavior. It usually (but not always) disappears when the user stops taking the drug Most Significant Problems • Strong possibility of a fatal overdose • Highly addictive • Strong, painful and potentially lethal withdrawal symptoms • Can cause (and/or prolong existing) depressions and anxiety symptoms • Using while pregnant can cause severe, permanent damage to the developing fetus. Psychedelics DEFINITON: generating hallucinations, distortions of perception, altered states of awareness, and occasionally states resembling psychosis. TYPES • LSD (Acid) • Psilocybin (Shrooms, Mushrooms) • MDMA (Love Drug, "X", Ecstasy) WHAT THEY LOOK LIKE: • Hallucinogens like LSD and MDMA typically appear in the form of prepared blotter paper, sugar cubes, pills etc. • Psilocybin most typically arrives in the form of dried mushrooms • Mescaline appears in the form of dried (peyote) cactus 'buttons', and in synthesized form HOW TO INGEST: • Mouth (swallowing pills, plant matter, sugar cubes, etc.) Short term effects (LSD): • LSD rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream. Effects appear within 30-45 min. & last for 10-12 hours. • Each experience is greatly influenced by a user's expectations, environment, etc. Typical effects of LSD may include: • • • • • • Auditory/visual hallucinations Perception of time may be distorted Concentration & thinking processes diminished Anxiety, exhilaration Rapid and wide ranging mood swings Muscle twitching and muscle weakness as well as impairment of coordination • Rapid breathing and an increase in blood pressure, body temperature and heart rate • Dizziness, nausea and vomiting LONG TERM EFFECTS (LSD): – An amotivational syndrome, similar to that seen in long term marijuana users – Flashbacks can occur years after a person stops using LSD SHORT TERM EFFECTS (Ectasy): • Sense of pleasure, empathy, & emotional insight. • Increased blood pressure, pulse & body temperature • Blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, chills & sweating • Muscle stiffness, jaw clenching & teeth grinding • High doses cause distortions in perception & hallucinations • Some effects felt the next day are: headache, loss of balance, fatigue, insomnia • A person may feel confused, depressed or anxious for weeks following a single dose. LONG TERM EFFECTS (Ectasy): – The longer a person uses, the worse the hangover effects become. – Some effects of long term use may include: weight loss, flashbacks, paranoia and depression. – There is evidence of liver and brain damage with long term, frequent use. Effects of Ecstacy MOST SIGNIFICANT PROBLEMS: •Overdose is a concern but is not typically fatal •Flashbacks during withdrawal and afterwards •May cause depression and anxiety. •"Bad" trips can occur which are highly negative and disturbing rather than peaceful INHALANTS DEFINITON: A medication, anesthetic, or other compound in vapor or aerosol form TYPES • Aerosol sprays Nitric Gasoline • Glues Paint Thinner WHAT THEY LOOK LIKE: • These are the commercially available solvents used in painting and gluing, and for fuel purposes. Ex. Model glue & paint thinner HOW TO INGEST • Nose & Lungs (inhaling solvent vapors, often called "Huffing") Signs and Symptoms • Detoxification takes 14 to 30 days. • Chills • Headaches • Muscular cramps • Abdominal pains • Tremors • (Possibly) Hallucinations. SHORT TERM EFFECTS: • Euphoria, dizziness, lightheadedness, or exhilaration. • Higher doses, cause confusion, agitated and disorientated. abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting or chest pain. • One of the effects of solvents is invincibility, solvent abusers tend to engage in reckless behavior which can result in injury or death to themselves and others. LONG TERM EFFECTS: • Symptoms of long term solvent use are: sores on mouth and nose; fatigue; weight loss; pale skin; numbness in hands and feet; kidney, lung and liver damage • Long term solvent use may cause brain damage. Some symptoms found in long term users: difficulty learning, memory loss, uncontrollable eye movements, hearing loss, inability to think clearly • Psychological effects of long term use may include depression, irritability, paranoia, hostility, MOST SIGNIFICANT PROBLEMS: • High possibility of a potentially fatal overdose • Strong possibility of brain damage! DESIGNER DRUGS DEFINITION Created to get around existing drug laws, usually by modifying the molecular structures of existing drugs to varying degrees, or less commonly by finding drugs with entirely different chemical structures that produce similar subjective effects to illegal drugs TYPES • Crystal Meth (jib, crank, speed or meth) • Ecstasy (X, E, XTC, Molly, and MDMA) • Gamma hydroxybutyrate (GHB or G) – – This drug causes relaxation and sleep. It makes people feel like everything is okay. It is sometimes described as a cross between alcohol and ecstasy. • Ketamine (K, ket, special K, vitamin K or cat valium) – Ketamine is a general anesthetic used in veterinary medicine. It is a strong pain reliever known to produce an ‘out-of-body’ experience. HOW TO INGEST • Inhaled, injected, or taken orally as a tablet. SIGNS/SYMPTOMS • Drowsiness • Irritability • Agitation • Loss of consciousness • Slowed breathing • Death MOST SIGNIFICANT PROBLEMS Extremely addictive Unintentional overdoses are common SHORT TERM EFFECTS • Euphoria • Changes in behavior • Slurred speech • Anxiety and depression • Muscle cramps • Dilated pupils • Sleepiness and • Hallucinations LONG TERM EFFECTS •Death •Addiction •Criminal charges & prison terms •Heart and breathing failure •Blood vessel damage and stroke •Raised/lowered pulse or blood pressure •Aggressive or suicidal behavior •Jaw clenching & teeth grinding •Nausea and vomiting •Muscle cramping or seizures •Panic attacks & feeling paranoid •Overheating and dehydration •Blackouts STERIODS DEFINITION Drugs taken to build muscle, enhance performance, and improve appearance. While some steroids are used medically to treat many conditions Using steroids for cosmetic or athletic purposes is not sanctioned in the United States. TYPES Illegal and Prescription HOW TO INGEST • Swallowed in tablets or liquid or injected. “Cycling”, means you take them over a period of time, stop, then start taking them again instead of continuously using them. Users also take different types of steroids in combination with other drugs. This is known as “Stacking”. SIGNS/SYMPTOMS • Rapid weight gain • Rapid muscle development • Acne flare up • Fluid retention • Yellow tint in the eyes and on skin (jaundice) • Mood swings, depression • Aggressive behavior • Premature balding Effects of Steroids SHORT TERM CONSEQUENCES • Increase muscle mass, strength, & endurance • Liver tumors, jaundice, water retention, & high blood pressure • Uncontrolled aggression & violent behavior called “Roid Rage” • severe mood swings • manic episodes and depression • often suffer from paranoid jealousy LONG -TERM CONSEQUENCES • Hypertension High cholesterol Kidney disease • Stunted growth Heart damage Diabetes • Women can experience irreversible deepening of the voice, shrinking breasts, menstrual irregularities, baldness & hair growth on other parts of the body • Men can experience baldness, breast enlargement, sterility, shrinking testicles and impotence MOST SIGNIFICANT PROBLEMS • High blood cholesterol levels - high blood cholesterol levels may lead to cardiovascular problems • Severe acne • Thinning of hair and baldness • Fluid retention • High blood pressure • Liver disorders (liver damage and jaundice) • Steroids can affect fetal development during pregnancy • Risk of contracting HIV and other bloodborne diseases from sharing infected needles • Sexual & reproductive disorders ANTI DEPRESSANTS DEFINITION- any medication used to alleviate mood disorders, such as major depression and anxiety disorders TYPES Fluoxetine (Prozac) Sertraline(Zoloft, Lustral) Methylphenidate(Ritalin, Concerta) Amphetamine(Adderall) HOW TO INGEST All antidepressants come in pill form SIGNS/SYMPTOMS • Allergy problems, increase in allergies (number, sensitivity, reactions, lengthier reactions) Back pain, stiffness, tension, pressure, soreness, spasms, immobility in the back or back muscles • Burning skin sensation on the face, neck, ears, scalp, or shoulders • Chest pain, chest tightness • Craving sugar, sweets, chocolate, usual craving for sugar and sweets • Excess of energy, you feel you can’t relax • Weight loss, weight gain SHORT-TERM EFFECTS • Nausea • Diarrhea • Agitation • Headaches LONG TERM EFFECTS • Chronic Insomnia • Weight Gain • Sexual Dysfunction (erectile dysfunction) Most Significant Problems • Suicide • Sexual dysfunctions- sexual desire, lack of interest in sex, and anorgasmia (trouble achieving orgasm). • Nausea, diarrhea, agitation, headaches GenerationRX: Abusing Prescription Drugs Part 2 GenerationRX: Abusing Prescription Drugs Part 1