* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answers Chapter 11 Islamic Civilization, Section 1 Daily Life in Early
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of the Quran wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
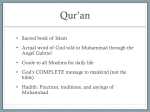
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Answers Chapter 11 Islamic Civilization, Section 1 Daily Life in Early Arabia (pp.371-378) 1. Although most of the Arabian Peninsula is very dry, where is there enough water for plants to grow? At oases, and in the mountains of the southwest 2. How were the Arab people organized, and what were their leaders called? They were organized into clans, people related by family, and tribes who were loyal to one another; sheiks 3. What were Bedouins? They were nomadic desert herders who went from oasis to oasis watering and grazing their camels, goats and sheep. 4. How was the lifestyle of Arab villagers different from the lifestyle of the Bedouins? Villagers farmed or raised animals, while the Bedouins were nomadic and lived in tents, eating dried fruits and nuts and drinking the milk of their animals, rarely eating their meat. 5. What was a caravan? A group of merchants who traveled across the desert in groups to fend off attacks by Bedouins. 6. Where did Arab merchants travel? They traveled between India and the Mediterranean Sea. 7. Why was Makkah (Mecca) so important? It was a crossroads for merchants and a religious site, because the holiest place in Arabia (the Kaaba) was in this city. 8. What was the Kaaba and what was inside it? It was a low, square building surrounded by statues of gods and goddesses, and it contained a stone (the Black Stone) that Arabs believed came from heaven. Muhammad: Islam’s Prophet 9. Describe Muhammad’s early life. Muhammad was born in Makkah. He was an orphan and was raised by his grandfather and then by an uncle. As a teenager, he worked as a caravan leader and became a successful merchant. He married and had children. 10. Why was Muhammad dissatisfied? He felt people should return to the old ways and honor their families, be fair in business, and help the poor. 11. What happened to Muhammad when he went to the hills to meditate? He said he was visited by an angel who told him to preach Islam. 12. What does “Islam” mean? “surrendering to the will of Allah.” 13. List the ideas that Muhammad preached to people. (Find six different ideas: Some were things they should do and some were things they should believe). (Bullet point answers are OK). Destroy statues of false gods Worship only Allah All people were equal The rich should share their goods Wealth was not as important as leading a good life On the Day of Judgment, God would reward the good people and punish evildoers 14. After his family, what people were particularly attracted to Muhammad’s teachings? The poor 15. What people felt threatened? What did they do? Wealthy merchants and religious leaders felt threatened because they thought he was trying to take away their power. They made his life difficult and beat and tortured his followers. 16. How did Muhammad and his followers escape persecution in Makkah (Mecca)? They moved to Yathrib. 17. What is the journey in the previous question called? How is it honored in the Muslim calendar? In what year of the Christian calendar did it take place? It is called the Hijrah, and it is the first year of the new Muslim calendar, A.D. 622 18. What new name did people of Yathrib give to their city? What does it mean? They renamed it Madinah, which means “city of the prophet.” 19. What type of government did Muhammad establish in Madinah? What was new for the Arabs about this form of government? He applied the laws he believed God had given him to all areas of life, and used the laws to settle disputes among the people. 20. What important event took place in 630 CE ? Muhammad’s soldiers conquered Makkah, and Muhammad made it a holy city of Islam. 21. By the time Muhammad died two years later (632 CE) how far had Islam spread? All of Arabia Islam’s Teachings 22. List five beliefs that Islam, Judaism, and Christianity all have in common ( bullet points OK) Belief in one God Belief that this one God holds all the power and created the universe Belief that God determines right and wrong Belief that people are expected to obey God’s laws if they want to be blessed in the afterlife Belief that God spoke to people through prophets 23. How do Christians and Muslims view Jesus differently? Muslims viewed Jesus as only a prophet, while Christians believed Jesus was the son of God and therefore divine (a god). 24. What is the holy book of Islam, and where do Muslims believe these writings come from? The Quran, and they believed it is God’s written word. 25. List five moral teachings in the Quran that are similar to those in the Bible (bullet points OK) To be honest & treat others fairly To honor their parents Show kindness to their neighbors Give generously to the poor Murder, lying, and stealing are forbidden. 26. According to rules in the Quran regarding daily life, what should Muslims NOT do? Eat pork, drink liquor, or gamble 27. What other aspects of daily life does the Quran have rules about? The Quran also has rules about marriage, divorce, family life, business, and property rights. 28. List and desribe the 5 Pillars of Islam. -Belief: Muslims must declare that is there is no God but Allah and that Muhammad is a prophet. - Prayer: Muslims must pray five times a day facing Makkah. -Charity: Muslims must give generously to the poor -Fasting: Muslims must not eat from dawn to dusk during the sacred month of Ramadan. -Pilgrimage: Muslims must visit Makkah once in their life. (the hajj) 29. What does the Islamic law code explain and what did Islamic scholars take it from? It explains how society should be run and it is taken from the Quran and the Sunna. 30. What is the Sunna? The Sunna is the name given to customs based on Muhammad’s words and deeds.