* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Criteria for Development of Message Ideas
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Elaboration likelihood model wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Social commerce wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Social media and television wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
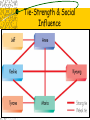
Chapter 11 Social Influences on Consumer Behavior Learning Objectives~ Ch. 11 To understand: 1. How general sources of influence differ in four key ways 2. The influence of opinion leaders-especially in the era of social media 3. The types/characteristics of reference groups 4. Both normative & informational influence Social Influences “. . . information pressures . . . [that have] a strong influence on consumers because the information source is very credible; . . . they have a strong influence simply because the source can communicate information widely.” Social Influences General Sources of Influence Marketer-dominated Non-marketer-dominated Delivered – Via mass media – Personally Sources differ? – Reach – Capacity for two-way communication – Credibility Sources of Influence Opinion Leaders Gatekeepers – Knowledgeable about products – Heavy users of mass media – Buy new products when introduced – Perceived as credible Market maven Marketing implications – Target – Use in marketing communications – Refer consumers Types of Reference Groups Aspirational – Associate products with Associative – Accurately represent – Brand communities Dissociative – Avoid using Reference Groups Characteristics Degree of Group Contact – Primary – Secondary Formality Homophily: Similarity among members Group attractiveness Density Degree of identity Tie strength Many facebook friends, LinkedIn contacts & twitter followers- a large social & or professional network Tie-Strength & Social Influence Marketing Implications Understand information transmission Target formal reference groups Target homophilous consumers Target the network Understand strength of weak ties – Embedded markets Reference Groups as Socializing Agents People Media & marketplace Celebrity Sorority/Fraternity Campus organizations Sport Adage.com In What Ways is Tiger an Influencer? Normative Influence “. . . derives from norms, society’s collective decisions about what behavior should be.” Implies Consumers Will Be – Sanctioned/punished if norms not followed – Rewarded for performing expected behaviors Sources & Types of Influence Normative Influence & CB Brand-choice congruence & conformity Compliance versus reactance Characteristics affecting strength – Product – Consumer – Group-coercive power – May be more visible in this era of social media & events Marketing Implications Rewards/sanctions for product use/nonuse Create norms for group behavior Create conformity pressures Use compliance techniques – Foot-in-the door – Door-in-the-face – Even-a-penny will help Ask consumers to predict behavior Provide freedom of choice Use service providers similar to customers Informational Influence “. . . influence, reference groups & other influence sources can exert . . . by offering information to help make decisions.” “. . . can affect how much time & effort consumers devote to information search & decision making.” Informational Influence Strength Is impacted by: Product characteristics Consumer & influencer characteristics Group characteristics Descriptive Dimensions of Information Valence: Information positive or negative? – Negative more likely to be communicated – People pay more attention to & give weight to negative Modality: Verbal or nonverbal? Pervasive/Persuasive: Word-of-mouth, viral marketing Restoring Public Trust Negative Wom/eWOM Pervasive & persuasive – Viral marketing What to do – Prevent & respond to negative word of mouth – Engineer favorable word of mouth – Handle rumors – Track word of mouth Handling Rumors & Scandals Do nothing Do something locally Do something discreetly Do something big Take responsibility for what is right Questions?