* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Radiation Dose Reduction in Pediatric CT
Brachytherapy wikipedia , lookup
Proton therapy wikipedia , lookup
Positron emission tomography wikipedia , lookup
Radiation therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear medicine wikipedia , lookup
Center for Radiological Research wikipedia , lookup
Neutron capture therapy of cancer wikipedia , lookup
Industrial radiography wikipedia , lookup
Radiosurgery wikipedia , lookup
Backscatter X-ray wikipedia , lookup
Image-guided radiation therapy wikipedia , lookup
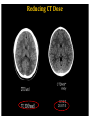
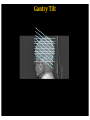
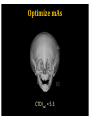
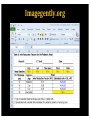
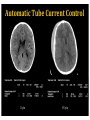
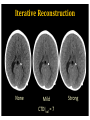
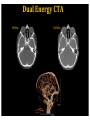
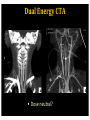
RadiationDoseReductionin PediatricCT ArastooVossough,MD,PhD AssociateProfessorofRadiology Disclosures: No relevant conflicts of Interest Objectives • To be aware of advances in CT applications and dose reduction in pediatrics. • To become familiar with resources available to help implementing radiation dose reduction. • To become familiar with the various modifications that can be done to reduce neuroradiological CT examination radiation doses in pediatrics (on both older and newer generation scanners). Source: WHO ThresholdvsnoThreshold CTDose: CTDIvol xZ-axislength=DLP(doselengthproduct) ReducingCTRadiationExposure • Don’tscanifunnecessary • TraumaHeadCTrules,panscan,ICUpatients,multiperfusion • Scanonlyspecificareasneeded (e.g.,entirevspartofspine,face,neck) (DLP=CTDIxlengthofscan) • Don’tdomultiphasestudiesifunnecessary • Considerothermodalities • Paradigmshift:fromhighestimagequalityto what’sgoodenoughfortheclinicalquestion ALARAPrinciple (i.e.,GoodEnough) “Considerationforradiationprotection shouldincludethefactthatimaging professionalsmustthinkaboutacceptable imagequalityasopposedtooptimal quality.” Frush,D.,Radiationsafety,PediatricRadiology(2009)39(Suppl 3):S385-S390 ReducingCTDose NeuroCTScenarios • • • • CT,s/ptrauma CT,checkventriclesize CT,r/ostroke CT,craniofacialdeformities Do they all need the same dose ? • HeadCTA,afterclippedaneurysm • HeadCTA,r/ostroke • NeckCTA,pencilinjurytoposteriorthroat What’sDifferentinPediatrics • Scanneroutputvs.patientdose – ConversionfactorfrommGy tomSv isdifferentinPeds • PitfallsofvolumeCTDIandDLP – CTDIisreferencedtophantom(32cm vs16cm) – Canunderestimatedosetoverysmall patients – Differentmanufacturers’ordifferent protocols’modellingmayvary – Size-specificdoseestimates(SSDE)vs CTDI(Siebert,JAetal,JACR2014) Turner et al, RSNA 2009 ACRAccreditationforCT CTDIvol:VolumetricCTDoseIndex • ADULT: – CTDIvol :80mGy • CHILDREN: – Diagnosticreferencelevel:CTDIvol :35mGy (1yo) – Pass/faillimit:CTDIvol :40mGy • (foraroutine1-year-oldheadexam- maybedifferent (higherorlower)foranindividualpatientwithunique indications). imagegently.org TechnicalfactorsinReducingCT RadiationDose • Tailordosetopatientsize – Age/sizebasedcategories,automatedtubecurrentmodulation, automatedtubevoltagemodulation • Useofradiationshields • UseoflowerkVp of80or100or120ifpossible • MinimizingZaxisscanlength • Optimizepitchperclinicalindication • Optimizecollimationperclinicalindication • Accuratepatientcenteringinthegantry • Iterativereconstructiontechniquesinsteadof backprojection ifavailable • Optimizethedoseperformanceofdetector,collimator, andbeam-shapingfilter ReducingCTRadiationDose 1. Tailortechnicalfactorstoindicationand patient– evenonoldscanners 1. Automaticexposurecontrol 1. Iterativereconstruction GantryTilt OptimizemAs • Tubecurrent(mA) =rateofx-rayproduction • Decreaseoftubecurrentandexposuretime(mAs) decreasesdosebutincreasesnoise/quantum mottle • Canbequitelowforairwayorlungparenchyma • Canbelowerforchildren OptimizemAs CTDIvol =5.3 Imagegently.org Optimizepitch • Pitch=distanceCTtableadvancesin1 rotation/widthofx-rayfanbeaminz direction– definitioninhighMDCT • Increasedpitchdecreasesdose&likelihood ofmotionartifactbutincreasesquantum mottle • Variablebasedonclinicalindication • NeedstobelowfortemporalboneCT studies X-raybeamonlessthanafull rotation AutomaticTubeCurrentControl • Tubecurrentchangesduringcourseofscan baseonpresets – Setupperlimit • Differentmanufacturers: – Translationofsamedoselevelsisnoteasy – Samedoselevelsmaynotproduceidentical imagequality AutomaticTubeCurrentControl 3 y/o 15 y/o CTScouts(Scanograms) • Centerthepatientinthegantry – Helpstheautomateddoesreductionmeasures workmoreaccurately – Reducesdose • APvs.APandlateral • Doseofscout IterativeReconstruction • Useaniterativereconstructioninsteadof filteredbackprojection • ASIR,SAFIRE,iDose4,AIDR • Newergeneration(modelbased):ADMIRE, Veo,IMR • Allowsacceptablequalityscansatmuch lowerdoses IterativeReconstruction None Mild CTDIvol =7 Strong ReducingCTADose K-edge of iodine Can go lower on kVp CTDIvol = 5 DualEnergyCTA 80kVp 140kVp DualEnergyCTA • Doseneutral? • DIR of the American College of Radiology Report > 100 pages ReducingCTRadiationDoseinPediatrics • ALARA– goodenoughscans • Technicalmodificationsregardlessof generationofscanner • Needssomedegreeofpersonalizationper eachindicationand/orpatient • Needsradiologisttimeinprotocolling