* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marketing Research
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Field research wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
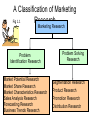
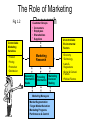
Marketing Research Overview • • • • • Introduction to marketing research Research design Data collection Data analysis Reporting results Redefining Marketing Research The American Marketing Association (AMA) redefined Marketing Research as: The function which links the consumer, the customer, and public to the marketer through INFORMATION Nature of marketing research (MR) • Systematic and objective process of planning, gathering, analysing and reporting data • Used to solve specific problem or opportunity Redefining Marketing Research Used to identify and define market opportunities and problems Generate, refine, and evaluate marketing performance Monitor marketing performance Improve understanding of marketing as a process Definition of Marketing Research Marketing research is the systematic and objective identification collection analysis dissemination and use of information for the purpose of improving decision making related to the identification and solution of problems and opportunities in marketing. Market Research • Specifies the information necessary to address these issues • Manages and implements the data collection process • Analyzes the results • Communicates the findings and their implications Classification of Marketing Research Problem Identification Research • Research undertaken to help identify problems which are not necessarily apparent on the surface and yet exist or are likely to arise in the future. Examples: market potential, market share, image, market characteristics, sales analysis, forecasting, and trends research. Problem Solving Research • Research undertaken to help solve specific marketing problems. Examples: segmentation, product, pricing, promotion, and distribution research. A Classification of Marketing Research Fig 1.1 Marketing Research Problem Identification Research Market Potential Research Market Share Research Market Characteristics Research Sales Analysis Research Forecasting Research Business Trends Research Problem Solving Research Segmentation Research Product Research Promotion Research Distribution Research Problem Solving Research Table 1.1 SEGMENTATION RESEARCH Determine the basis of segmentation Establish market potential and responsiveness for various segments PRODUCT RESEARCH Select target markets Test concept Create lifestyle profiles: demography, media, and product image characteristics Determine optimal product design Package tests Product modification Brand positioning and repositioning Test marketing Control score tests Problem Solving Research PROMOTIONAL RESEARCH Table 1.1 cont. 0.00% APR PRICING RESEARCH Optimal promotional budget Sales promotion relationship Optimal promotional mix Copy decisions Media decisions Creative advertising testing Evaluation of advertising effectiveness Claim substantiation Pricing policies Importance of price in brand selection Product line pricing Price elasticity of demand Initiating and responding to price changes $ALE Problem Solving Research Table 1.1 cont. DISTRIBUTION RESEARCH Determine… Types of distribution Attitudes of channel members Intensity of wholesale & resale coverage Channel margins Location of retail and wholesale outlets Marketing Research Process Step 1: Problem Definition Step 2: Development of an Approach to the Problem Step 3: Research Design Formulation Step 4: Fieldwork or Data Collection Step 5: Data Preparation and Analysis Step 6: Report Preparation and Presentation The Role of Marketing Fig 1.2 Research Customer Groups • • • • Consumers Employees Shareholders Suppliers Uncontrollable Environmental Factors Controllable Marketing Variables Marketing Research •Product •Pricing •Promotion •Distribution Assessing Information Needs Providing Information Marketing Decision Making Marketing Managers • Market Segmentation • Target Market Selection • Marketing Programs • Performance & Control •Economy •Technology •Laws & Regulations •Social & Cultural Factors •Political Factors Characteristics of MR • • • • Quantitative vs. qualitative Applied vs. basic research Can be inaccurate Time and budget constrains Remember the benefits of marketing research – Page 8 Role of MR in decision making • Provides info • Functional roles – Descriptive – Diagnostic – Predictive • Factors influencing MR – Time – Data availability – Nature of decision – Cost-benefit – Lack of resources IMPORTANCE OF MARKETING RESEARCH IN DECISION MAKING • Necessary to keep existing customers • Provides insight to an ever changing market ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS • Participants should be comfortable • Participants should not be deceived • Participants should be willing and informed • Data should be held in confidence SECONDARY RESEARCH • Advantages and disadvantages • Internal data sources • External data sources • The Internet SURVEY RESEARCH • Errors • Types of surveys – Personal • Door-to-door • Executive • Mall intercepts – Telephone – Mail • Internet • Self-administered interviews OBSERVATION • Advantages and disadvantages • Methods – – – – – Human vs. machine Natural vs. contrived Disguised vs. undisguised Structured vs. unstructured Direct vs. indirect EXPERIMENTS • Laboratory vs. field • Internal vs. external validity • Test marketing MEASUREMENT CONCEPTS • Levels of measurement of scales • Open-ended response format • Fixed –alternative response – Comparative scales – Non-comparative scales QUESTIONNAIRE DESIGN • Considerations – – – – – – Info requirements Question content Question structure Question wording Question sequence Layout • Reliability issues SAMPLING • Define population • Determine sample frame • Select sampling technique – Probability – Non-probability • Determine sample size • Execute sampling process FIELDWORK • • • • • Selecting fieldworkers Training fieldworkers Supervising fieldworkers Validating fieldworkers Evaluating fieldworkers DATA PREPARATION • Validation • Editing • Coding • Data entry • Data cleaning DATA ANALYSIS • Tabulation • Graphic • Descriptive statistics HYPOTHESIS TESTING • • • • • Formulate null hypothesis Choose appropriate statistical test Decide on desired significance level Calculate value of test statistic Compare observed value of test statistic with critical value and arrive at conclusion RESEARCH REPORT • • • • • • • • Title page Letter of transmittal Table of contents Executive summary Introduction Methodology Findings Conclusions and recommendations