* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
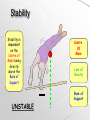
PE - Biomechanics Today we’ll look at… Newtons laws 1,2,3 Forces and what they can do? Centre of mass and stability Types of motion Newton’s First Law of Motion A body continues in a state of rest or uniform velocity unless acted upon by an external force. Sporting Examples: “ A football will stay on the penalty spot until kicked” “A hockey ball will remain still until hit by the stick” “ A football will roll until slowed by friction or another player” “ A hockey ball will not fall from the air without the application of gravity” Newton’s First Law of Motion A body continues in a state of rest or uniform velocity unless acted upon by an external force. Newton’s First Law of Motion A body continues in a state of rest or uniform velocity unless acted upon by an external force. PUSH or PULLS can alter a body (object) in the following ways •Cause a body to move (as seen in the previous slide) •Cause a body to accelerate •Cause a body to decelerate •Cause a body to change direction •Cause a body to change shape Forces Can Cause a body to accelerate Sporting example: Sailing boat. The force that causes the boat to acceleration is the wind. Forces Can Cause a body to decelerate Sporting example: Sailing boat. The force that causes the boat to deceleration is the wind. Forces Can Cause a body to change direction Sporting example: Tennis The force that causes the Ball to change direction is the racquet impact. Forces Can - Ball shape is compressed by the force of the club head on impact Cause a body to change shape Sporting example: Golf The force that causes the ball to change shape is the impact from the club head. Newton’s Second Law of Motion When a force acts on an object, the motion experienced by the object is proportional to the size of the force and in the direction in which it is applied. Sporting Examples: “If you kick a football hard, it will go a long way” “If you kick a football softly it wont go very far” “If you hit a hockey ball to the left, it will go left” “If you hit a hockey ball to the right, it will go right” Newton’s Third Law of Motion For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Sporting Examples: “If a rugby player pushes to the left with their foot, they swerve to the right.” “A high jumper needs to push down on the ground to be able to go up.” A football goalkeeper needs to push to the left with their feet in order to dive to the right.” Reaction force is the goal keeper lifting into the air in the opposite direction Action force is the goal keeper pushing down into the floor Centre of Mass An imaginary point which is movable and is where the mass of an object is concentrated. Centre Of Mass As the mass of the arms move up so will the centre of mass Centre Of Mass Stability Stability is dependant on the Centre of Mass being directly above the Base of Support Centre Of Mass Base of Support Stability Centre Of Mass Stability is dependant on the Centre of Mass being directly above the Base of Support Line of Gravity Base of Support STABLE Stability Stability is dependant on the Centre of Mass being directly above the Base of Support UNSTABLE Centre Of Mass Line of Gravity Base of Support Centre of Mass Remember Centre Of Mass doesn’t always need to be inside the body Stability is dependant on 4 things Position of the centre of mass? Size of the base of support? Mass of the Athlete? Where the line of gravity is? Motion - Linear When a body moves in a straight line with all its parts moving the same DISTANCE, DIRECTION, and SPEED Everything is moving in the same direction at the same speed SPORTING EXAMPLE = THE BOB SLEIGH (TOBOGGAN) Motion - Angular When a body or part of a body moves in a circle or part of a circle about a point (the axis of rotation). Circular motion about a point. i.e. The elbow being fixed when the forearm moves in a half circle in a tennis serve Axis of rotation SPORTING EXAMPLE = BENDING YOUR ARM IN A TENNIS SERVE Motion – General General = Angular +Linear General motion is a combination of Linear and Angular motion Sporting examples •Javelin •Wheel chair athletics •Swimming •Running