* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
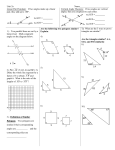
Chapter 2.1 Common Core G.CO.9, G.CO.10 & G.CO.11 Prove theorems about lines, angles, triangles and parallelograms. Objective – To use inductive reasoning to make conjectures. Ch 2.1 Notes Inductive Reasoning – is reasoning based on patterns you observe. Conjecture – is a conclusion you reach using inductive reasoning. Counterexample – is an example that shows that a conjecture is incorrect Chapter 2.2 Common Core G.CO.9, G.CO.10, & G.CO.11 Prove theorems about lines, angles, triangles, and parallelograms. Objectives – To recognize conditional statements and their parts. To write converses, inverses, and contrapositives of conditionals. Ch 2.2 Notes Conditional Statements – is an if-then statement If I am in Geometry class, then I am in my favorite class at IWHS. Hypothesis Conclusion • Original Sentence – • Converse – • Inverse – • Contrapositive - Chapter 2.3 Common Core Common Core G.CO.9, G.CO.10, & G.CO.11 Prove theorems about lines, angles, triangles, and parallelograms. Objective – To write biconditionals and recognize good definitions. Chapter 2.3 Notes Biconditional Statement – if and only if statement I am having fun if and only if I am in Geo. Class. * A true biconditional statement is true both forward and backwards. New way to write Conditional & Biconditional statements ~ - means not - means if-then statement - means if and only if statement Chapter 2.4 Common Core GCommon Core G.CO.9, G.CO.10, & G.CO.11 Prove theorems about lines, angles, triangles, and parallelograms. Objective – To use the Law of Detachment and the Law of Syllogism. Ch 2.4 Notes Deductive Reasoning – (sometimes called logical reasoning) is the process of reasoning logically form given statements or facts to a conclusion. Two laws of Deductive Reasoning * Law of Detachment – If p q is a true conditional statement and p is true, then q is true. * Law of Syllogism – If p q and q r is a true conditional statement, then p r is true. Chapter 2.5 Common Core GCommon Core G.CO.9, G.CO.10, & G.CO.11 Prove theorems about lines, angles, triangles, and parallelograms. Objective – To connect reasoning in algebra and geometry. Ch 2.5 Notes • • • • Addition Property – If a = b, then a + c = b + c Subtraction Property - If a = b, then a - c = b – c Multiplication Property - If a = b, then a * c = b * c Division Property - If a = b, then a / c = b / c • • • • Reflexive Property - for any real # a, a = a Symmetric Property – if a = b then b = a Transitive Property - if a = b and b = c, then a = c Substitution Property - if b = c, then where I see a b I can substitute in a c *Distributive Property – a(b+c) = Proof – is a convincing argument that uses deductive reasoning. A proof logically shows why a conjecture is true. Two-Column Proof – lists each statement on the left and justifies it with a statement on the right. Paragraph Proof – is written as sentences in a paragraph (Ch 2.6) Chapter 2.6 Common Core G.CO.9 Prove theorems about lines and angles. Theorems include…vertical angles are congruent. Objective – To prove and apply theorems about angles. Ch 2.6 Notes Vertical Angles Thm – Vertical angles are congruent Congruent Supplements Thm – If 2 angles are supp. to the same angle then they are congruent. Congruent Complements Thm – If 2 angles are comp. to the same angle then they are congruent. Right Angle Congruence Thm – all right angles are congruent Theorem 2.5 – if two angles are congruent and supplementary, then each is a right angle.