* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 Review!
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Möbius transformation wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rotation matrix wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Plane of rotation wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rotation group SO(3) wikipedia , lookup
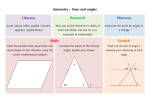
Unit 2 Review! Objective: to review the concept of congruence Common Core State Standards: 8.G.1; 8.G.2; 8.G.5; 8.G.6; 8.G.7 Types of Angles Matching! Transversal Exterior angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal (equal to each other) Alt Int. Angles Angles in the same position with respect to the lines and transversal (equal to each other) Alt Ext. Angles Angles that are opposite from each other formed by the intersection of 2 lines (equal to each other) Corr. Angles Vertical Angles A line that cuts across two or more (usually parallel) lines Interior angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal (equal to each other) All About Triangles! The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180° y° x° + y° + z° = 180° x° z° The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of its two remote interior angles. y° x° x° + y° = p° p° Pythagorean Theorem: In a right triangle, the square of the lengths of the hypotenuse c is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs a and b. a c a2 + b2 = c2 b Midpoint & Distance on the Coordinate Plane Midpoint x1 x2 y1 y2 M , 2 2 Distance d ( x2 x1 ) ( y2 y1 ) . 2 2 Transformations The four main Transformations are: Translation (Slide) Reflection (Flip) Rotation (Turn) Dilation (Scale) A translation is a transformation that slides a figure in any direction. Translation Rule: Ta,b (x, y) = (x + a, y + b) Example T0,4 (2, 3) = (2 + 0, 3 + 4) = (2, 7) A rotation is a transformation that turns a figure about a fixed point called the center of rotation. The measure of the rotation is the angle of rotation. Rotation Rules: A reflection is a transformation that flips a figure over a line of reflection. The distance from a point to the line of reflection is the same as the distance from the point's image to the line of reflection. Reflection Rules: Y axis: (x, y) (-x, y) X-Axis: (x, y) (x, -y) Y=X: (x, y) (y, x) Y=-X: (x, y) (-y, -x) A dilation is a transformation that makes a figure larger or smaller. This means the two figures are similar (same shape/different size). A scale factor is the ratio of the side lengths of the image to the corresponding side lengths of the original figure. Dilation Rule: (x,y) (kx, ky) k>1: enlargement 0<k<1: reduction Let’s Practice! MAP PLUS BOOKLET QUESTIONS #8, 18, 34, 36, 43, 44, 56, 64 Exit Ticket After reviewing and practicing Unit 2, rate yourself on how you feel about the same questions in the MAP Plus Book.