* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Session-1-topics_in_ten
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
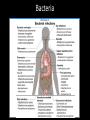
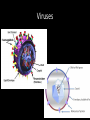
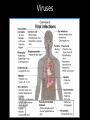
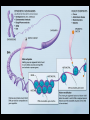
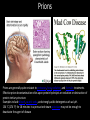
Topics in ten… Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria • • • • • • Size (500nm – several um) Genetics (HGT) Gram type (peptidoglycan) Metabolism Reproduction Pathogenesis Viruses Viruses Viruses • • • • Size (30nm – several um) Genetics - type Proteins – env, Reproduction Epigenetics: the study of changes in gene expression or cellular phenotype, caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence Epigenetics: the study of changes in gene expression or cellular phenotype, caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence Prions Prions are generally quite resistant to proteases, heat, radiation, and formalin treatments. Effective prion decontamination relies upon protein hydrolysis or reduction or destruction of protein tertiary structure. Examples include bleach, caustic soda, and strongly acidic detergents such as LpH. 134 °C (274 °F) for 18 minutes in a pressurized steam autoclave may not be enough to deactivate the agent of disease Prions Affected animal(s) sheep, goat cattle mink[42] white-tailed deer, elk, mule deer, moose[42] cat[42] nyala, oryx, greater kudu[42] ostrich[43] Disease Scrapie[42] Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), mad cow disease[42] Transmissible mink encephalopathy (TME) Chronic wasting disease (CWD) Feline spongiform encephalopathy (FSE) Exotic ungulate encephalopathy (EUE) Spongiform encephalopathy (Has not been shown to be transmissible.) Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD)[42] Iatrogenic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (iCJD) Variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (vCJD) Familial Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (fCJD) human Sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (sCJD) Gerstmann–Sträussler–Scheinker syndrome (GSS)[42] Fatal familial insomnia (FFI)[44] Kuru[42]