* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transposition of great vessels (D-TGA)
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
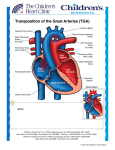
Parent’s Section: Frequently asked questions: (Queries: [email protected]) Blue Babies II Transposition of great vessels (D-TGA) What is the Transposition of great vessels? The transposition of the great vessels is a congenital problem of the babies. Here the atria and ventricles are connected normally. But the great vessels exchange or switch their respective places i.e Aorta gets connected to the right sided ventricle (RV). The lung artery gets connected to left sided ventricle (LV). This kind of circulation is known as parallel circulation. It means all oxygen poor blood collected from the body entering into the RA, is again going back to the aorta and to the body. Similarly, all oxygen rich blood from LA reaches again to pulmonary arteries and lungs. In uterus this system is not harmful as the RA blood coming from placenta contains maximum oxygen and doesn’t need to be circulated through the lungs. After the event of birth , lungs are only source of oxygen and they are completely bypassed unless intra uterine channels like foramen ovale and patent ductus arteriosus remain patent. What are the classical clinical features of Transposition of great vessels? A baby born with the classical TGA is diagnosed in first few hours of life due to deep cyanosis. Cyanosis is the hallmark of this entity. However, some of the babies may not become symptomatic very early due to presence of large atrial (ASD/PFO)vor ventricular septal defect(VSD) or patent ductus arteriosus.( PDA). These babies may suffer from increased heart rate, respiratory rate, feeding difficulties or failure to gain weight. These babies suffer from early demise in absence of shunt lesions. Im presence of large shunt lesions, they may have lesser cyanosis but early risk of getting permanent changes in pulmonary vascular bed (Eisenmeger syndrome). If baby is getting very blue, what must be done as a first step? The deepening cyanosis in a TGA baby is grave and immediate hospitalization must be done, so that measures to open the inter-atrial connection (ASD/ PFO) or ductus arteriosus can be taken. Prostaglandin E1 is a costly but effective treatment to keep ductus arteriosus patent. It can be started as an infusion at any place. It has some side effects but is only way out form this grave situation. Subsequently a ballooning procedure can be undertaken to create and atrial septal defect. What is the Balloon Atrial Septostomy? The balloon atrial septostomy is the procedure done in a well equipped set-up where pediatric cath lab is available. Baby is put on cath table in chest up posture and sedation or general anesthesia is given . Then femoral vein is accessed from groin. A balloon tip catheter is advanced from femoral vein up to left atrium crossing the foramen ovale. With a swift backstroke of wrist, inflated balloon is withdrawn in to RA creating a tear in atrial septum. This artificially created atrial septal defect provides a good site where oxygen rich blood of LA can be mixed with oxygen poor blood of RA and may improve over all saturation of body. After successful balloon atrial septostomy can baby be discharged? After successful BAS baby become stable and can go home if corrective surgery has to be delayed. Can D-TGA be corrected completely? Fortunately, if detected early and operated timely total correction and subsequently good quality life is expected. What are the treatment modalities available for D-TGA? In first 2-3 weeks arterial switch. Operation is done. It’s a open heart procedure and requires bypass surgery. Nowadays, it is done with great success. The arteries are cut above the valve and switched over so that aorta is shifted back to LV and PA is shifted to the RV. Hence , normal heart structure is achieved. If baby is diagnosed late then this operation can not be done as LV loses its strength. Sometimes, surgeon can do the arterial switch in stages. Surgeons try to put pressure on LV by putting a band on pulmonary artery. When LV becomes stronger then the actual operation can be done. Risk of poor outcome after surgery are 5-10 %. If a baby presents late then what can be done? For these babies a procedure called senning procedure or atrial switch operation is performed. We call it a physiological correction. In this procedure , the blood streams are redirected. The oxygen poor blood goes along the newly created channel in to the left ventricle, to be pumped in to the lungs. The oxygen rich blood is made to travel towards the RV to be pumped in to the aorta. Here role of pumping chambers ie ventricles is changed. The LV still supports the lungs and RV supports the body unlike the normal heart but due to redirected systemic venous blood towards LV and pulmonary venous blood towards RV a physiologically normal heart is achieved. Is natural or medical cure is possible in D-TGA patients? No. D-TGA is essentially a complex disease and unlike the VSD, ASD or PDA natural process or medical treatment can not heal it. Is surgical correction is unavoidable? In absence of natural cure and an effective medical therapy, surgical correction is mandatory. How much time is taken for the surgery? How much blood is needed? The usual operating time for the TOF is 5-6 hours. Usually, the donation of 4-6 units of blood is required before the surgery. Nowadays blood of any group can be donated and hospital can arrange the appropriate blood group. Specific blood group donors are required in cases of rare blood group or when fresh blood is needed. What is the prognosis of operated D-TGA Babies? Timely operated babies enjoy a good life and can carry on their profession as well as married life efficiently. How often an operated D-TGA go for a follow-up check-up? Usually first few follow-up are planned more frequently like 15 days, 1month, 3 months then 6 months. Later these visits can be reduced to 1-3 year depending on the follow-up findings. What are the recommendations for live vaccination in these kids? According to current norms followed by various tertiary centres world over- no specific protocol to be followed for closed heart shunt procedures. Live vaccines are to be avoided for 4-6 weeks in case of open heart surgery. Is pregnancy is contraindicated in operated D-TGA patients? Once the baby is repaired successfully, the risk with pregnancy is very low. Queries: [email protected] www.cardioiap.org