* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Teaching Through E
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Mars observation wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Naming of moons wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
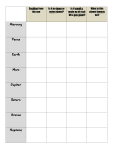
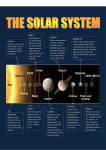
4th Grade Science Lesson Eight Planets 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Mercury • It is the closest planet to the sun • The eighth largest • Given separate names for its apparitions as a morning star and as an evening star. Venus • The second planet from the sun and the sixth largest • Venus is the goddess of love and beauty • The brightest object in the sky except for the sun and the moon. • Like Mercury it was thought to be two separate bodies – Eosphorus as the morning star – Hesperus as the evening star Earth • The third planet from the sun and the fifth largest • The crust varies considerably in thickness – It is thinner under the ocean – Thicker under the continents • The inner core and crust are solid • The outer core and mantle layers are plastic or semi-fluid. Mars • The fourth planet from the sun and the seventh largest. • Mars is the God of War • Sometimes referred to as the Red Planet • Even though Mars is much smaller than Earth, its surface area is about the same as the land surface area of Earth. Jupiter • The fifth planet from the sun and the largest. • Jupiter is more than twice as massive as all the other planets combined – The mass of Jupiter is 318 times that of Earth • Jupiter was the King of the Gods, the ruler of Olympus and the patron of the Roman state. • The fourth brightest object on the sky. After the Sun, the Moon and Venus. • Known since prehistoric times as a bright “wandering star”. Saturn • The sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest. • In Roman mythology, Saturn is the god of agriculture • Saturn is the least dense of the planets – Its specific gravity (0.7) is less than that of water Uranus • The seventh planet from the sun and the third largest (by diameter). – The largest in diameter but smaller than Neptune. • Uranus is the ancient Greek deity of the Heavens, the earliest supreme god. • The first planet discovered in modern times by William Herschel • Has 27 named moons Neptune • The eighth planet from the Sun and the fourth largest (by diameter). – Smaller in diameter but larger in mass than Uranus • In Roman mythology Neptune was the god of the Sea. • Like Jupiter and Saturn, Neptune has an internal heat source. – Its radiates more than twice as much energy as it receives from the Sun,