* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
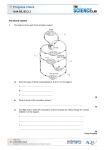
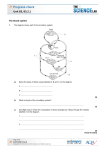
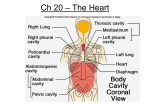
GCSE to AS Biology… In this pack you will find: An introduction to A-level Biology A copy of the AS Specification Information on the 1st topic covered at AS 2 tasks (presentation and exam questions) Useful websites Success criteria for the presentation An introduction to AS Biology: Syllabus: Edexcel Salters-Nuffield Biology AS 2 exams (Unit 1 6BI01 and Unit 2 6BI02) Coursework (Unit 3 6BI03): Assessed on core practicals written up during the course and an issue report. Topic 1 The first unit that we will study in September is Lifestyle and Risk To prepare you for AS Biology you will need to revise some of the GCSE work that you have covered in Biology. This will be from B2 (Keeping Healthy) and C3 (Food Matters) Your task: 1. To prepare a short presentation (5-7) minutes on one of the following topics: a. The structure and function of the heart b. The structure and function of blood vessels – arteries, veins and capillaries c. The chemical structure of carbohydrates d. The chemical structure of lipids 2. To answer the attached exam questions You will need to revise B2 and C3 (use your notes, revision guide, SAM learning, BBC bitesize). Here are a list of useful websites: www.s-cool.co.uk www.biologyguide.net www.biologymad.com www.biology-innovation.co.uk What to include in your presentation: Topic The structure and function of the heart Specification points Explain why many animals have a heart and circulation. Describe the cardiac cycle (atrial systole, ventricular systole and diastole) and relate the structure and operation of the mammalian heart to its function. The structure and function of blood vessels – arteries, veins and capillaries The chemical structure of carbohydrates Explain how the structures of blood vessels (capillaries, arteries and veins) relate to their functions. Distinguish between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides (glycogen and starch – amylase and amylopectin) and relate their structures to their roles in providing and storing energy. Describe how monosaccharides join to form disaccharides (sucrose, lactose and maltose) and polysaccharides (glycogen and amylase) through condensation reactions forming glycosidic bonds and how these can be split through hydrolysis reactions. Describe the synthesis of a triglyceride by the formation of ester bonds during condensation reactions between glycerol and three fatty acids and recognise differences between saturated and unsaturated lipids. The chemical structure of lipids Answer the following: 1. The table below refers to two disaccharides, sucrose and maltose. If the statement is correct, place a tick ( ) in the appropriate box and if the statement is incorrect, place a cross ( ) in the appropriate box. Statement Sucrose Maltose Contains glucose Is a reducing sugar Contains glycosidic bonds Is transported in the phloem of flowering plants (Total 4 marks) 2. The table below refers to some disaccharides, their constituent monomers and their roles in living organisms. Complete the table by writing in the appropriate word or words in the empty boxes. Disaccharide Constituent monomers One role in living organisms Carbohydrate source in mammalian milk Lactose Glucose + glucose Form in which sugars are transported in plants (Total 5 marks) 3. Starch is a storage carbohydrate found in plants. Starch is composed of many α-glucose molecules that bond together by condensation reactions. (a) The diagram below shows the structure of α-glucose. (i) In the space below, draw a diagram to show the products formed when two αglucose molecules join together by means of a condensation reaction to form maltose. (3) (ii) Name the bond that joins the two α-glucose molecules together. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Describe the structure of starch and explain why this structure makes it a suitable molecule for storing energy. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 8 marks) 4 (a) The diagram below shows the structure of a triglyceride. Ch2 O Bond A CHO CH2 O O C O C O C triglyceride (i) Name Bond A on the diagram. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Name the type of reaction that will break down the triglyceride into its constituent parts during digestion by lipase enzymes. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Name two products formed when triglycerides are completely digested. 1 ........................................................................................................................ 2 ........................................................................................................................ (2) (iv) Some triglycerides have several double bonds (C C), others have none. Describe one way in which the physical property of triglycerides which include several double bonds will differ from triglycerides which have no double bonds. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) 5 The diagram below shows cross-sections of three different types of blood vessel, A, B and C. A B 5 mm (a) C 5 mm 0.005 mm Name the blood vessels A and B. A ............................................................................................................................... B ............................................................................................................................... (1) (b) State two ways in which blood vessel C is adapted to enable the formation of tissue fluid. 1 ................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................... 2 ................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Give one function of tissue fluid. ……………………………………………….……………………………………… (1) (d) When tissue fluid is not efficiently reabsorbed, it collects in tissues causing swelling (oedema). Suggest one factor that could cause oedema. ……………………………………………….……………………………………… ……………………………………………….……………………………………… (1) (Total 5 marks) 6 The diagram below shows a transverse section of a blood vessel, as seen using low magnification of a light microscope. A (a) Name the type of blood vessel shown in the diagram. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) The layer labelled A contains smooth muscle fibres, collagen and elastic fibres. (i) Name layer A. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Describe the function of the collagen fibres. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 7 The diagram below shows the structure of the heart and some associated blood vessels. (a) Name the parts labelled A, B and C. A ................................................................................................................................... B ................................................................................................................................... C ................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Describe how the structure of the left ventricle and the parts labelled B and C enable the left ventricle to carry out its function. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (4) (c) Many organs such as the uterus, heart and kidneys of a pregnant woman use more oxygen than when she is not pregnant. The graph below shows the increased usage of oxygen by these organs near the end of pregnancy, as compared with the oxygen used before pregnancy. 8 7 6 Increase in 5 oxygen used / cm3 min–1 4 3 2 1 0 Uterus Heart Kidneys Suggest why the use of oxygen by each of the following organs increases during pregnancy. (i) Uterus ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... (ii) Heart ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 10 marks) 8 (a) The diagram below shows a ventral (front) external view of a mammalian heart. X Y Z (i) Name the structures labelled X, Y and Z. X ....................................................................................................................... Y ....................................................................................................................... Z ....................................................................................................................... (3) (ii) There are four boxes on the heart diagram. Place a tick (�) in the box that correctly identifies the position where electrical activity of the heart is initiated. (1) (iii) Name the structure that initiates electrical activity in the heart. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Blood pressure within the heart varies throughout the cardiac cycle. (i) Explain what is meant by the term cardiac cycle. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) The table below shows the range of blood pressures found in the left ventricle and in the right ventricle during one complete cardiac cycle. Ventricle Blood pressure / kPa Right 0.0 to 3.3 Left 0.0 to 15.8 Explain why the maximum blood pressure is higher in the left ventricle than in the right ventricle. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (iii) Explain why blood pressure varies in a ventricle during the cardiac cycle. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Apart from high blood pressure, state two other risk factors for heart disease. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 12 marks) 9. The figure below shows a simplified diagram of the heart. (i) Draw arrows on the diagram to show the direction of blood flow through both sides of the heart during diastole. (1) (ii) Name the part of the heart responsible for the initiation of the cardiac cycle. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 2 marks) 10. The diagrams below show the left side of the heart at two stages of the cardiac cycle. X Diagram A (a) (i) Diagram B Name structure X shown on the diagram. X ....................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Name the part of the cardiac cycle illustrated by diagram B. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) With reference to structures shown on diagram B, describe and explain what happens during this phase of the cardiac cycle. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (b) Balloon angioplasty is regularly used to unblock coronary arteries that have been affected by atherosclerosis. The procedure is shown in the diagram below. Guiding catheter Narrowed coronary artery Balloon catheter with uninflated balloon Balloon catheter with partially inflated balloon Balloon catheter with inflated balloon Unblocked coronary artery (i) Suggest why the patient may experience chest pain as a result of this partial blocking of one of the coronary arteries. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (ii) Suggest why the walls of the artery return to their original position once the balloon is removed. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Explain why doctors may advise a patient to try a balloon angioplasty in preference to an operation such as a coronary bypass. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (d) Suggest why atherosclerosis usually affects coronary arteries but not coronary veins. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 12 marks)