* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sample 5.3.B.2 Complete
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
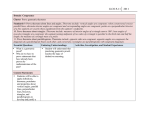
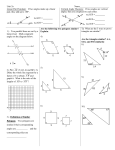
G.CO.9-11 2011 Domain Congruence Cluster Prove geometric theorems Standards 9. Prove theorems about lines and angles. Theorems include: vertical angles are congruent; when a transversal crosses parallel lines, alternate interior angles are congruent and corresponding angles are congruent; points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those equidistant from the segment’s endpoints. 10. Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180°; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a triangle meet at a point. 11. Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, and conversely, rectangles are parallelograms with congruent diagonals. Essential Questions Enduring Understandings What is a geometric proof? Why do we have to prove statements that have already been proven by mathematicians of the past? Content Statements Students will be able to apply definitions, theorems, postulates and properties about vertical angles, parallel lines, perpendicular lines, bisectors, triangles, and parallelograms to Student will understand that practicing geometric proofs teaches the logic of deductive reasoning. Activities, Investigation, and Student Experiences 1. PowerPoint lessons, Interactive Examples, Worksheets, Activities 2. SMARTboard lessons and examples 3. Multiple Sample Lessons and Examples G.CO.9-11 2011 develop and justify a geometric proof. Assessments Student Participation Questioning Quizzes (Teacher Given and Self Quizzes) Benchmark/Test (Click here for Resources Folder.) Homework Equipment Needed: SMARTboard Projector Paper and pencil Calculator (Graphing and Scientific) Compass Protractor Ruler Straightedge Graph Paper Isometric Dot Paper Hands-on and virtual two- and three-dimensional manipulatives (i.e. prisms) Geo-boards Teacher Resources: 1. Math Warehouse Website: http://www.mathwarehouse.com/geometry/angle/interactivetransveral-angles.php 2. Click here for Resources Folder. 3. Click here for Resources Folder. G.CO.9-11 Geometer’s Sketchpad 2011