* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit Exam
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
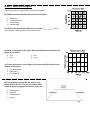
Unit 3: Physics Unit Exam Day 10 Unit Essential Questions: 1. 2. 3. What is everything in the Universe made of? What is the Periodic Table, and how is it organized? Why do different substances react differently with each other? Formulas: Reminders Speed = Distance/Time Force = Mass x Acceleration Work = Force x Distance You will have roughly 60 minutes to finish Show strategies and justification for answers 8.6A – Balanced vs. Unbalanced Forces 1) Four forces act on a block seen below. 2) Four forces are acting on a box, as shown below. In which directions will this box increase in speed? As a result of these forces, the block a. b. c. d. Moves at a constant speed to the right Moves at a constant speed to the left Accelerates to the right Accelerates to the left 3) A ball is dropped from the top of a tall building. As the ball falls, the upward force of air resistance becomes equal to the downward pull of gravity. When these two forces become balanced, the ball will a. Flatten due to the forces b. Fall at a constant speed c. Continue to speed up d. Slow to a stop a. b. c. d. Downward and to the left Downward and to the right Upward and to the left Upward and to the right 4) Which situation describes an object that has balanced forces acting on it? a. an apple in falling towards the Earth b. a rocket launching into space c. a hockey puck moving at constant velocity across ice d. a car accelerating to merge onto the highway 5) Two forces act concurrently on an object on a horizontal, frictionless surface, as shown in the diagram below. 12 N 8N What additional force, when applied to the object, will create a balanced force? a. 20 N toward the right c. 20 N toward the left b. 4 N toward the right d. 4 N toward the left 8.6C – Newton’s Laws 6) The illustrations show soccer balls of different masses being kicked with equal force. Which ball will have the greatest acceleration? 7) A stone on the end of a string is whirled clockwise at a constant speed in a horizontal circle as shown in the diagram below. According to Newton’s 1st Law, if the stone flew off the string at the exact moment seen in the diagram, which direction would it move? a. c. b. d. 8) Which situation is explained by Newton’s First Law of Motion, the “Law of Inertia?” a. b. c. d. A basketball bounces upward when it is dropped on the floor You can lift more mass with the same force using a long lever Even though you stop pedaling your bicycle, you keep moving forward at a constant speed More fuel is required to accelerate a large truck than is required to accelerate a small car 9) Tasha notices that even though she stops pulling the wagon, her brother’s body moves forward. Which of Newton’s laws of motion explains Tasha’s observation? a. The first law, in which an object moves forward in a straight line unless acted upon by an outside force b. The second law, in which force is a product of an object’s acceleration and mass c. The third law, in which every action has an equal and opposite reaction d. The fourth law, in which energy is never lost but is transformed from one object to another. 10) At a certain location, a gravitational force with a magnitude of 350 N acts on a 70 kg astronaut. What is the astronaut’s acceleration at this point? Write your answer in the grid with correct unit. 1. A A B C D 2. B the front of the car to tip backward. air to expand the balloon's volume. the wheels of the car to spin clockwise. air to rush from the balloon's opening. 3. C 4. D A B C D Different surfaces affect how fast a toy car accelerates. Different toy cars travel at different speeds. Gravity has little effect on the speed of toy cars on different surfaces. Air resistance is the greatest factor in limiting the acceleration of different toy cars. 15. Two cars with different masses travel at the same speed down a hill toward a stop sign. What will happen when both cars apply brakes at the same time to stop? A The car with the smaller mass will require less force to stop than the car with the larger mass. B The car with the larger mass will maintain its velocity while traveling down the hill. C The car with the smaller mass will take longer to stop than the car with the larger mass. D The car with the larger mass will have less inertia than the car with the smaller mass. 16. While in outer space a rocket engine is able to produce thrust on a spacecraft. Identify the correct action-reaction pair which allows the spacecraft to propel itself forward. A rocket engine-spacecraft B rocket engine nozzle-exhaust gasses C exhaust gasses-air behind the spacecraft D exhaust gasses-ground 8.6B – Speed vs. Velocity vs. Acceleration 6.8C – Calculate Speed 17) Juan is riding on a motor cycle for 30 seconds, and traveled 600 meters. What was his average speed? a. 200 m/s b. 20 m/s c. 180 m/s d. 30 m/s 18) Jennifer travels on a train from Austin to Dallas at a speed of 60 km/h for a total of 4 hours. How many kilometers did she travel? a. 24 km b. 240 km/h c. 240 km d. 240 m 19) In which of these situations is the object accelerating? a. b. c. d. A book on a shelf A rock sitting on the ground A helium balloon tied to a lamppost A ball that has been thrown upward 20) The speedometer in a car does not measure the car’s velocity because velocity a. b. c. d. Has direction associated with it Does not have direction associated with it Does not change Should point at the gas pedal 21) The data table below lists the mass and force of four different objects. Which one is accelerating at the fastest rate? Object Mass (kg) Force (N) 1. A 3. C A 4 12 2. B 4. D B 6 5 C 8 20 D 16 4 1. 22) A high school baseball team in Dallas travels south to Austin to participate in a tournament. The trip from Dallas to Austin is about 322 kilometers. The trip requires about 3.5 hours to complete on a school bus. Which of the following best represents the VELOCITY of the bus? A 92 km/h B 92 km/h South C D 23. 112.7 km/h 112.7 km/h South A group of 4 students is performing an experiment to determine the velocity and acceleration of a radio controlled toy race car. Which of the following equipment could be used to measure the desired quantities? I: stopwatch II: thermometer III: meter stick IV: measuring tape V: bathroom scale A B C D E I only II & III I & IV I&V I, II & V 6.8D – Motion Graphs Use the graph on the right for BOTH questions 24 and 25. 24) Which term best describes the motion of this object? a. b. c. d. Stationary Constant speed Accelerating Decelerating 25) What is the speed of this object at 3.0 seconds? ____________ Write your answer in question #25 on your answer sheet 26) Refer to the graph on the right. What was the distance traveled by the object at 8 seconds? a. 0 m b. 8 m c. 16 m d. 24 m 27) From 0.0 seconds to 4.0 seconds, which term would best describe the motion of this object? a. Constant speed b. Stationary c. Accelerating 28) The graph below describes the motion of an object. Notice that the Y-Axis is not labeled. What would be the most appropriate label for the y-axis? a. b. c. d. Acceleration Distance Displacement Speed Try them out! 6.8A – Potential vs. Kinetic 6.9C – Energy Transformations 30) Look at the diagram to the right. At which point does the girl have the most potential energy due to position? a. A c. C b. B d. D 31) A ball rolls down a hill. When does it have the most kinetic energy? a. A c. C b. B d. D A B A C B D C D