* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Year 7 Biological Science Program
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
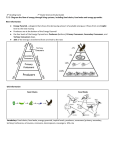
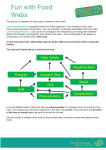
Year 7 – Biological Science Student Program 2016 Week Program Classification 1 Jun 20 – Jun 26 Define classification. Explain why classification is useful. Give examples of classification in daily life. Give examples of classification in Science. Explain why Biologists classify living things. Explain the change from 2 to 5 kingdoms, now have Domains (Bacteria) Explain how organisms are classified into the Five kingdoms. (Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plants, Animals) Describe characteristics of each kingdom. Jun 27 – Jul 24 AB 6.1 Similar and different P75 WS Seven features of Living Things Classification can be applied to structural features of everyday objects. Identify characteristics (structure and function) of organisms that can be used to classify them Use structural and functional characteristics to classify living things. Classify objects as living or non-living using the 7 features of living things. (Movement, Respiration, Sensitivity, Growth, Reproduce, Excretion, and Nutrition (MRSGREN)) and being composed of cells. (e.g. plant, animal, fungi) Biological Classification 2&3 Pearson 7 Activity book Pearson 7 Student book Pearson 7 E book Worksheet SB 6.1 What is classification P196–199, 202 - 203 Identify how organism are classified from kingdom level to class level, it is grouped with other organisms that are increasingly similar (e.g. mammals have hair and suckle their young) Identify how organisms are classified from Kingdom level to species, in groups with other organisms that are increasingly similar. (Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species) Name and identify the major characteristics of the Phyla of the Animal Kingdom Name and identify the major characteristics of the Divisions of the Plant Kingdom. Explain how the Linnaeus system of classification works. Scientific name of organisms made up of: o Genus species. E.g. Homo sapiens o Genus name capital, species lower case. o Underlined if written, italics if typed. Identify other classification and naming systems e.g. Indigenous Australians SB 6.2 Classifying living things P205 – 209, 213 - 215 SB 6.3 Animals and Plants P216 - 229 AB 6.6 Arthropods P84 WS Classification features of Chordates and Insects WS Species Discovery WS The Wonderful World of Animals WS Who Wants to be a Zoologist SB 6.2 Classifying living things P209 - 214 AB 6.4 What’s in a name? P79 AB 6.5 Naming living things P82 WS Classification of Living Things: Scientific Names SB 6.4 Other classification systems P230 - 237 WS Classification using Indigenous Terms Week Program Dichotomous Key 4 Jul 25 – Jul 31 Explain that keys are used as a tool for classifying. Describe how Dichotomous keys are used in Biology to classify living things. Identify features of a strong key. Use provided branching and sentence dichotomous keys to identify organisms. Construct a simple branching and sentence dichotomous key using structural characteristics that do not change over time. Constructing a Dichotomous Key Assessment Habitats and Interactions Define biosphere, ecosystem, environment and habitat of an organism. Describe how organism’s characteristics (adaptations) help them survive in their natural habitat. Identify types of interactions between organisms. (e.g. mutualism, parasitism, predator - prey) Food Chains and Food Webs 5&6 Aug 1 – Aug 14 Identify the sun as the source of energy for ecosystems. Describe how plants and animals gain their energy. (producers photosynthesis, consumers-eat producers or other consumers, decomposers-consume dead or decaying matter.) Explain how feeding relationships can be represented by food chains and food webs. Classify organisms in food chains and food webs as producers, consumers or decomposers Explain why producers always start a food chain/web. Identify herbivores as 1st order consumers, Omnivores can be 1st or 2nd order consumers, Carnivores can be 2nd or higher order consumers. Explain why recycling is important in an ecosystem and which organisms are responsible. Describe how decomposers release energy and nutrients back into the ecosystem for producers. Construct food chains and food webs. Explain how organisms depend on each other in a food chain/web. Describe what happens to other organisms in a food chain/web if its prey/predator or competition is changed. Changes in the population of one level of a food chain affects populations at the other levels (e.g. if the mosquitoes are killed by spraying, this will decrease the amount of food for the frogs) Food Chains and Food Webs Assessment Pearson 7 Activity book Pearson 7 Student book Pearson 7 E book Worksheet SB 6.1 What is classification P199 – 203 AB 6.2 I know what it is! P76 AB 6.3 Creating the key P78 WS Using a Key WS Identification keys - sharks & rays WS Construct a key of the class. SB 5.1 Living Places P162 – 171 WS Adapting to the environment SB 5.2 Food Chains and food webs P172 – 178 AB 5.6 Food chains P66 AB 5.7 Food webs P67 WS Look at my tree house WS Food chains and webs Week Pearson 7 Activity book Pearson 7 Student book Pearson 7 E book Worksheet Program Human activity on Ecosystems 7 Aug 15 – Aug 21 Describe how the following human activities have caused changes in food chains/webs: o deforestation, o agriculture o introduction of new species, such as the effect of cane toads o the use of fire by traditional Aboriginal people o and the effects of palm oil harvesting in Sumatra and Borneo SB 5.3 Impacts on ecosystems P179 – 189 AB 5.8 Human influence on habitats p68 AB 5.9 Human impacts in Antarctica p69 AB 5.10 Growing crops P72 WS Human Impacts on the Environment WS Fire-stick farming END OF TOPIC TEST Assessment Structure Assessment When Yearly Weighting (%) Constructing a Dichotomous Key Thursday 28th July 2016 5 Investigation Thursday 4th August 2016 3 Food Chains and Food Webs Thursday 11th August 2016 5 End of Topic Test Thursday 18th August 2016 10