* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 22 Friday March 20
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
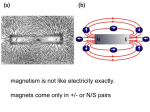
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
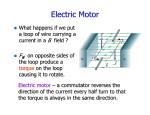
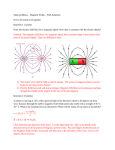
Lecture 22 Friday March 20, Magnetic force on a magnetic dipole, MRI 1. Take 2. Demos a. Motor-generator pair as motor b. Gyroscope c. Magnet with coil 3. Quick Review 4. 24: 7 Torque on a magnetic dipole a. Current loop is a magnetic dipole i. Start with a rectangular loop a x b 1. torque on a current loop B F b φ a. b. Fupper = I*a*B, Flower = I*a*B but in opposite direction i. Sum of forces on loop = 0 ii. Sum of torques = F *(b/2)*sin φ + F *(b/2)*sin φ = I a b B sin φ = I*A*B*sin φ iii. If loop is a coil of N turns, the torque is N times larger. c. Magnetic moment defined by IA d. Result is correct for all planar loops in an uniform magnetic field, not just rectangular loops e. Direct current motors –Demo 5. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging a. The nucleus of atoms, including hydrogen atoms (protons) are little magnets. i. In an external magnetic field dipole wants to align with the magnetic field with its north pole in the direction of the field. This means the energy of the dipole is lower when aligned parallel with the field than when oriented opposite the field direction. ii. Nuclei have only two orientations, not a continuously variable orientation. Either with or against the magnetic field. The energy difference corresponds to radio frequencies. E = h f, where h is Planck’s constant and 6.63 x 10-34 J•s. For a proton, f = 42.576 MHz in a field of 1 T. However, the protons see a magnetic field = BEXTERNAL +BLOCAL. 1. BLOCAL is caused by neighbors, so can tell something about different neighborhoods of the proton. 6. Homework due today a. Problems: 24: 32, 34, 37 i. 32: field strength and direction to levitate wire given mass and I ii. 34: F with wire not perpendicular to field iii. 37: force on current loop with radial field (loud speaker). 7. Homework due Friday a. Read: 25: 1-3 Faraday’s Law and electromagnetic induction b. Problems: 24: 38, 39, WB 24:23-30 i. 38: torque on current loop ii. 39: ditto iii. WB 24: 23-30 forces on straight wires and torques on loops