* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
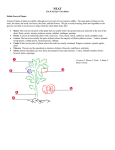
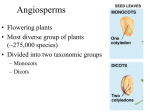
Plants Botany = the study of plants Nonvascular plants have no vessels, no roots, no stems or leaves. Examples: Mosses & Liverworts Vascular Tissue Xylem: transports water Phloem: transports food & nutrients Gymnosperms "naked seeds" cone bearing plants (seeds grow on cones) needle like leaves usually stay green year round wind pollinated Examples: pine trees & evergreens Angiosperms flowering plants seeds are enclosed in a fruit most are pollinated by birds & bees have finite growing seasons Examples: grasses, tulips, oaks, dandelions Flowering Plants are divided into two main groups: Dicots Monocots Parts of the Plant Roots / Stems / Leaves Roots: water and minerals are absorbed (taproots vs fibrous roots) also used to anchor the plant movement of water up to leaves is influenced by TRANSPIRATION Stems Support plant transports water and nutrients Two types of stems: herbaceous and woody A celery stalk soaked in food coloring will absorb the food coloring, you can see the xylem. Leaves Photosynthetic organ of the plant, used to convert sunlight into food Photosynthesis Equation: Stomata: pores within the leaf that open to let CO2 in and O2 out. Guard cells open and close. Cuticle: waxy covering on leaf that prevents water loss Flower Plant Reproduction Pollen is produced by the stamen, which is carried by wind or pollinators to the stigma of another flower. Once the ovules are fertilized, they develop into seeds and the ovary of the flower becomes the FRUIT Pollen Grains Pollen contains plant sperm, and fills the air during the springtime, which often causes seasonal allergies. Asexual Reproduction Many plants can make clones of themselves; this is called VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION How Plants Grow Germination occurs when a seed sprouts (usually caused by changes of temperature and moisture) Monocots have 1 seed leaf (cotyledon), Dicots have 2 seed leaves Perennials - live several years, and reproduce many times, woody plants are perennials Annuals - a plant that completes its life cycle in one growing season (grows, flowers, reproduces and then dies) Biennials - takes two growing seasons to complete, it reproduces in the second growing season PRIMARY GROWTH makes a plant taller at roots and stems SECONDARY GROWTH makes a plant wider, or adds woody tissue Tree Rings tell the age of a tree, each ring represents a growing season. The photo shows a tree who has been through four growing seasons. The lighter thinner rings are winter periods. VASCULAR CAMBIUM: area of the tree that makes more xylem and phloem and forms the annual rings