* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Weather Tools and Symbols - Milton 7th Grade Advanced Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
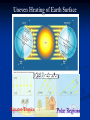
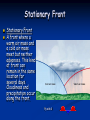
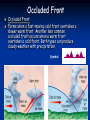
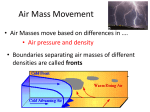
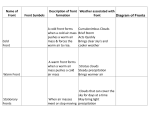
Meteorology: The Science of Weather Follow along with this PowerPoint and take notes in your Meteorology Foldable Foldable Topics Convection Humidity Air Pressure Fronts Jet Stream Air Masses Winds Gyres Ocean Currents Weather Tools & Equipment Convection Heating of Earth’s surface and atmosphere by the Sun drives convection within the atmosphere and oceans, producing winds and ocean currents. Warm air Rises, Cool air sinks !! Warm air rises because the molecules become excited and spread out making it less dense Cool air sinks as molecules become more dense Types: Moist convection- occurs over bodies of water and produces clouds Dry convection- occurs over land and produces clear skies (no clouds) Convection and Breezes Sea Breeze: Wind comes from the sea toward the land Land Breeze: Wind comes from the land toward the sea. Uneven Heating of Earth Surface Equator-Tropics Humidity Humidity: How much water vapor is in the air. The amount of water vapor in the air affects the density of the air. Relative Humidity: Measure of the amount of water vapor actually in the air compared to the maximum amount the air could hold at a certain temperature. Meteorologists use % to show relative humidity Relative Humidity - This graph shows how temperature affects the amount of water vapor that air can hold Humidity Dew Point: Temperature at which condensation forms because the air is holding all the water vapor it can hold. Air Pressure Air Pressure differences cause WIND! “High to Low makes the WIND BLOW!” Isobars: Lines on a weather map that connect areas of equal pressure. Common Weather Map Symbols: Pressure Low pressure is caused from warm air rising (warm air is less dense which has less pressure) High pressure is caused from cold air sinking (cold air is more dense which causes more pressure) Fronts A front is a boundary between air masses of different temperatures (Example: warm air meets cold air) Fronts cause a change in weather (Example: warm air meets cold air) Cold Fronts Cold Front When cold air pushes into warm air, forcing the warm air up quickly, causing it to cool, condense, and form clouds. Severe weather could result. Symbol: Warm Fronts Warm Front The front that occurs when warm air is pushed into cold air. This forces the warm air up, causing it to cool, condense, and form clouds. Symbol: Stationary Front Stationary Front A front where a warm air mass and a cold air mass meet but neither advances. This kind of front can remain in the same location for several days. Cloudiness and precipitation occur along the front. Symbol Occluded Front Occluded Front Forms when a fast-moving cold front overtakes a slower warm front. Another less common occluded front occurs when a warm front overtakes a cold front. Both types can produce cloudy weather with precipitation. Symbol: Common Weather Map Symbols