* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 22: Introduction to Plants
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
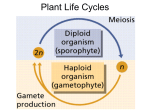
Sections 1-4 Organisms in Kingdom Plantae are eukaryotes that have cell walls containing cellulose and carry out photosynthesis using chlorophyll a and b Sunlight –photosynthesis Leaves broad and flat, arranged on stem to maximize light absorption Gas exchange –oxygen for cellular respiration, carbon dioxide for photosynthesis Gases exchanged with atmosphere/soil without losing too much water Water and minerals – structures limit water loss, faster uptake of water from soil; some have specialized tissues to carry water/nutrients Ancestors of land plants water-dwellers, similar to green algae Simpler, have cell walls, identical photosynthetic pigments, similar reproductive cycles to plants So genetically similar they should be plants First land plants had a water problem – grew close to ground in damp places, dependent on water for life cycle Several groups evolved – one line lead to mosses, another to ferns, cone-bearing plants and flowering plants Five major groups based on embryo formation, specialized water-conducting tissues, seeds, and flowers Alternation of generations – shifting between a diploid (2n) phase and a haploid (n) phase Multicellular diploid called sporophyte produces haploid spores by meiosis Spores grow into multicellular haploids called gametophytes Gametophytes produce gametes – egg and sperm Zygote forms through fertilization, which develops into new sporophyte Reduction in gametophyte size, increase in sporophyte size “Algae” refers to any photosynthetic eukaryote other than a land plant Classified in group of seedless plants Mostly aquatic (fresh and salt) or on land in damp/moist areas Absorb moisture and nutrients directly from surroundings – no specialized tissues Many alternate between haploid and diploid forms, but not necessarily with each generation Example: Chlamydomonas Favorable conditions – haploid cell reproduces asexually by mitosis Unfavorable conditions – switches to sexual reproduction Cells fuse to form zygote (sporophyte) with thick protective covering which will grow when conditions improve, divide by meiosis into 4 haploids Green algae can form colonies Spirogyra form filaments Volvox form colonies of up to 5000 – shows some specialization Mosses have protective coating that makes them resistant to drying, rhizoids to anchor them to soil and absorb water and minerals Group including mosses, liverworts, and hornworts Specialized reproductive organs enclosed by nonreproductive cells Higher degree of cell specialization Among first land plants Small because they do not make lignin, which is used to harden cell walls, and do not have vascular tissues Alternation of generations Gametophyte dominant, sporophyte depends on it Produce sperm cells with flagella for swimming so water must be present at some point in year When a moss spore lands in a moist place, it grows into a gametophyte Forms rhizoids that grow into ground, shoots that grow into air Gametes formed at tips of gametophyte Eggs produced in archegonia Sperm produced in antheridia Egg/sperm fuse to form diploid zygote – beginning of sporophyte stage Sporophyte grows within gametophyte – dependent Eventually grows out of gametophyte, develops stalk ending in sporangium Sporangium produces haploid spores by meiosis Spores released Plants growing high above ground appeared ~ 420 mya Had vascular tissues – carry water and nutrients more efficiently than bryophytes Vascular plants called tracheophytes because of tracheids – water-conducting cells that are hollow, tube-like, cell walls strengthened with lignin Tracheids arranges end to end make up xylem, the tissue that carries water upwards from the roots – pits between tracheids increase water movement Phloem is the other vascular tissue – transports solutions of nutrients and photosynthetic products Three phyla, commonly known as club mosses, horsetails, and ferns (most) Ferns have vascular tissues, strong roots, rhizomes (stems underground), fronds Thrive with little light Wet environments Spores produced by the sporophyte grow into thin, heart-shaped haploid gametophytes (independent) Sperm/eggs produced on gametophytes in antheridia and archegonia Sperm swim to eggs – water needed Zygote develops into a new sporophyte plant (dominant) Haploid spores develop on the undersides of the fronds in sporangia Seeds contain tiny living plant ready to sprout Plant embryo and a food supply – diploid, early stage sporophyte Common ancestor for all modern seed plants Ability to survive on dry land – developed adaptations Cones and flowers Pollen Seeds In seed plants, male and female gametophytes grow/mature within sporophyte – in cones or flowers Gymnosperms (naked seeds – cone-bearing plants) bear seeds on scales of cones Angiosperms (flowering plants) bear seeds in flowers within protective tissue Male gametophyte is contained in a pollen grain Carried to the female reproductive structure by wind or animals The transfer of pollen from the male reproductive structure to the female reproductive structure is called pollination After fertilization, the zygote within seed grows into a tiny plant (sporophyte embryo) A tough seed coat surrounds and protects the embryo, keeps it from drying out The embryo begins to grow when conditions are right Uses nutrients from stored food supply until it can carry out photosynthesis on its own Seeds exposed on scaled within cones Reproduction occurs in cones produced by mature sporophyte Pollen cones (male) produce pollen grains (male gametophyte) One haploid nucleus within pollen grain later divides to produce 2 sperm nuclei Seed cones (female) produce female gametophytes Scales contain 2 ovules , where meiosis produces haploid cells that develop into female gametophytes Each gametophyte contains multiple egg cells In spring, pollen cones release pollen grains which are carried by wind Female cones secrete sticky substance to trap pollen which is pulled inside the ovule Fertilization without open water Pollen grains landing near ovules split open, grow a structure called a pollen tube containing 2 haploid sperm nuclei Once the pollen tube reaches the female gametophyte, one sperm nucleus disintegrates; the other fertilizes the egg Zygote develops into embryo Seed encases embryo, dispersed by wind Angiosperms most abundant plants Most recent to evolve Develop flowers, which contain ovaries to surround and protect seeds Flowers attract pollinators More efficient than relying on wind After pollination, ovary develops into a fruit, containing at least one mature embryo Wall of fruit helps distribute seeds – animals eat, seeds go through digestive system Increases range Used to be classified by numbers of leaves in their embryos – cotyledons Monocots – one cotyledon Dicots – two cotyledons Now, monocots single group, dicots in several Differences in stems Woody plants are made of cells with thick cell walls that support the plant body Herbaceous plants have stems that are smooth and nonwoody