* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure of the Earth
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
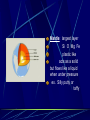
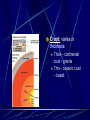
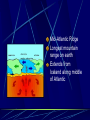
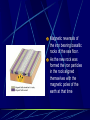
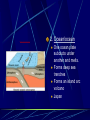
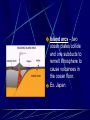
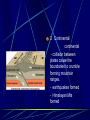
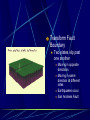
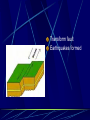
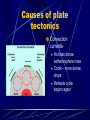
Earth layers, plates Chapter 11 Inner core: solid pressure from above layers. temp 5500°C Fe Ni Outer core: liquid Fe Ni temp 5500°C Mantle: largest layer Si O Mg Fe plastic like acts as a solid but flows like a liquid when under pressure ex. Silly putty or taffy Crust: varies in thickness Thick – continental crust - granite Thin – oceanic crust – basalt Crust is divided into sublayers Lithosphere – crust and upper mantle - broken into 12 large plates that float on the mantle. Asthenosphere – plastic like layer below the lithosphere Mohorovicic' discontinuity – boundary between crust and mantle. Lithosphere Continental Drift Alfred Wegener – 1912 proposed theory of continental drift continents have moved to their current locations Theory of continental drift One continent – Pangaea 200 m years ago Panthalassa – one sea Pangaea separated into Laurasia Gondwanaland Separated by the Tethys Sea Clues that support Continental Drift Pieces of continents fit together like a jigsaw puzzle Fossil clues – Mesosaurus(lived on land and in fresh water) - found in South American and Africa Glossopteris – found in Africa, Australia, India, South America and Antarctic - various climates - must have once been joined Climate clues – fossils of warm plants found in the arctic Glacial deposits – grooved marks in bedrock found in SA, Africa, India, and Australia - must have been covered with glaciers at one time near south pole Rock clues – If continents connected than rocks that make them up should be the same. - similar rock structures are found on different continents ex; Appalachian Mts similar to mountains in western Europe and Greenland Wegener’s theory was laughed at even though he had evidence After his death more evidence of how the continents were able to move were discovered to prove Wegener correct. Mid-Atlantic Ridge Longest mountain range on earth Extends from Iceland along middle of Atlantic Mid-Atlantic Ridge Harry Hess Discovered seafloor spreading Evidence of Seafloor spreading Rocks along rift areas were younger than those farther away. New lava rocks were being laid on either side of the rift Magnetic reversals of the iron bearing basaltic rocks of the sea floor. As the new rock was formed the iron particles in the rock aligned themselves with the magnetic poles of the earth at that time Plate Tectonics Earth’s crust and upper mantle are separated into plates. Plates float on the mantle. Make contact with each other. Cause earthquakes and volcanoes, mountains Composition of plates Crust and upper mantle – lithosphere Less dense layer floats on more dense layer Asthenosphere – mantle More dense Plates flow on this Plate Boundaries Divergent Boundaries Move away from each other mid-Atlantic Ridge Great Rift Valley in eastern Africa Great Rift Valley of Africa Convergent Plates Plates that come together. 1. Ocean/continental the ocean sinks below the continent. remelts in mantle Subduction zone- where ocean plate goes under continental plates Volcanoes form here. Andes Mts. Oceanic-Oceanic Convergence 2. Ocean/ocean One ocean plate subducts under another and melts. Forms deep sea trenches Forms an island arc volcano Japan Island arcs – two ocean plates collide and one subducts to remelt lithosphere to cause volcanoes in the ocean floor. Ex. Japan Deep sea trench – forms where subducted plate melts into the mantle. Ex. Mariana Trench Pacific Ocean 3. Continental/ continental - collision between plates cause the boundaries to crumble forming mountain ranges. - earthquakes formed - Himalayan Mts formed Transform Fault Boundary Two plates slip past one another Moving in opposite directions Moving in same direction at different rates Earthquakes occur San Andreas Fault Transform fault Earthquakes formed Causes of plate tectonics Convection currents Hot less dense asthenosphere rises Cools – more dense drops Reheats cycle begins again Effects of plate tectonics Volcanoes Earthquakes Mountain building FAULT/BLOCKCompression forces fault causes weakness. Part of the land drops. Leaving behind higher ground. Ex. Sierra Nevadas. http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/dl/free/0078617006/164213/00038307.html Folded mountains Two plates collide with each other. Ex. Appalachian Mts. Anticline – upward fold in rocks Syncline – downward fold in rocks. Strike-slip Faults – plates moving past each other. Snag onto each other storing up stress Ex. San Andreas Fault Strike slip fault Rio Grand Rift Rio Grand Rift Found from Colorado, New Mexico and Texas Hidden underground below sediment and basalt Wrangell Mountains Alaska Wrangell Mt. Alaska Formed on floor of the Pacific ocean 9600 km from present location Theory; they were scraped off ocean plate as it was subducted Red Sea Formed due to divergence along a triple junction of the Great Reft Valley in Africa and the Gulf of Aden. Page 113 Critical thinking Section: 3 page 289 1, 2, 3, 4, Page 294 Vocab Checking concepts Thinking Critically 15,16, 17, 18, 20 23,24, 25