* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I. Pericardium (Pericardial Sac) - 2 Layers A. Fibrous Layer of
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
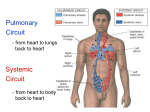
I. Pericardium (Pericardial Sac) - 2 Layers The Heart and Its Vessels A. Fibrous Layer of Pericardial Sac y Fibrous C.T. y Outer layer y Tough protective layer y Prevents over distention of heart y Anchors heart within the mediastinum §Diaphragm (below), Pleural Sacs (to R & L) §Sternal wall (front), & large blood vessels of the heart s(Overview) do not write from this slide sA. Fibrous layer of pericardium - outer layer sB. Serous layer of the pericardium - 3 regions B. Serous Layer Pericardial Sac (3 regions) parietal layer - attaches to the inside of the fibrous layer pericardial cavity - filled with pericardial fluid »watery fluid surrounds hear »reduces friction as heart beats visceral layer (epicardium) * * * Parietal layer * Pericardial cavity 1 II. Disorders yA. Pericarditis - Inflammation parietal pericardium yB. Cardiac Tamponade - Excess fluid,blood, and/or pus that results in compression of the heart Walls of the Heart Epicardium (Visceral layer of Serous Pericardium) Myocardium Endocardium Heart Chambers y B. Bottom Chambers Ventricles –1. Left ventricle (Thickest because it pumps blood to body) –2. Right ventricle ∗ Interventricular septum = wall separating the R & L Ventricles III. Walls of the Heart O A. Epicardium - outside covering of the heart O B. Myocardium - cardiac heart muscle § heart contractions (involuntary, striated, lg. # of mitochondria, dimpled in appearance) O C. Endocardium - inside lining of the heart, valves, & blood vessels IV. Heart Chambers y A. Top Chambers Atria (Atrium) - With appendage/ extension called auricle which increases capacity for blood volume –1. Right atrium –2. Left atrium ∗ Interatrial septum = wall separating the R & L Atria V. Heart Valves y A. Atrioventricular valves (between the atrium and the ventricles) 1. (right side) tricuspid valve - 3 flaps 2. (left side) bicuspid valve also called mitral valve - 2 flaps 2 Heart Valves - (Function of A.V. Valves) y Chordeae Tendinae Ìstring like strands of connective tissue Ìattach to valve flap (superior) and papillary muscle (inferior) Heart Valves - (Function of A.V. Valves) y Papillary Muscle Ìcontracts when back pressure of blood pushes on valve Ìholds Chordeae Tendinae taught to prevent valve from opening backwards Heart Valves A.V. Valve Flap Chordea Tendinea Papillary Muscle VI. Heart Valve Disorders y A. Heart Murmurs = diseased or malformed valves, blood flows the “wrong” way through the valve Result: Turbulence, abnormal flow, detected by abnormal heart sounds y B. Semilunar valves (between the ventricles and the vessels that exits the heart) 1. (right side) pulmonary semilunar valve - between rt. ventricle & Pulmonary trunk 2. (left side) aortic semilunar valve between left ventricle & Aorta Aortic Semilunar Valve Pulmonary Semilunar Valve 3 Heart Valves Pulmonary Semilunar Valve VII. Heart Vessels Aortic Semilunar Valve Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve Tricuspid Valve Heart Vessels y B. Leaving the right ventricle 1. Pulmonary Trunk which branches into: –Right Pulmonary Artery (Going to right lung) –Left Pulmonary Artery (Going to left lung) • Both release CO2 & O2 y A. Entering the right atrium 1. Superior Vena Cava (from the upper part of the body) 2. Inferior Vena Cava (from the lower part of the body) 3. Coronary Sinus (returns blood from coronary circulation) Heart Vessels y C. Entering the left atrium 1. Right Pulmonary Vein (Coming from the right lung) 2. Left Pulmonary Vein (Coming from the left lung) Heart Vessels D. Leaving the left ventricle 1. Aorta ( Major artery will branch into all other arteries carrying blood to the body) y 4