* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11.6 Patterns in Evolution
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
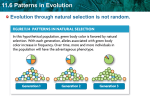
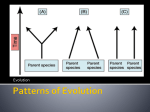
11.6 Patterns in Evolution KEY CONCEPT Evolution occurs in patterns. 11.6 Patterns in Evolution Evolution through natural selection is not random. • Natural selection can have direction. • The effects of natural selection add up over time. 11.6 Patterns in Evolution • Convergent evolution describes evolution toward similar traits in unrelated species. – Analogous structures have a similar function, but no common ancestor – Just similar adaptation due to natural selection 11.6 Patterns in Evolution • Divergent evolution describes evolution toward different traits in closely related species. – To move apart kit fox red fox • Speciation is the rise of two or more species from one existing species. • To become a new species Did Humans Evolve? Video ancestor 11.6 Patterns in Evolution • Coevolution: two or more species evolve together. – evolutionary paths become connected: species evolve in response to changes in each other – Mutualism: both species benefit – Competition: share food or resources – Predator and prey: one eats the other 11.6 Patterns in Evolution • Coevolution can occur in competitive relationships, sometimes called evolutionary. 11.6 Patterns in Evolution Species can become extinct. • Extinction is the elimination of a species from Earth. 11.6 Patterns in Evolution Speciation often occurs in patterns. • A pattern of punctuated equilibrium exists in the fossil record. – theory proposed by Eldredge and Gould in 1972 – episodes of speciation occur suddenly in geologic time – followed by long periods of little evolutionary change – revised Darwin’s idea that species arose through gradual transformations 11.6 Patterns in Evolution • Many species evolve from one species during adaptive radiation. – ancestral species diversifies into many descendent species – descendent species usually adapted to wide range of environments