* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit 4 CCSS
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Tensors in curvilinear coordinates wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
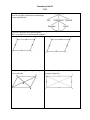
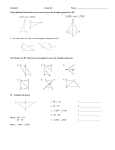
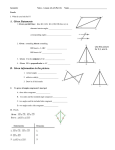
Geometry Unit #4 CCSS BEGIN ON FEBRUARY 2, 2016 & END ON March 4, 2016 4 Quizzes, 1 Test, 1 Project PROJECT ASSIGNED ON FEBRUARY 17 & COLLECTED ON MARCH 2 ********************************************** *HSG-CO.C.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, and conversely, rectangles are parallelograms with congruent diagonals. *HSG-GPE.B.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle. *HSG-GPE.B.5 Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems. *HSG-CO.9 Prove theorems about lines and angles. Theorems include: vertical angles are congruent, when a transversal crosses parallel lines alternate interior angles are congruent and corresponding angles are congruent; points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those equidistant from the segment’s endpoints. *HSG-GPE.B.7 Use coordinates to compute perimeters or polygons and areas of triangles and rectangles, e.g. using the distance formula. ********************************************** VOCABULARY: QUADRILATERAL, POLYGON, SQUARE, RECTANGLE, RHOMBUS, KITE, TRAPEZOID, ISOSCELES, REGULAR, IRREGULAR, BISECTOR, DIAGONAL, CONGRUENT, DISTANCE FORMULA, MIDPOINT FORMULA, MIDPOINT, PARALELLOGRAM, POLYGON ANGLE SUM THEOREM, CONSECUTIVE, OPPOSITE, MIDSEGMENT, BASE ANGLES, SLOPE FORMULA ********************************************** Geometry Unit #4 CCSS Prior Knowledge: Describe and justify hierarchical relationships among quadrilaterals. I can prove theorems about parallelograms. Hint: use parallel lines and congruent triangles. I can prove opposite sides are congruent. I can prove opposite angles are congruent. I can prove the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other I can prove rectangles are parallelograms with congruent diagonals. Geometry Unit #4 CCSS I can use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. I can prove or disprove that a figure defined I can use the distance formula to show when by four given points is a rectangle. given a rectangle in the coordinate plane its diagonals are congruent. I can use slope for parallel and perpendicular lines to justify whether a shape is a special quadrilateral. I can use slope to show opposite sides are I can use slope to show trapezoids have exactly parallel in parallelograms. one pair of opposite sides parallel. Geometry Unit #4 CCSS