* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test 1 - spring 2005
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
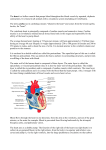
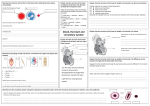
A&P 2 – Spring 2005 Test 1 – Cardiology Form A Name ________________________ Lab ____________ Match one of the following with numbers 1 – 5. Answers may be used more than once and some answers may not be used at all. a. cardiac cells only b. skeletal cells only c . both cardiac and skeletal cells d. neither cardiac nor skeletal cells 1. Voluntary 2. Crossbanded or striated 3. The two types are autorythmic and contractile 4. Interrelated discs 5. Many nuclei per cell 6. Which correctly follows the correct path of the intrinsic conduction system? a. AV node – AV bundle – SA node – perkinje fibers b. AV node – SA node – SA bundle – AV branches c. SA node – AV node – AV bundle – perkinje fibers d. SA node – AV bundle – AV node – perkinje fibers 7. A cardiac cycle can be described as: a. lub-dub b. PQRST waves of an ECG c. AV valves opening and closing d. all of the above 8. Cardiac output is: a. measured by MAP and HR b. volume differences in the left ventricle compared to the right ventricle c. the amount of blood each ventricle pumps per minute d. the amount of blood pumped out of the heart per beat 9. Which chamber of the heart sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs? a. right ventricle b. right atrium c. left ventricle d. left atrium 10. The pericardium contains two layers. They are a. the visceral and parietal b. the visceral and serous c. the myocardium and autocardium d. the parietal and temporal 11. Which of the following drain the blood from the vessels supplying the heart wall into the right atrium? a. pulmonary artery b. superior vena cava c. coronary sinus d. inferior vena cava 12. The atrioventricular valve on the same side of the heart as the origin of the aorta is the: a. aortic semilunar b. tricuspid c. bicuspid d. pulmonary semilunar 13. Which valve does the blood go through just before entering the pulmonary trunk on the way to the lungs? a. tricuspid b. pulmonary semilunar c. aortic semilunar d. bicuspid 14. The pointed end of the heart that projects inferiorly and to the left is the: a. costal surface b. base c. apex d. arrowhead 15. Which of these structures is the deepest? a. fibrous pericardium b. visceral layer of serous pericardium c. parietal layer of serous pericardium d. myocardium 16. The lining of the heart chambers is referred to as the: a. endocardium b. myocardium c. epicardium d. pericardium 17. The depression in the interatrial septum corresponding to the foramen ovale of fetal circulation is the a. interventricular sulcus b. ductus arteriosis c. ligametum arteriosum d. fossa ovalis 18. Malfunction of the __________ valve would interfere with the flow of blood from the right atrium to the right ventricle. a. pulmonary semilunar b. aortic semilunar c. tricuspid d. bicuspid 19. Deoxygenated blood is sent to the lungs through the __________. a. aorta b. pulmonary artery c. pulmonary vein d. pulmonary capillary 20. Which is a serous membrane? a. lining of mouth b. lining of urinary bladder c. lining of trachea d. lining of the thoracic cavity 21. The two inferior chambers of the heart are separated by the __________. a. epicardium b. fibrous skeleton c. interventricular septum d. interatrial septum 22. The earlike flap of tissue on each atrium is called a(n) __________. a. auricle b. fibrous cardiac skeleton c. papillary muscle d. A-V valves 23. The large vein that drains blood from most parts of the body superior to the heart and empties into the right atrium is the __________. a. coronary sinus b. pulmonary artery c. pulmonary vein d. superior vena cava 24. The cusps of atrioventricular valves are prevented from inverting by the presence of cords called __________, which are attached to papillary muscle. a. fibrous cardiac skeleton b. chordae tendonae c. traceculeae carnae d. bungee cords 25. The largest of the circulatory circuits is the: a. systemic circuit b. pulmonary circuit c. coronary circuit d. electrical circuit 26. All arteries of the systemic circulation branch from the: a. superior vena cava b. aorta c. pulmonary artery d. coronary artery 27. If a person is diagnosed with “heart block”, it means the electrical activity is taking too long to get from the atriums to the ventricles. What part of the intrinsic conduction system is at fault? a. SA node b. AV node c. AV bundle d. bundle branches 28. Which is not found in the mediastinum? a. visceral pericardium b. esophagus c. lung d. superior vena cava 29. The distal, terminal part of the aorta is called: a. ascending aorta b. descending aorta c. aortic arch d. trunk 30. The T-wave in an ECG measures the: a. depolarization of the atrium b. depolarization of the ventricle c. repolarization of the atrium d. repolarization of the ventricle 31. The inferior vena cava is formed by the union of: a. small arteries and arterioles b. capillaries c. small veins and venules d. veins from the head, neck and arms 32. The circulatory system functions to: a. send hormones to target organs b. exchange gases in the cells of the body c. fight against antigens d. all of the above 33. When ventricular pressure drops below atrial pressure, what occurs? a. ventricles fill with blood b. ventricles eject blood c. ventricles contract d. all four valves close 34. During which phase of an ECG are all four chambers in diastole and the heart is totally relaxed? a. just before the T wave b. just after the T wave c. just before the QRS complex d. just after the QRS complex 35. An ECG measures: a. electrical activity in the heart b. blood pressure c. amount of blood pumped out of each ventricle per beat d. average pressure per heart beat 36. The two distinct heart sounds, described as lub and dub, represent a. contraction of the ventricles and relaxation of the atria b. contraction of the atria and relaxation of the ventricles c. the closing of the atrioventricular and semilunar valves d. surging of blood into the pulmonary artery and aorta 37. Systole and diastole of both atria plus systole and diastole of both ventricles is called __________. a. pulse pressure b. cardiac output c. stroke volume d. cardiac cycle 38. Blood continues to fill within the left ventricle. This ventricular phase is called: a. systole b. diastole c. mean arterial pressure d. blood pressure 39. When does blood move into the aorta? a. ventricular diastole b. ventricular systole c. isovolumetric contraction d. isovolumetric relaxation 40. The heart has an intrinsic conduction system. Which cells within the ICS leak to threshold the fastest?: a. AV node b. SA node c. bundle branches d. AV bundle 41. Marci has a resting HR of 70 and a resting stoke volume of 70. What is her resting cardiac output? a. 4900 liters per beat b. 4900 ml per beat c. 4900 liters per minute d. 4900 ml per minute 42. The typical ECG produces three clearly recognizable waves. The first wave, which indicates depolarization of the atria, is called the __________. a. Q b. PQR c. P d. RST 43. Ashley’s blood pressure is 125/95. What is her MAP (mean arterial pressure)? a. 30mm Hg b. 105mm Hg c. 125mm Hg d. 135mm Hg 44. The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure is called __________. a. stroke volume b. blood pressure c. mean arterial pressure d. pulse pressure 45. An average blood pressure value for an adult is __________. a. 80 systolic and 120 diastolic b. 120 systolic and 80 diastolic c. 220 diastolic and 80 systolic d. 80 diastolic and 220 systolic 46. Knock, Knock……… “Who’s there?”……… Duane………. “Duane who?” a. Duane the sink it’s over fwowing b. Duane the bathtub, I’m dwowning c. Duane the pool it’s yewwow d. Duane the ventricles when they contwact 47. Which of the following exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with the cells of your body? a. capillaries b. veins c. venules d. arteries 48. Why is there more of the heart on your left side compared to your right side? a. because blood goes in and out through the base of the heart b. because blood goes in and out through the apex of the heart c. because the left ventricle is bigger than the left atrium d. because the left ventricle is bigger than the right ventricle 49. The cardiac fibrous skeleton is made of __________ and functions to _________. a. connective tissue; deliver blood to heart b. cardiac muscle cells; connect atriums and ventricles c. trees; photosynthesize d. collagen; anchor myocardium 50. Why do the AV valves open? a. pressure is less in the pulmonary trunk compared to the right ventricle b. pressure is less in the aorta compared to the left ventricle c. pressure is greater in the atriums compared to the ventricles d. pressure is greater in the ventricles compared to the atriums