* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rock Cycle {PowerPoint}
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Sedimentary rock wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
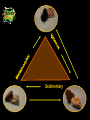
TAKS Objective 5 The student will demonstrate an understanding of earth and space systems. TEKS Objective: 8.12 The student knows that cycles exist in Earth systems. The student is expected to A analyze and predict the sequence of events in the lunar and rock cycles. Prior Knowledge • TEKS 6.6 C – Students identify forces that shape the feature of the earth including uplifting, movement of water, and volcanic activity. • TEKS 7.14 B – Student analyze effects of regional erosional deposition and weathering. Learning Objectives The student will be able to predict the events in the rock cycle. The student will be able to diagram and explain the rock cycle. All rocks are heavy. True or False A heavy piece of rock? Think again! All rocks are hard. True or False False • Chalk • Pumice • Talc Rocks never change. True or False False • Rocks are changed by processes such as: – Melting – Pressure – Heat – Weathering and Erosion Teacher Background Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools. http://www.fi.edu/fellows/fellow1/oct98/c reate/igneous.htm Melting Sedimentary rocks are formed when layers of earth have been deposited in the bottoms of bodies of water. Over time these layers are pressed together forming sedimentary rocks. http://www.fi.edu/fellows/fellow 1/oct98/create/sediment.htm Weathering and Erosion Metamorphic rocks were once sedimentary or igneous rocks that have been placed under tons of pressure and heat. http://www.fi.edu/fellows/fellow1/oct98/c reate/metamorph.htm Sedimentary Rock Cycle Diagram ENGAGE Photos by Sandra Woodruff A rock can be a thing of beauty. •Explore Explore Chocolate Rocks! Explain • How did you simulate weathering and erosion? • How are sedimentary rocks formed? • How are metamorphic rocks formed? • How are igneous rocks formed? Elaborate Rock Cycle Pictures and Arrows Evaluate Draw Your Own Rock Cycle Use the words below. The words may be used more than once. Igneous Rock Melting Lithofication Sedimentary Rock Magma Cementation Metamorphic Rock Cooling Compaction Heat and Pressure Pressure Weathering & Erosion Sediments