3D dose verification for advanced radiotherapy
... dosimetry). This thesis deals with both strategies. First, the pre-treatment verification part deals with verification methods and procedures that are applied before the first fraction of a treatment is given. These pretreatment verification strategies are useful for detecting errors made during tre ...
... dosimetry). This thesis deals with both strategies. First, the pre-treatment verification part deals with verification methods and procedures that are applied before the first fraction of a treatment is given. These pretreatment verification strategies are useful for detecting errors made during tre ...
portal dosimetry in radiotherapy
... photon beam treatment with linear accelerators (LINACs)4‐6. With these devices, electrons are generated and accelerated to high energies of 4‐25 MeV. The accelerated electrons produce X‐rays when they collide with a tungsten target and the resulting photon beam can be use ...
... photon beam treatment with linear accelerators (LINACs)4‐6. With these devices, electrons are generated and accelerated to high energies of 4‐25 MeV. The accelerated electrons produce X‐rays when they collide with a tungsten target and the resulting photon beam can be use ...
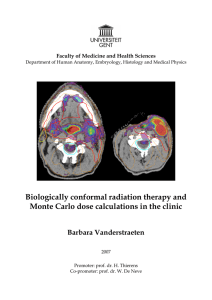
Biologically conformal radiation therapy and Monte
... changes in physical properties within patients. Additionally, tumor biology plays an important role in the diagnosis, treatment decisionmaking and the assessment of therapeutic response. Recent advances in biological imaging techniques, mainly based on positron emission tomography (PET), offer the o ...
... changes in physical properties within patients. Additionally, tumor biology plays an important role in the diagnosis, treatment decisionmaking and the assessment of therapeutic response. Recent advances in biological imaging techniques, mainly based on positron emission tomography (PET), offer the o ...
An X-ray Source Model and Characterization Method for Computing
... minimizing the irradiation of healthy tissues. While this conformality increases the radiation treatment plan quality, it also causes higher dose gradients near the edges of the treated area. These plans therefore require more precise patient positioning[135, 35]. Historically, patients were positio ...
... minimizing the irradiation of healthy tissues. While this conformality increases the radiation treatment plan quality, it also causes higher dose gradients near the edges of the treated area. These plans therefore require more precise patient positioning[135, 35]. Historically, patients were positio ...
A literature review of electronic portal imaging for
... from paper to electronic systems, or from manual to automatic systems. Regardless of whether the treatment technique is conventional or advanced, the department is large or small, or the treatment makes use of the latest technology or not, errors can, and often do, occur during the delivery process. ...
... from paper to electronic systems, or from manual to automatic systems. Regardless of whether the treatment technique is conventional or advanced, the department is large or small, or the treatment makes use of the latest technology or not, errors can, and often do, occur during the delivery process. ...
3 Prostate Ragab Hani Donkol and Ahmad Al Nammi
... prostate. The first clinically applicable images of the prostate obtained with TRUS were described in 1967 by Watanabe et al, they used a 3.5 MHz transducer, which at that time was considered to be state of the art, to obtain images that were clinically meaningful. As US technology has become more r ...
... prostate. The first clinically applicable images of the prostate obtained with TRUS were described in 1967 by Watanabe et al, they used a 3.5 MHz transducer, which at that time was considered to be state of the art, to obtain images that were clinically meaningful. As US technology has become more r ...
Development and testing of extra-cranial tumour tracking
... respiratory signal is extracted from the external surface displacement and modelled to derive the instantaneous values of amplitude and phase variables. To take into account possible inter-fraction anatomical variations that may occur between planning and treatment time, the tumour baseline in the ...
... respiratory signal is extracted from the external surface displacement and modelled to derive the instantaneous values of amplitude and phase variables. To take into account possible inter-fraction anatomical variations that may occur between planning and treatment time, the tumour baseline in the ...
Imaging dose from cone beam computed tomography in radiation
... There have been over 500 publications since early 2000s that include terms such as “cone beam CT” or “CBCT” and “radiation therapy” or “radiotherapy” as a key word, based on the advanced search performed using the engine Scopus.com (Elsevier B.V., The Netherlands). This review was conducted by searc ...
... There have been over 500 publications since early 2000s that include terms such as “cone beam CT” or “CBCT” and “radiation therapy” or “radiotherapy” as a key word, based on the advanced search performed using the engine Scopus.com (Elsevier B.V., The Netherlands). This review was conducted by searc ...
American Association of Physicists in Medicine 40th Annual
... This is a landmark year for the Annual Meeting for two prominent reasons. For the first time, both the positions of Scientific Program Director and Co-Director are filled by women members of the Association. Drs. Mary Martel and Maryellen Giger have worked diligently to develop an outstanding scient ...
... This is a landmark year for the Annual Meeting for two prominent reasons. For the first time, both the positions of Scientific Program Director and Co-Director are filled by women members of the Association. Drs. Mary Martel and Maryellen Giger have worked diligently to develop an outstanding scient ...
CT Dosimetry: Com- parison of Measure- ment
... CT provides an image of normalized tissue attenuation values. Also, image noise is reduced if radiation is increased; consequently, a CT image looks fine (often better) if excessive radiation is used. Thus, without dose measurements, the CT user lacks the visual cues needed to appropriately adjust t ...
... CT provides an image of normalized tissue attenuation values. Also, image noise is reduced if radiation is increased; consequently, a CT image looks fine (often better) if excessive radiation is used. Thus, without dose measurements, the CT user lacks the visual cues needed to appropriately adjust t ...
The management of imaging dose during image-guided
... quality will be acquired at a total dose that is at least several times that of a single high-quality CT and potentially as much as the cumulative dose from ten individual CTs. If organ motion is going to be accommodated in a planning target volume 共PTV兲 margin then the CT can provide the margin inf ...
... quality will be acquired at a total dose that is at least several times that of a single high-quality CT and potentially as much as the cumulative dose from ten individual CTs. If organ motion is going to be accommodated in a planning target volume 共PTV兲 margin then the CT can provide the margin inf ...
The management of imaging dose during image-guided
... quality will be acquired at a total dose that is at least several times that of a single high-quality CT and potentially as much as the cumulative dose from ten individual CTs. If organ motion is going to be accommodated in a planning target volume 共PTV兲 margin then the CT can provide the margin inf ...
... quality will be acquired at a total dose that is at least several times that of a single high-quality CT and potentially as much as the cumulative dose from ten individual CTs. If organ motion is going to be accommodated in a planning target volume 共PTV兲 margin then the CT can provide the margin inf ...
Characterization of the homogeneous tissue mixture approximation
... the use of dose estimates in absolute terms, such as for risk estimates, and may impact some comparative studies, such as when modalities or techniques with different x-ray energies are used. The error introduced by the homogeneous tissue mixture approximation in higher energy x-ray modalities, such ...
... the use of dose estimates in absolute terms, such as for risk estimates, and may impact some comparative studies, such as when modalities or techniques with different x-ray energies are used. The error introduced by the homogeneous tissue mixture approximation in higher energy x-ray modalities, such ...
article in press - The EndoExperience
... Ludlow et al. shows a good overall reproducibility (2.5% variation between repeated identical examinations), although some specific TLD locations showed a large variation [11]. It is clear that effective dose estimations are dependent on many factors which are not standardised, such as the phantom i ...
... Ludlow et al. shows a good overall reproducibility (2.5% variation between repeated identical examinations), although some specific TLD locations showed a large variation [11]. It is clear that effective dose estimations are dependent on many factors which are not standardised, such as the phantom i ...
Assessing The Clinical Application Of The Van Herk Margin Formula
... 4.3 Investigation of tissue density................................................................................................. 86 4.4 Evaluation of VHMF dose model ........................................................................................... 89 4.4.1 Investigation of the van Herk ...
... 4.3 Investigation of tissue density................................................................................................. 86 4.4 Evaluation of VHMF dose model ........................................................................................... 89 4.4.1 Investigation of the van Herk ...
The concept and challenges of TomoTherapy accelerators
... points of content expansion for keen readers. Radiotherapy is an essential element in the treatment of cancer patients; it is used alone or in combination with surgery or chemotherapy, and it has become a well-recognized curative and palliative therapy. Because of localization uncertainties, a margi ...
... points of content expansion for keen readers. Radiotherapy is an essential element in the treatment of cancer patients; it is used alone or in combination with surgery or chemotherapy, and it has become a well-recognized curative and palliative therapy. Because of localization uncertainties, a margi ...
Breast Microcalcifications - Diagnostic Centers of America
... severity of a patient's clinical condition should dictate the selection of appropriate imaging procedures or treatments. Only those exams generally used for evaluation of the patient's condition are ranked. Other imaging studies necessary to evaluate other co-existent diseases or other medical conse ...
... severity of a patient's clinical condition should dictate the selection of appropriate imaging procedures or treatments. Only those exams generally used for evaluation of the patient's condition are ranked. Other imaging studies necessary to evaluate other co-existent diseases or other medical conse ...
International Workshop on Monte Carlo Techniques in Medical
... artificial implants from CAD modeling (screws, hip replacements, brachytherapy seeds, etc) or anatomical details extracted from other imaging modalities, such as for example MRI (arteries, spinal cord, atheroma, etc). A potential solution based on the use of smaller voxels for modeling complex objec ...
... artificial implants from CAD modeling (screws, hip replacements, brachytherapy seeds, etc) or anatomical details extracted from other imaging modalities, such as for example MRI (arteries, spinal cord, atheroma, etc). A potential solution based on the use of smaller voxels for modeling complex objec ...
Computed Tomography Radiation Safety Issues in Ontario
... and guidance of interventional and therapeutic procedures. It allows rapid acquisition of high-resolution three-dimensional images, providing radiologists and other physicians with cross-sectional views of the patient’s anatomy. CT can be used to image many types of tissues, such as soft tissues, bo ...
... and guidance of interventional and therapeutic procedures. It allows rapid acquisition of high-resolution three-dimensional images, providing radiologists and other physicians with cross-sectional views of the patient’s anatomy. CT can be used to image many types of tissues, such as soft tissues, bo ...
Breast Ultrasound for the Mammography Technologist
... Guidance of interventional procedures Evaluation of problems associated with breast implants Treatment planning for radiation therapy ...
... Guidance of interventional procedures Evaluation of problems associated with breast implants Treatment planning for radiation therapy ...
Chapter 15: Special Procedures and Techniques in
... radiation to pre-selected and stereotactically localized lesions. ...
... radiation to pre-selected and stereotactically localized lesions. ...
06. Radiation Protection of Children During Computed Tomography
... Without a reduction in tube current (mA) this leads to a significantly higher dose. 100 kVp or 80 kVp is usually adequate for children. Lowering of kVp enhances contrast 10 kg patient transmits 3-4% while an adult transmits less than 0.1%. Be aware that images with high noise, even if they do not lo ...
... Without a reduction in tube current (mA) this leads to a significantly higher dose. 100 kVp or 80 kVp is usually adequate for children. Lowering of kVp enhances contrast 10 kg patient transmits 3-4% while an adult transmits less than 0.1%. Be aware that images with high noise, even if they do not lo ...
Process Management and Quality Assurance for Intracranial
... implement a new treatment technique as well as the treatment technique process itself, to ensure state-of-the-art treatments, i.e. safe treatments with a high quality. The reason is three-fold. First, choices made by the departmental management influence, in a positive or negative way, the quality a ...
... implement a new treatment technique as well as the treatment technique process itself, to ensure state-of-the-art treatments, i.e. safe treatments with a high quality. The reason is three-fold. First, choices made by the departmental management influence, in a positive or negative way, the quality a ...
Radiation Dose and Safety: Informatics Standards and Tools
... such as those performed in most diagnostic imaging exams to a whole-body exposure of radiation with the same risk. The technical basis of computing effective dose requires that a collection of organ doses be assessed (in absorbed dose units, mGy); then, a series of tissue-weighting factors are used ...
... such as those performed in most diagnostic imaging exams to a whole-body exposure of radiation with the same risk. The technical basis of computing effective dose requires that a collection of organ doses be assessed (in absorbed dose units, mGy); then, a series of tissue-weighting factors are used ...
PDF
... different regions: the exposed breast region and the unexposed air-background (non-breast) region. Breast regions can be partitioned into: 1. Near-skin tissue region, which contains uncompressed fatty tissue, positioned at the 2. periphery of the breast, close to the skin-air interface where the bre ...
... different regions: the exposed breast region and the unexposed air-background (non-breast) region. Breast regions can be partitioned into: 1. Near-skin tissue region, which contains uncompressed fatty tissue, positioned at the 2. periphery of the breast, close to the skin-air interface where the bre ...